一、居中
行内元素:
- 水平居中:text-align:center
- 垂直居中:单行——行高等于盒子高度
- 垂直居中:多行——display:table-cell、vertical-align: middle
块级元素:
- 水平居中:margin:0 auto、absolute+left50%+margin-left/translateX(-50%)、
flex+ justify-content: center- 垂直居中:absolute+top50%+margin-top/translateY(-50%)、
flex+ align-items: center
水平垂直居中:同时使用水平居中和垂直居中
二、水平居中
1. 行内元素水平居中
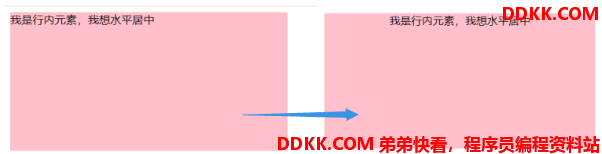
行内元素水平居中:text-align:center
<style>
.father {
width: 400px;
height: 200px;
background-color: pink;
/* 主要代码:text-align: center; */
text-align: center;
}
.son {
}
</style>
<body>
<div class="father">
<span class="son">我是行内元素,我想水平居中</span>
</div>
</body>
2. 块级元素水平居中
2.1 使用margin: 0 auto
<head>
<style>
.father {
width: 400px;
height: 200px;
background-color: pink;
}
.son {
width: 200px;
height: 100px;
background-color: skyblue;
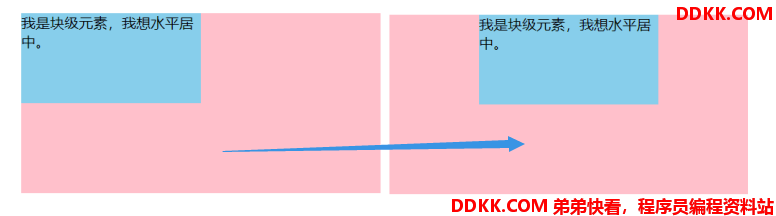
margin: 0 auto;
}
</style>
</head>
<body>
<div class="father">
<div class="son">我是块级元素,我想水平居中。</div>
</div>
</body>
2.2 使用position
<head>
<style>
.father {
width: 400px;
height: 200px;
background-color: pink;
position: relative;
}
.son {
width: 200px;
height: 100px;
background-color: skyblue;
position: absolute;
left: 50%;
/* 如果元素没有设置宽度,不能使用margin-left,可以使用transform: translateX(-50%); 效果相同*/
margin-left: -100px;
}
</style>
</head>
<body>
<div class="father">
<div class="son">我是块级元素,我想水平居中。</div>
</div>
</body>
</html>

2.3 使用flex
<head>
<style>
.father {
width: 400px;
height: 200px;
background-color: pink;
display: flex;
justify-content: center;
}
.son {
width: 200px;
height: 100px;
background-color: skyblue;
}
</style>
</head>
<body>
<div class="father">
<div class="son">我是块级元素,我想水平居中。</div>
</div>
</body>
</html>

三、垂直居中
1. 行内元素
1.1 单行行内元素垂直居中
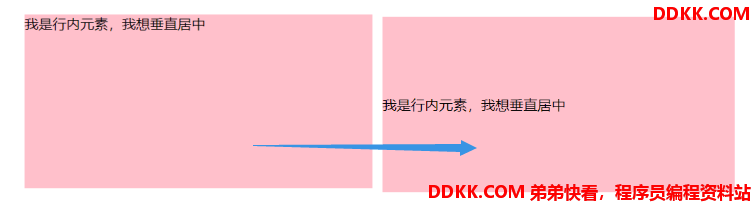
单行行内元素垂直居中:行高等于盒子高度
<head>
<style>
.father {
width: 400px;
height: 200px;
/* 行高等于盒子高度:line-height: 200px; */
line-height: 200px;
background-color: pink;
}
.son {
}
</style>
</head>
<body>
<div class="father">
<span class="son">我是行内元素,我想垂直居中</span>
</div>
</body>
1.2 多行行内元素垂直居中
多行行内元素垂直居中:display:table-cell、vertical-align: middle
单行行内元素垂直居中方式不适合多行文本,会变成下图:
<head>
<style>
.father {
width: 400px;
height: 200px;
/* 主要代码:display: table-cell; vertical-align: middle;*/
display: table-cell;
background-color: pink;
vertical-align: middle;
}
.son {
}
</style>
</head>
<body>
<div class="father">
<span class="son">我是行内元素,我想垂直居中。我是行内元素,我想垂直居中。我是行内元素,我想垂直居中。我是行内元素,我想垂直居中。我是行内元素,我想垂直居中。我是行内元素,我想垂直居中。</span>
</div>
</body>

2. 块级元素
2.1 使用position
<head>
<style>
.father {
width: 400px;
height: 200px;
background-color: pink;
position: relative;
}
.son {
width: 200px;
height: 100px;
background-color: skyblue;
position: absolute;
top: 50%;
/* 如果元素没有设置高度,不能使用margin-top,可以使用transform: translateY(-50%); 效果相同*/
margin-top: -50px;
}
</style>
</head>
<body>
<div class="father">
<div class="son">我是块级元素,我想垂直居中。</div>
</div>
</body>
</html>

2.2 使用flex
<head>
<style>
.father {
width: 400px;
height: 200px;
background-color: pink;
display: flex;
align-items: center;
}
.son {
width: 200px;
height: 100px;
background-color: skyblue;
}
</style>
</head>
<body>
<div class="father">
<div class="son">我是块级元素,我想垂直居中。</div>
</div>
</body>
</html>

