我们一般部署服务的时候,都会部署一个网关服务,内部所有的其他微服务的调用,都将通过网关路由过去,不对外直接暴露,对外只暴露网关服务。而且一般内部服务会部署多个实例,zuul集成了ribbon,会自动负载均衡的方式去调用内部服务。
当内部服务滚动重启的时候,通过网关的一个请求刚好路由到重启的那个实例的话,因为默认没有开启zuul的请求重试策略,该请求将会报错,其实理想的方式可以通过重试路由到另外一个活动的服务实例上去。
要开启zuul网关请求重试,首先需要添加spring-retry依赖:
<dependency>
<groupId>org.springframework.retry</groupId>
<artifactId>spring-retry</artifactId>
</dependency>
然后配置:
zuul.retryable=true
这样,所有路由都将会进行重试。(此属性默认是false,所以不会重试)
有时候我们不希望所有路由都有重试机制,我们可以配置指定路由进行重试:
zuul.routes.<routename>.retryable=true
这里的routename默认情况下就是你的服务名(我们可以通过管理端点/routes看到都有哪些路由
也可以查看更详细的路由信息:/routes?format=details,
端点实现类:org.springframework.cloud.netflix.zuul.RoutesMvcEndpoint)。
例如我有一个rcmd-service-data的服务,我可以这样配置:
zuul.retryable=false
zuul.routes.rcmd-service-data.retryable=true
这样,就只有rcmd-service-data这个服务开启了重试机制。我们通过/routes?format=details端点也可以看到:
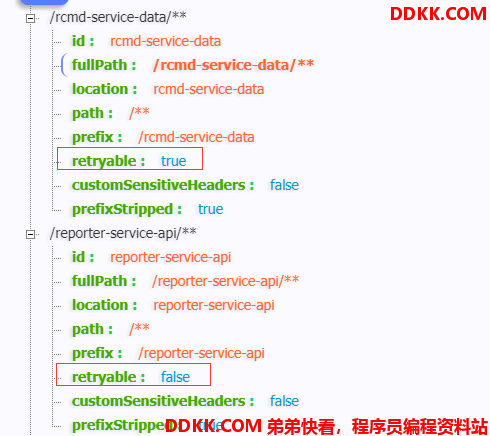
我们知道zuul请求也是通过Ribbon负载均衡客户端去调用其他服务的,所以我们的重试策略也是在具体的ribbon配置中指定:
rcmd-service-data:
ribbon:
# Max number of retries on the same server (excluding the first try)
MaxAutoRetries: 1
# Max number of next servers to retry (excluding the first server)
MaxAutoRetriesNextServer: 2 #当允许在其他服务器上重试的时候,会调用IRule.choose选择可用服务实例中的其他一台服务实例进行调用
# Whether all operations can be retried for this client
OkToRetryOnAllOperations: true #默认为false,则只允许GET请求被重试
ReadTimeout: 5000
ConnectTimeout: 2000
重试的时候还有补偿策略,例如重试时间间隔
默认是没有间隔:org.springframework.retry.backoff.NoBackOffPolicy
我们可以实现自己的补偿策略,也可以用内部实现的一些补偿策略(需要定义一个bean),如指数级的补偿策略(1秒,2秒,4秒类似这种指数级睡眠间隔增长,不超过10秒):
@Configuration
public class MyConfiguration {
@Bean
LoadBalancedBackOffPolicyFactory backOffPolciyFactory() {
return new LoadBalancedBackOffPolicyFactory() {
@Override
public BackOffPolicy createBackOffPolicy(String service) {
return new ExponentialBackOffPolicy();
}
};
}
}
也可以正对某些响应状态码进行重试(当调用rcmd-service-data返回404,502的时候,进行重试,其他状态码不重试):
rcmd-service-data:
ribbon:
retryableStatusCodes: 404,502
以上差不多就是网关重试相关的能够配置的点了.
下面从源码层面看看重试的实现。
首先我们需要大致有个概念就是,zuul网关是通过ribbon负载均衡客户端来调用内部服务的,然后ribbon客户端默认是用HttpClient来发起http请求调用(当然还可以通过配置使用okhttp或者ribbon自带的RestClient),在org.springframework.cloud.netflix.ribbon.apache.HttpClientRibbonConfiguration中进行自动装配的:
@Bean
@ConditionalOnMissingBean(AbstractLoadBalancerAwareClient.class)
@ConditionalOnClass(name = "org.springframework.retry.support.RetryTemplate")
public RetryableRibbonLoadBalancingHttpClient retryableRibbonLoadBalancingHttpClient(
IClientConfig config, ServerIntrospector serverIntrospector,
ILoadBalancer loadBalancer, RetryHandler retryHandler,
LoadBalancedRetryPolicyFactory loadBalancedRetryPolicyFactory, CloseableHttpClient httpClient,
LoadBalancedBackOffPolicyFactory loadBalancedBackOffPolicyFactory,
LoadBalancedRetryListenerFactory loadBalancedRetryListenerFactory) {
RetryableRibbonLoadBalancingHttpClient client = new RetryableRibbonLoadBalancingHttpClient(
httpClient, config, serverIntrospector, loadBalancedRetryPolicyFactory,
loadBalancedBackOffPolicyFactory, loadBalancedRetryListenerFactory);
client.setLoadBalancer(loadBalancer);
client.setRetryHandler(retryHandler);
Monitors.registerObject("Client_" + this.name, client);
return client;
}
ribbon内部优惠构造hystrix command来执行请求
所以我们常说ribbon的超时时间设置要大于等于hystrix 超时时间,不然导致command还没执行完,ribbon却超时了
由HttpClientRibbonCommand.run方法发起请求
org.springframework.cloud.netflix.zuul.filters.route.support.AbstractRibbonCommand#run
@Override
protected ClientHttpResponse run() throws Exception {
final RequestContext context = RequestContext.getCurrentContext();
RQ request = createRequest();
RS response;
boolean retryableClient = this.client instanceof AbstractLoadBalancingClient
&& ((AbstractLoadBalancingClient)this.client).isClientRetryable((ContextAwareRequest)request);
if (retryableClient) {
response = this.client.execute(request, config); //此处的client就是
RetryableRibbonLoadBalancingHttpClient
} else {
response = this.client.executeWithLoadBalancer(request, config);
}
context.set("ribbonResponse", response); // Explicitly close the HttpResponse if the Hystrix command timed out to// release the underlying HTTP connection held by the response.//if (this.isResponseTimedOut()) {if (response != null) {response.close();}}return new RibbonHttpResponse(response);}
如果可以重试的话,调用的是RetryableRibbonLoadBalancingHttpClient.execute方法:
@Override
public RibbonApacheHttpResponse execute(final RibbonApacheHttpRequest request, final IClientConfig configOverride) throws Exception {
final RequestConfig.Builder builder = RequestConfig.custom();
IClientConfig config = configOverride != null ? configOverride : this.config;
builder.setConnectTimeout(config.get(
CommonClientConfigKey.ConnectTimeout, this.connectTimeout));
builder.setSocketTimeout(config.get(
CommonClientConfigKey.ReadTimeout, this.readTimeout));
builder.setRedirectsEnabled(config.get(
CommonClientConfigKey.FollowRedirects, this.followRedirects));
final RequestConfig requestConfig = builder.build();
final LoadBalancedRetryPolicy retryPolicy = loadBalancedRetryPolicyFactory.create(this.getClientName(), this);
RetryCallback<RibbonApacheHttpResponse, IOException> retryCallback = new RetryCallback<RibbonApacheHttpResponse, IOException>() {
@Override
public RibbonApacheHttpResponse doWithRetry(RetryContext context) throws IOException {
//on retries the policy will choose the server and set it in the context
