1.为什么使用自定义 Realm
- 我们使用 JDBCRealm 的时候发现,shiro 的底层自己封装了数据库表的名称和字段的名称,这样就造成了使用起来非常不方便
2.解决方案
- 自定义 Realm
- 我们如果自己定义 realm 的话,可以实现这个接口AuthorizingRealm
3.代码实现
导包:
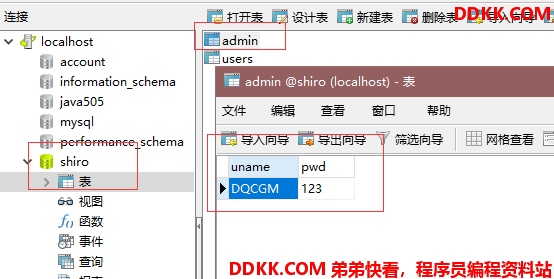
数据库创建:
[main]
#设置securityManager中realm
userRealm=com.shiro2.UserRealm
securityManager.realms=$userRealm
package com.shiro2;
import org.apache.shiro.authc.AuthenticationException;
import org.apache.shiro.authc.AuthenticationInfo;
import org.apache.shiro.authc.AuthenticationToken;
import org.apache.shiro.authc.SimpleAuthenticationInfo;
import org.apache.shiro.authz.AuthorizationInfo;
import org.apache.shiro.realm.AuthorizingRealm;
import org.apache.shiro.subject.PrincipalCollection;
import java.sql.Connection;
import java.sql.DriverManager;
import java.sql.PreparedStatement;
import java.sql.ResultSet;
public class UserRealm extends AuthorizingRealm {
//认证
@Override
protected AuthenticationInfo doGetAuthenticationInfo(AuthenticationToken authenticationToken) throws AuthenticationException {
//System.out.println(authenticationToken.getPrincipal());
try {
Class.forName("com.mysql.jdbc.Driver");
Connection conn = DriverManager.getConnection("jdbc:mysql://127.0.0.1:3306/shiro", "root", "Root");
PreparedStatement prepareStatement = conn.prepareStatement("select pwd from admin where uname =? ");
prepareStatement.setObject(1, authenticationToken.getPrincipal());
ResultSet rs = prepareStatement.executeQuery();
while (rs.next()) {
SimpleAuthenticationInfo info = new SimpleAuthenticationInfo(authenticationToken.getPrincipal(), rs.getString("pwd"), "userRealm");
return info;
}
} catch (Exception e) {
e.printStackTrace();
}
return null;
}
//授权
@Override
protected AuthorizationInfo doGetAuthorizationInfo(PrincipalCollection principalCollection) {
return null;
}
}
package com.shiro2;
import org.apache.shiro.SecurityUtils;
import org.apache.shiro.authc.IncorrectCredentialsException;
import org.apache.shiro.authc.UnknownAccountException;
import org.apache.shiro.authc.UsernamePasswordToken;
import org.apache.shiro.config.IniSecurityManagerFactory;
import org.apache.shiro.mgt.SecurityManager;
import org.apache.shiro.subject.Subject;
import org.apache.shiro.util.Factory;
public class TestB {
public static void main(String[] args) {
/*Realm*/
//[1]解析shiro.ini文件
Factory<SecurityManager> factory = new IniSecurityManagerFactory("classpath:shiro-jdbc2.ini");
//[2]通过SecurityManager工厂获得SecurityManager实例
SecurityManager securityManager = factory.getInstance();
//[3]把SecurityManager对象设置到运行环境中
SecurityUtils.setSecurityManager(securityManager);
//[4]通过SecurityUtils获得主体subject
Subject subject = SecurityUtils.getSubject();
//[5]书写自己输入的账号和密码---相当于用户自己输入的账号和密码
//我们拿着自己书写用户名密码去和shiro.ini 文件中的账号密码比较
UsernamePasswordToken token = new UsernamePasswordToken("DQCGM", "123");
try {
//[6]进行身份的验证
subject.login(token);
//[7]通过方法判断是否登录成功
if (subject.isAuthenticated()) {
System.out.println("登录成功");
}
} catch (IncorrectCredentialsException e) {
System.out.println("登录失败");
} catch (UnknownAccountException e) {
System.out.println("用户名不正确");
}
}
}
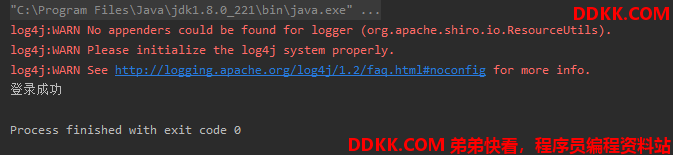
运行结果: