根据之前文章的学习,我们已经可以实现微服务的授权了,目前我们采用的方案是在每个资源服务器校验Token然后完成资源的授权,业界还有一种比较常用的方案就是在网关层统一校验Token,下面我们来探讨一下
1.统一鉴权方案
在“微服务授权方案”中我们就已经探讨了,在微服务中有两种授权方案,一者是不使用网关,即鉴权工作交给资源服务器,二者是使用网关统一鉴权,如果不使用网关那么我们就只需要在每个资源服务做同样的资源服务配置即可,如果要使用网关,那么就需要把资源服务的配置搬到网关中实现统一鉴权(网关充当了资源服务器实现鉴权功能)。这样就避免了资源服务重复的鉴权工作。
当网关实现了统一鉴权那么我们的下游资源服务器就不再需要做Oauth2鉴权的工作了,只需要基于WebSecurity做对具体资源的授权即可。还需要注意的是既然zuul校验了Token那它就可以获取到Token中的明文的认证授权信息,那么zuul只需要使用Filter把明文数据(明文Token)通过Header转发给下游资源服务即可,不再转发密文的Token,而下游资源服务也需要需要使用Filter接收Header中的“明文Token”,如下图:
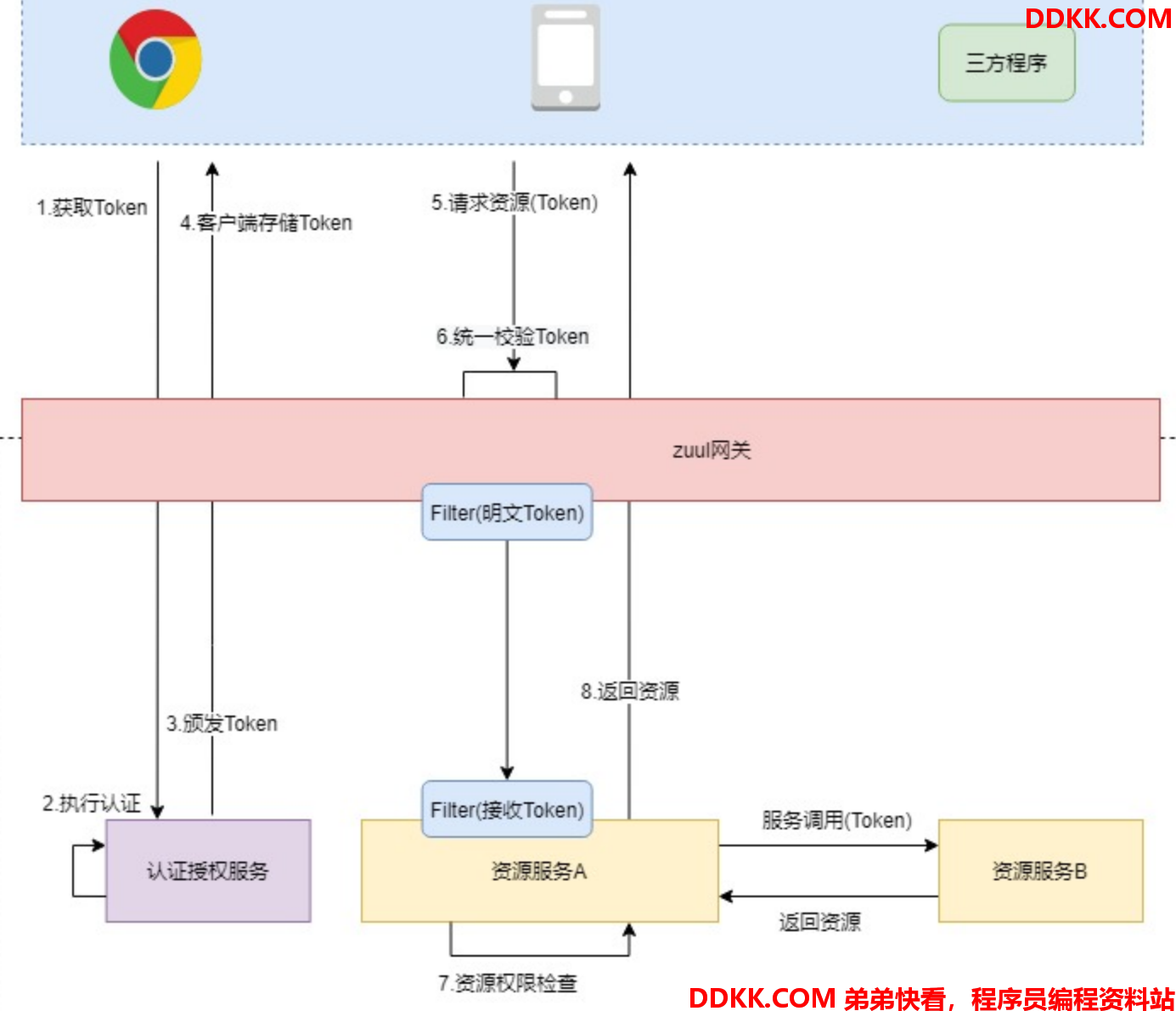
需要注意的是,zuul负责的是统一鉴权,负责检查Token的合法性,而下游被调用的资源服务器负责对具体的资源进行授权
2.Zuul的Oauth2配置
2.1.导入依赖
修改Zuul网关,加入如下oauth2依赖
<dependency>
<groupId>org.springframework.cloud</groupId>
<artifactId>spring-cloud-starter-oauth2</artifactId>
</dependency>
2.2.资源服配置
Zuul需要统一鉴权,需要进行Oauth2配置,这里配置了两个资源服务,一个针对于AuthServer微服务的的资源配置,一个是针对于ResourceServer微服务的资源配置,使用内部类的方式配置如下:
@Configuration
public class ResourceServerConfig{
//配置资源id ,跟AuthorizationServerConfig.configure配置的resourceIds一样
public static final String RESOURCE_ID = "res1";
//JWT相关配置===============================================
@Bean
public TokenStore tokenStore(){
return new JwtTokenStore(jwtAccessTokenConverter());
}
//设置JWT签名密钥。它可以是简单的MAC密钥,也可以是RSA密钥
private final String sign_key = "123";
//JWT令牌校验工具
@Bean
public JwtAccessTokenConverter jwtAccessTokenConverter(){
JwtAccessTokenConverter jwtAccessTokenConverter = new JwtAccessTokenConverter();
//设置JWT签名密钥。它可以是简单的MAC密钥,也可以是RSA密钥
jwtAccessTokenConverter.setSigningKey(sign_key);
return jwtAccessTokenConverter;
}
//zuul资源服务配置,针对认证服务器的配置
@Configuration
@EnableResourceServer
public class AuthConfig extends ResourceServerConfigurerAdapter{
@Autowired
private TokenStore tokenStore;
//资源服务器安全性配置
@Override
public void configure(ResourceServerSecurityConfigurer resources) throws Exception {
//资源ID
resources.resourceId(RESOURCE_ID)
.tokenStore(tokenStore)
//无状态
.stateless(true);
}
@Override
public void configure(HttpSecurity http) throws Exception {
//针对于直接放行的资源
http.authorizeRequests().antMatchers("/**").permitAll();
}
}
//微服务 资源服务配置
@Configuration
@EnableResourceServer
public class ResourceConfig extends ResourceServerConfigurerAdapter{
@Autowired
private TokenStore tokenStore;
//资源服务器安全性配置
@Override
public void configure(ResourceServerSecurityConfigurer resources) throws Exception {
//资源ID
resources.resourceId(RESOURCE_ID)
.tokenStore(tokenStore)
//无状态
.stateless(true);
}
@Override
public void configure(HttpSecurity http) throws Exception {
//如果是其他微服务资源需要 oauth2 认证
http.authorizeRequests()