//extract the server and update the request being made
RibbonApacheHttpRequest newRequest = request;
if(context instanceof LoadBalancedRetryContext) {
ServiceInstance service = ((LoadBalancedRetryContext)context).getServiceInstance();
if(service != null) {
//Reconstruct the request URI using the host and port set in the retry context
newRequest = newRequest.withNewUri(UriComponentsBuilder.newInstance().host(service.getHost())
.scheme(service.getUri().getScheme()).userInfo(newRequest.getURI().getUserInfo())
.port(service.getPort()).path(newRequest.getURI().getPath())
.query(newRequest.getURI().getQuery()).fragment(newRequest.getURI().getFragment())
.build().encode().toUri());
}
}
newRequest = getSecureRequest(newRequest, configOverride);
HttpUriRequest httpUriRequest = newRequest.toRequest(requestConfig);
final HttpResponse httpResponse = RetryableRibbonLoadBalancingHttpClient.this.delegate.execute(httpUriRequest);
if(retryPolicy.retryableStatusCode(httpResponse.getStatusLine().getStatusCode())) {
throw new HttpClientStatusCodeException(RetryableRibbonLoadBalancingHttpClient.this.clientName,
httpResponse, HttpClientUtils.createEntity(httpResponse), httpUriRequest.getURI());
}
return new RibbonApacheHttpResponse(httpResponse, httpUriRequest.getURI());
}
};
RibbonRecoveryCallback<RibbonApacheHttpResponse, HttpResponse> recoveryCallback = new RibbonRecoveryCallback<RibbonApacheHttpResponse, HttpResponse>() {
@Override
protected RibbonApacheHttpResponse createResponse(HttpResponse response, URI uri) {
return new RibbonApacheHttpResponse(response, uri);
}
};
return this.executeWithRetry(request, retryPolicy, retryCallback, recoveryCallback);
}
进而又调用了自身的executeWithRetry方法:
private RibbonApacheHttpResponse executeWithRetry(RibbonApacheHttpRequest request, LoadBalancedRetryPolicy retryPolicy,
RetryCallback<RibbonApacheHttpResponse, IOException> callback,
RecoveryCallback<RibbonApacheHttpResponse> recoveryCallback) throws Exception {
RetryTemplate retryTemplate = new RetryTemplate();
boolean retryable = isRequestRetryable(request); //从org.springframework.cloud.netflix.zuul.filters.route.RibbonCommandContext中获取retryable配置
retryTemplate.setRetryPolicy(retryPolicy == null || !retryable ? new NeverRetryPolicy()
: new RetryPolicy(request, retryPolicy, this, this.getClientName()));
BackOffPolicy backOffPolicy = loadBalancedBackOffPolicyFactory.createBackOffPolicy(this.getClientName());
retryTemplate.setBackOffPolicy(backOffPolicy == null ? new NoBackOffPolicy() : backOffPolicy);
RetryListener[] retryListeners = this.loadBalancedRetryListenerFactory.createRetryListeners(this.getClientName());
if (retryListeners != null && retryListeners.length != 0) {
retryTemplate.setListeners(retryListeners);
}
return retryTemplate.execute(callback, recoveryCallback);
}
private boolean isRequestRetryable(ContextAwareRequest request) {
return request.getContext() == null ? true :
BooleanUtils.toBooleanDefaultIfNull(request.getContext().getRetryable(), true);
}
executeWithRetry方法又会调回execute方法中定义的RetryCallback匿名实现类的doWithRetry方法:
RetryCallback<RibbonApacheHttpResponse, IOException> retryCallback = new RetryCallback<RibbonApacheHttpResponse, IOException>() {
@Override
public RibbonApacheHttpResponse doWithRetry(RetryContext context) throws IOException {
