文件描述符复制
让新的文件描述符指向旧的文件描述符(新旧文件描述符指向同一个文件)
使用函数dup、dup2
1 dup函数
系统调用从系统寻找最小可用的文件描述符作为oldfd的副本,新文件描述符通过dup的返回值返回
#include <unistd.h>
int dup(int oldfd);
参数:
oldfd:需要复制的文件描述符
返回值:
返回成功复制后的文件描述符
例
#include <stdio.h>
#include <unistd.h>
#include <string.h>
int main(int argc, char const *argv[])
{
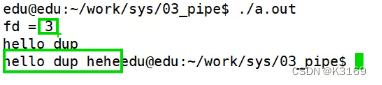
//复制描述符1(输出终端)
int fd = dup(1);
printf("fd = %d\n", fd); //3
//输出字符串
printf("hello dup\n");
write(fd, "hello dup hehe",strlen("hello dup hehe"));
close(fd);
return 0;
}
2 dup2函数
指定一个文件描述符做另一个文件描述符的副本
dup2与dup基本一致,没什么区别
#include <unistd.h>
int dup2(int oldfd, int newfd);
参数:
oldfd:需要拷贝的文件描述符
newfd:需要成为副本的文件描述符
(将newfd作为oldfd的副本)
例
#include <stdio.h>
#include <unistd.h>
#include <string.h>
int main(int argc, char const *argv[])
{
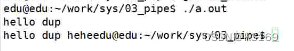
//复制描述符1(输出终端)
dup2(1, 4);
//输出字符串
printf("hello dup\n");
write(4, "hello dup hehe",strlen("hello dup hehe"));
close(4);
return 0;
}
注:如果newfd事先存在,dup2会先close(newfd),然后将newfd作为oldfd的副本