//校验scope必须为all , 针对于/resource/路径的请求需要oauth2验证有ROLE_API的权限才能访问
.antMatchers("/services/resource/**").access("#oauth2.hasScope('resource1')")
.antMatchers(HttpMethod.OPTIONS, "/**").permitAll()
.and().cors().and().csrf().disable();
}
}
//微服务 资源服务配置
@Configuration
@EnableResourceServer
public class Resource2Config extends ResourceServerConfigurerAdapter{
@Autowired
private TokenStore tokenStore;
//资源服务器安全性配置
@Override
public void configure(ResourceServerSecurityConfigurer resources) throws Exception {
//资源ID
resources.resourceId(RESOURCE_ID)
.tokenStore(tokenStore)
//无状态
.stateless(true);
}
@Override
public void configure(HttpSecurity http) throws Exception {
//如果是其他微服务资源需要 oauth2 认证
http.authorizeRequests()
//校验scope必须为all , 针对于/resource/路径的请求需要oauth2验证有ROLE_API的权限才能访问
.antMatchers("/services/resource2/**").access("#oauth2.hasScope('resource2')")
.antMatchers(HttpMethod.OPTIONS, "/**").permitAll()
.and().cors().and().csrf().disable();
}
}
//如果有其他的资源服务还需要配置其他的 ResourceConfig
}
这里做了两个资源配置,针对于“/services/resource/” 访问路径的要求拥有“#oauth2.hasScope(‘resource1’)”的作用域才能访问,针对于“/services/resource2/”需要有resource2的作用域才能访问,这里相当于做了一个粗粒度的鉴权(注意路径需要加上zuul统一前缀),那么就要求令牌中的scope需要包含对应的授权范围,而其他路径“antMatchers("/**").permitAll();”直接放行。
注意:如果这里有很多的ResourceServer微服务那么这里就需要再增加ResourceServerConfigurerAdapter配置
2.3.WebSecurity配置
配置了资源服务器之后,WebSecurity直接放行即可,所有的鉴权都交给资源服务配置
@Configuration
public class WebSecurityConfig extends WebSecurityConfigurerAdapter{
@Override
protected void configure(HttpSecurity http) throws Exception {
//针对于zuul本身的请求直接放行 , 当访问某个资源的时候会通过oauth2检查权限
http.authorizeRequests().antMatchers("/**").permitAll()
.antMatchers(HttpMethod.OPTIONS, "/**").permitAll()
.and().csrf().disable();
}
}
2.4.跨域配置
@Component
public class CorsFilter implements Filter {
@Override
public void doFilter(ServletRequest req, ServletResponse res, FilterChain chain) throws IOException, ServletException {
HttpServletRequest request = (HttpServletRequest) req;
HttpServletResponse response = (HttpServletResponse) res;
/* String curOrigin = request.getHeader("Origin");
System.out.println("###跨域过滤器->当前访问来源->"+curOrigin+"###"); */
response.setHeader("Access-Control-Allow-Origin", "*");
response.setHeader("Access-Control-Allow-Methods", "*");
response.setHeader("Access-Control-Max-Age", "3600");
response.setHeader("Access-Control-Allow-Headers", "x-requested-with");
chain.doFilter(req, res);
}
@Override
public void init(FilterConfig filterConfig) {
}
@Override
public void destroy() {
}
}
2.5.转发认证信息
当zuul鉴权成功之后,我们希望以明文方式获取到token中的认证信息传送给下游微服务,这里采用zuul的filter实现。
import com.fasterxml.jackson.databind.ObjectMapper;