//on retries the policy will choose the server and set it in the context
//extract the server and update the request being made
RibbonApacheHttpRequest newRequest = request;
if(context instanceof LoadBalancedRetryContext) {
ServiceInstance service = ((LoadBalancedRetryContext)context).getServiceInstance();//这个getServiceInstance在next server retry的时候会变
if(service != null) {
//Reconstruct the request URI using the host and port set in the retry context
newRequest = newRequest.withNewUri(UriComponentsBuilder.newInstance().host(service.getHost())
.scheme(service.getUri().getScheme()).userInfo(newRequest.getURI().getUserInfo())
.port(service.getPort()).path(newRequest.getURI().getPath())
.query(newRequest.getURI().getQuery()).fragment(newRequest.getURI().getFragment())
.build().encode().toUri());
}
}
newRequest = getSecureRequest(newRequest, configOverride);
HttpUriRequest httpUriRequest = newRequest.toRequest(requestConfig);
final HttpResponse httpResponse = RetryableRibbonLoadBalancingHttpClient.this.delegate.execute(httpUriRequest);
if(retryPolicy.retryableStatusCode(httpResponse.getStatusLine().getStatusCode())) { //这里就是跟配置中配置的状态码进行匹配
throw new HttpClientStatusCodeException(RetryableRibbonLoadBalancingHttpClient.this.clientName,
httpResponse, HttpClientUtils.createEntity(httpResponse), httpUriRequest.getURI());
}
return new RibbonApacheHttpResponse(httpResponse, httpUriRequest.getURI());
}
};
我们需要缕一缕这部分代码逻辑,首先是这句:
boolean retryable = isRequestRetryable(request); //从org.springframework.cloud.netflix.zuul.filters.route.RibbonCommandContext中获取retryable配置
表名了从org.springframework.cloud.netflix.zuul.filters.route.RibbonCommandContext获取到的是否可以重试的配置,而
RibbonCommandContext又是从:
org.springframework.cloud.netflix.zuul.filters.route.RibbonRoutingFilter#buildCommandContext中创建出来的:
protected RibbonCommandContext buildCommandContext(RequestContext context) {
HttpServletRequest request = context.getRequest();
MultiValueMap<String, String> headers = this.helper
.buildZuulRequestHeaders(request);
MultiValueMap<String, String> params = this.helper
.buildZuulRequestQueryParams(request);
String verb = getVerb(request);
InputStream requestEntity = getRequestBody(request);
if (request.getContentLength() < 0 && !verb.equalsIgnoreCase("GET")) {
context.setChunkedRequestBody();
}
String serviceId = (String) context.get(SERVICE_ID_KEY);
Boolean retryable = (Boolean) context.get(RETRYABLE_KEY);
Object loadBalancerKey = context.get(LOAD_BALANCER_KEY);
String uri = this.helper.buildZuulRequestURI(request);
// remove double slashes
uri = uri.replace("//", "/");
long contentLength = useServlet31 ? request.getContentLengthLong(): request.getContentLength();
return new RibbonCommandContext(serviceId, verb, uri, retryable, headers, params,
requestEntity, this.requestCustomizers, contentLength, loadBalancerKey);
}
这句:
Boolean retryable = (Boolean) context.get(RETRYABLE_KEY);
retryable又是从:
com.netflix.zuul.context.RequestContext中获取的,那么从RequestContext里面的这个key又是从哪设置进去的呢?我们进而搜索发现在:
org.springframework.cloud.netflix.zuul.filters.pre.PreDecorationFilter
这个zuul filter中设置的该值,run方法代码片段:
Route route = this.routeLocator.getMatchingRoute(requestURI);
if (route.getRetryable() != null) {
ctx.put(RETRYABLE_KEY, route.getRetryable());
}
此处的routeLocator是:org.springframework.cloud.netflix.zuul.filters.CompositeRouteLocator.
这里用了一种设计模式(组合模式),不过里面就一个locator:
org.springframework.cloud.netflix.zuul.filters.discovery.DiscoveryClientRouteLocator,继承自:
org.springframework.cloud.netflix.zuul.filters.SimpleRouteLocator
最终会调用到:
org.springframework.cloud.netflix.zuul.filters.SimpleRouteLocator#getRoute方法:
protected Route getRoute(ZuulRoute route, String path) {
if (route == null) {
return null;
}
if (log.isDebugEnabled()) {
log.debug("route matched=" + route);
}
String targetPath = path;
String prefix = this.properties.getPrefix();
if(prefix.endsWith("/")) {
prefix = prefix.substring(0, prefix.length() - 1);
}
if (path.startsWith(prefix + "/") && this.properties.isStripPrefix()) {
targetPath = path.substring(prefix.length());
}
if (route.isStripPrefix()) {
int index = route.getPath().indexOf("*") - 1;
if (index > 0) {
String routePrefix = route.getPath().substring(0, index);
targetPath = targetPath.replaceFirst(routePrefix, "");
prefix = prefix + routePrefix;
}
}
Boolean retryable = this.properties.getRetryable();
if (route.getRetryable() != null) {
retryable = route.getRetryable();
}
return new Route(route.getId(), targetPath, route.getLocation(), prefix,
retryable,
route.isCustomSensitiveHeaders() ? route.getSensitiveHeaders() : null,
route.isStripPrefix());
}
看到这句:
Boolean retryable = this.properties.getRetryable();
最终取的就是本文开头的配置文件中的配置属性。
看到这里,我们终于把retryable属性的来龙去脉搞清楚了,下面说说怎么重试到另外一个实例上去的。
我们在看回:
org.springframework.cloud.netflix.ribbon.apache.RetryableRibbonLoadBalancingHttpClient#execute方法。
其中有一段代码:
RetryCallback<RibbonApacheHttpResponse, IOException> retryCallback = new RetryCallback<RibbonApacheHttpResponse, IOException>() {
@Override
public RibbonApacheHttpResponse doWithRetry(RetryContext context) throws IOException {
//on retries the policy will choose the server and set it in the context
//extract the server and update the request being made
RibbonApacheHttpRequest newRequest = request;
if(context instanceof LoadBalancedRetryContext) {
ServiceInstance service = ((LoadBalancedRetryContext)context).getServiceInstance();
if(service != null) {
//Reconstruct the request URI using the host and port set in the retry context
newRequest = newRequest.withNewUri(UriComponentsBuilder.newInstance().host(service.getHost())
.scheme(service.getUri().getScheme()).userInfo(newRequest.getURI().getUserInfo())
.port(service.getPort()).path(newRequest.getURI().getPath())
.query(newRequest.getURI().getQuery()).fragment(newRequest.getURI().getFragment())
.build().encode().toUri());
}
}
newRequest = getSecureRequest(newRequest, configOverride);
HttpUriRequest httpUriRequest = newRequest.toRequest(requestConfig);
final HttpResponse httpResponse = RetryableRibbonLoadBalancingHttpClient.this.delegate.execute(httpUriRequest);
if(retryPolicy.retryableStatusCode(httpResponse.getStatusLine().getStatusCode())) {
throw new HttpClientStatusCodeException(RetryableRibbonLoadBalancingHttpClient.this.clientName,
httpResponse, HttpClientUtils.createEntity(httpResponse), httpUriRequest.getURI());
}
return new RibbonApacheHttpResponse(httpResponse, httpUriRequest.getURI());
}
};
前面已经提到过:
ServiceInstance service = ((LoadBalancedRetryContext)context).getServiceInstance();
这一行代码getServiceInstance可能会变,即跟你最开始的路由不同,比如我有A,B两个实例,最开始的时候确定路由到A实例上,当A挂了,再重试的时候可能这个ServiceInstance可能是 Instance B。既然有get那么肯定有set它的地方.前面我们说了要实现重试,必须引入spring-retry依赖,然后才会通过org.springframework.retry.support.RetryTemplate#doExecute来执行重试请求,我们看看这个方法的代码片段:
while (canRetry(retryPolicy, context) && !context.isExhaustedOnly()) {
try {
if (this.logger.isDebugEnabled()) {
this.logger.debug("Retry: count=" + context.getRetryCount());
}
// Reset the last exception, so if we are successful
// the close interceptors will not think we failed...
lastException = null;
return retryCallback.doWithRetry(context); //这里调用了RetryableRibbonLoadBalancingHttpClient#execute中定义的RetryCallback的doWithRetry方法
}
catch (Throwable e) {
lastException = e;
try {
registerThrowable(retryPolicy, state, context, e);//在失败的时候执行的逻辑,这里是关键,里面有重新选择服务实例的逻辑
}
catch (Exception ex) {
throw new TerminatedRetryException("Could not register throwable",
ex);
}
finally {
doOnErrorInterceptors(retryCallback, context, e);
}
if (canRetry(retryPolicy, context) && !context.isExhaustedOnly()) {
try {
backOffPolicy.backOff(backOffContext);
}
catch (BackOffInterruptedException ex) {
lastException = e;
// back off was prevented by another thread - fail the retry
if (this.logger.isDebugEnabled()) {
this.logger
.debug("Abort retry because interrupted: count="
+ context.getRetryCount());
}
throw ex;
}
}
if (this.logger.isDebugEnabled()) {
this.logger.debug(
"Checking for rethrow: count=" + context.getRetryCount());
}
if (shouldRethrow(retryPolicy, context, state)) {
if (this.logger.isDebugEnabled()) {
this.logger.debug("Rethrow in retry for policy: count="
+ context.getRetryCount());
}
throw RetryTemplate.<E>wrapIfNecessary(e);
}
}
/*
* A stateful attempt that can retry may rethrow the exception before now,
* but if we get this far in a stateful retry there's a reason for it,
* like a circuit breaker or a rollback classifier.
*/
if (state != null && context.hasAttribute(GLOBAL_STATE)) {
break;
}
}
这行代码是关键,在请求发生异常的时候catch住异常,然后会执行:
registerThrowable(retryPolicy, state, context, e)
其中的retryPolicy是在RetryableRibbonLoadBalancingHttpClient中定义的内部类:
org.springframework.cloud.netflix.ribbon.apache.RetryableRibbonLoadBalancingHttpClient.RetryPolicy,所以其实调用委托给了:
org.springframework.cloud.netflix.ribbon.RibbonLoadBalancedRetryPolicy#registerThrowable方法:
@Override
public void registerThrowable(LoadBalancedRetryContext context, Throwable throwable) {
//if this is a circuit tripping exception then notify the load balancer
if (lbContext.getRetryHandler().isCircuitTrippingException(throwable)) {
updateServerInstanceStats(context);
}
//Check if we need to ask the load balancer for a new server.
//Do this before we increment the counters because the first call to this method
//is not a retry it is just an initial failure.
if(!canRetrySameServer(context) && canRetryNextServer(context)) {
context.setServiceInstance(loadBalanceChooser.choose(serviceId));
}
//This method is called regardless of whether we are retrying or making the first request.
//Since we do not count the initial request in the retry count we don't reset the counter
//until we actually equal the same server count limit. This will allow us to make the initial
//request plus the right number of retries.
if(sameServerCount >= lbContext.getRetryHandler().getMaxRetriesOnSameServer() && canRetry(context)) {
//reset same server since we are moving to a new server
sameServerCount = 0;
nextServerCount++;
if(!canRetryNextServer(context)) {
context.setExhaustedOnly();
}
} else {
sameServerCount++;
}
}
这个类中就用到了最开始说到的MaxAutoRetries,MaxAutoRetriesNextServer,OkToRetryOnAllOperations这三个属性。
主要看这段:
if(!canRetrySameServer(context) && canRetryNextServer(context)) {
context.setServiceInstance(loadBalanceChooser.choose(serviceId));
}
当能在其他服务器上重试的时候,然后通过loadBalanceChooser.choose(serviceId)重新选择了另外一个服务实例。然后set进了context。
整个流程大致上就是这样,具体的实现细节可以自行深入查看一下以上提及的类的代码。
另外还有一个注意事项,此源码是基于Edgware.SR2版本,在Edgware.SR1的时候有BUG,在:
org.springframework.cloud.netflix.ribbon.apache.RetryableRibbonLoadBalancingHttpClient#execute中定义的匿名类RetryCallback中这行代码
newRequest = getSecureRequest(newRequest, configOverride);
在SR1版本的时候是:
newRequest = getSecureRequest(request, configOverride);
导致retry next server无效,每次都被设置回了最开始route的实例,我也是在debug的时候发现的,开始用的SR1版本,我说怎么retry老是无效。。。后面去翻了一下官方的issue,发现:
https://github.com/spring-cloud/spring-cloud-netflix/issues/2667
此BUG在spring-cloud-netfix 1.4.3修复,SR1用的是1.4.2,SR2用的是1.4.3.
小伙伴们发现有问题,请确认你的版本是否和我说的版本一致,根据需要升级一下spring cloud版本。。。
版权声明:「DDKK.COM 弟弟快看,程序员编程资料站」本站文章,版权归原作者所有