import com.netflix.zuul.ZuulFilter;
import com.netflix.zuul.context.RequestContext;
import com.netflix.zuul.exception.ZuulException;
import lombok.SneakyThrows;
import org.springframework.cloud.netflix.zuul.filters.support.FilterConstants;
import org.springframework.security.core.Authentication;
import org.springframework.security.core.GrantedAuthority;
import org.springframework.security.core.context.SecurityContextHolder;
import org.springframework.security.oauth2.provider.OAuth2Authentication;
import org.springframework.stereotype.Component;
import org.springframework.util.Base64Utils;
import java.util.*;
//定义filter,从上下文中拿到认证信息,授权信息,封装成 JSON,
// 通过请求头转发给下游微服务
@Component
public class TokenForwardFilter extends ZuulFilter {
@Override
public String filterType() {
return FilterConstants.PRE_TYPE ;//"pre";
}
@Override
public int filterOrder() {
return 0;
}
@Override
public boolean shouldFilter() {
return true;
}
@SneakyThrows
@Override
public Object run() throws ZuulException {
//1.拿到上下文中的认证对象
Authentication authentication = SecurityContextHolder.getContext().getAuthentication();
//2.拿到认证对象中的用户信息
if(! (authentication instanceof OAuth2Authentication)){
return null;
}
//用户主体,包含用户别名
Object principal = authentication.getPrincipal();
//请求参数
Map<String, String> requestParameters = ((OAuth2Authentication) authentication).getOAuth2Request().getRequestParameters();
//3.拿到认证对象中的权限列表
Collection<? extends GrantedAuthority> authorities = authentication.getAuthorities();
//转一下权限列表
List<String> authoritiesList = new ArrayList<>(authorities.size());
authorities.forEach( authoritie ->{
authoritiesList.add(authoritie.getAuthority());
});
//4.把用户信息和权限列表封装成map,转成JSON
Map<String,Object> map = new HashMap<>(requestParameters);
map.put("principal",principal);
map.put("authorities",authoritiesList);
//5.把JSON设置到请求头传给下游微服务
byte[] header = new ObjectMapper().writeValueAsBytes(map);
String jsonToken = Base64Utils.encodeToString(header) ;
RequestContext.getCurrentContext().addZuulRequestHeader("token",jsonToken);
return null;
}
}
网关配置结束,其他内容比如yml配置,主启动类按照正常配置走就行。
3.资源服务器配置
网关层转发过来的Token已经是明文的了,我们需要在资源服务器定义一个Filter去接收请求头中的内容 ,其实资源服务器已经可以不做Oauth2配置了,不需要导入spring-cloud-starter-oauth2的包,导入spring-cloud-starter-security包即可,为了代码公用,我们可以把接收Token的Filter定义在一个公共的模块中security-resource-common中
3.1.增加依赖
<dependencies>
<dependency>
<groupId>org.springframework.boot</groupId>
<artifactId>spring-boot-starter-web</artifactId>
</dependency>
<dependency>
<groupId>org.springframework.cloud</groupId>
<artifactId>spring-cloud-starter-security</artifactId>
</dependency>
<dependency>
<groupId>com.alibaba</groupId>
<artifactId>fastjson</artifactId>
<version>1.2.58</version>
</dependency>
</dependencies>
3.2.定义Filter
Filter的目的是接收zuul转发过来的明文的Token,绑定到Security上下文中,访问资源的时候Security自然可以获取到授权列表对方法进行授权
//过滤器从请求头中获取到用户授权信息,封装成 UsernamePasswordAuthenticationToken 并设置到 securityContext中
//security在授权的时候会从 UsernamePasswordAuthenticationToken获取认证信息和授权信息进行授权
@Component
public class TokenAuthenticationFilter extends OncePerRequestFilter {
@Override
protected void doFilterInternal(HttpServletRequest request, HttpServletResponse response,
FilterChain filterChain) throws ServletException, IOException {
//1.获取请求头中的明文token
String tokenJson = request.getHeader("token");
if(StringUtils.hasLength(tokenJson)){
String authTokenJson = new String(Base64Utils.decodeFromString(tokenJson));
Map<String,Object> map = JSON.parseObject(authTokenJson,Map.class);
//2.获取到用户主体信息,权限列表
String username = map.get("principal").toString();
//权限列表
List<String> authoritiesStr = (List<String>)map.get("authorities");
//转换权限列表
List<SimpleGrantedAuthority> authorities = new ArrayList<>(authoritiesStr.size());
authoritiesStr.forEach( authStr ->{
authorities.add(new SimpleGrantedAuthority(authStr));
});
//3.把用户主体信息,权限列表,交给Security
//把用户信息和权限封装成 UsernamePasswordAuthenticationToken
UsernamePasswordAuthenticationToken token = new UsernamePasswordAuthenticationToken(
username,null,authorities );
//设置detail,根据请求对象创建一个detail
token.setDetails(new WebAuthenticationDetailsSource().buildDetails(request));
//把UsernamePasswordAuthenticationToken填充到security上下文
SecurityContextHolder.getContext().setAuthentication(token);
}
//放行
filterChain.doFilter(request,response);
}
}
Filter定义好了,需要让Spring扫描到该类,然后在资源服务器中去依赖security-resource-common模块即可接收请求中的Token了
3.3.Security配置
下游资源服务器根据自身情况做web安全配置,下面配置中我开启了方法授权注解
//security 的配置
@Configuration
@EnableWebSecurity //开启Security
@EnableGlobalMethodSecurity(prePostEnabled = true)
public class WebSecurityConfig extends WebSecurityConfigurerAdapter {
//授权规则配置
@Override
protected void configure(HttpSecurity http) throws Exception {
http.csrf().disable() //屏蔽跨域防护
.authorizeRequests() //对请求做授权处理
.antMatchers("/**").permitAll(); //其他路径都要拦截
}
}
3.4.资源授权
对方法进行授权
@RequestMapping(value="/employee/list",method= RequestMethod.GET)
@PreAuthorize("hasAuthority('employee:list')")
public AjaxResult list(){
...
}
4.总结
给用户分配好权限,让用户去认证中心获取Token,然后通过zuul访问,应该是能够访问到/employee/list资源的。
它的请求流程是:
- 客户端请求到zuul,资源根据资源服务器配置校验Token,
- 校验通过zuul的Filter转发明文Token(认证授权信息)到下游微服务
- 下游微服务的Filter接收明文Token并绑定到Security上下中
- security获取到Token中的权限列表对方法进行授权
- 授权成功返回资源给客户端