DML&DQL
我们接下来操作这张emp表:
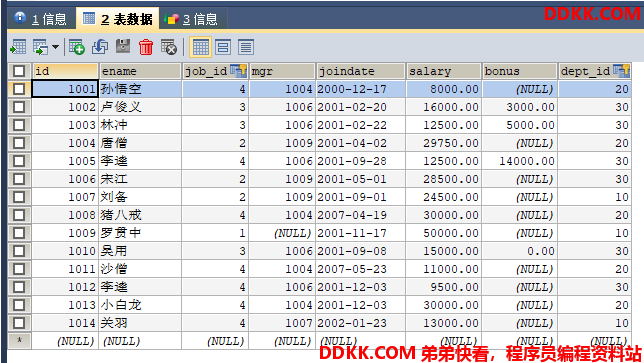
需求:
1、 修改1号数据的salary为1000;
2、 添加一条记录;
3、 删除刚才添加的记录;
4、 查询id为1的记录,将其封装为Map集合;
5、 查询所有的记录,将其封装为List;
6、 查询所有的记录,将其封装为Emp对象的List集合;
7、 查询总记录数;
我们继续使用之前写好的Emp类,如下:
Junit测试工具
我们如果要一个一个去测试需求,要修改7次main方法,过于繁琐,我们使用Junit测试工具来减轻负担,如下:
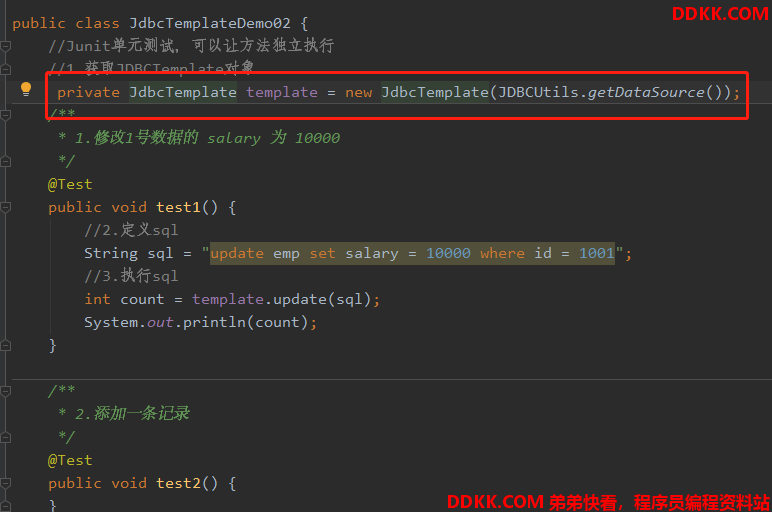
1.修改1号数据的 salary 为 1000
/**
* 1.修改1号数据的 salary 为 10000
*/
@Test
public void test1() {
//1.获取JDBCTemplate对象
JdbcTemplate template = new JdbcTemplate(JDBCUtils.getDataSource());
//2.定义sql
String sql = "update emp set salary = 10000 where id = 1001";
//3.执行sql
int count = template.update(sql);
System.out.println(count);
}
2.添加一条记录
我们把连接对象写在成员变量里面,就不用每次都去获取
/**
* 2.添加一条记录
*/
@Test
public void test2() {
String sql = "insert into emp(id,ename,dept_id) values(?,?,?)";
int count = template.update(sql, 1015, "郭靖", 10);
System.out.println(count);
}
3.删除刚才添加的记录
/**
* 3.删除刚才添加的记录
*/
@Test
public void test3() {
String sql = "delete from emp where id = ?";
int count = template.update(sql,1015);
System.out.println(count);
}
4.查询id为1的记录,将其封装为Map集合
/**
* 4.查询id为1的记录,将其封装为Map集合
*/
@Test
public void test4() {
String sql = "select * from emp where id = ?";
Map<String, Object> map = template.queryForMap(sql, 1001);
System.out.println(map);
}
运行结果:
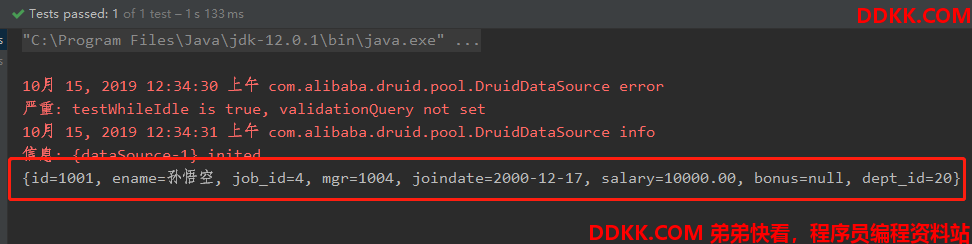
注意:这个方法查询的结果集长度只能是1,将列名作为key,将值作为value,将这条记录封装成一个map集合
5.查询所有的记录,将其封装为List
/**
* 5.查询所有记录,将其封装为List
*/
@Test
public void test5() {
String sql = "select * from emp";
List<Map<String, Object>> list = template.queryForList(sql);
System.out.println(list);
for (Map<String, Object> stringObjectMap : list) {
System.out.println(stringObjectMap);
}
}
注意:
遍历Map和List都可以使用快捷键iter
将每一条记录封装成一个Map集合,再将Map集合装载到List集合中
运行效果:
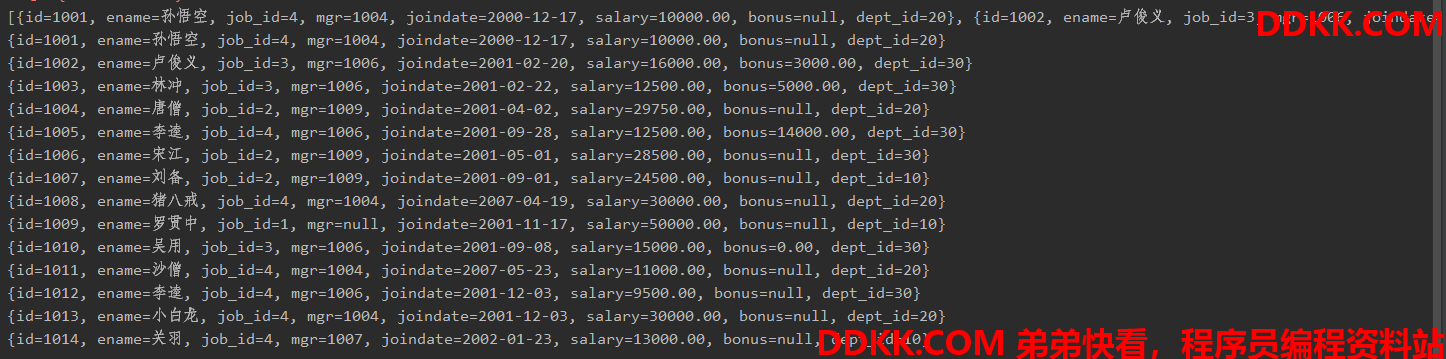
6.查询所有的记录,将其封装为Emp对象的List集合
我们先自己写一个RowMapper<Emp>()方法,如下:
/**
* 6.查询所有的记录,将其封装为Emp对象的List集合
*/
@Test
public void test6() {
String sql = "select * from emp";
List<Emp> list = template.query(sql, new RowMapper<Emp>() {
@Override
public Emp mapRow(ResultSet rs, int i) throws SQLException {
Emp emp = new Emp();
int id = rs.getInt("id");
String ename = rs.getString("ename");
int job_id = rs.getInt("job_id");
int mgr = rs.getInt("mgr");
Date joindate = rs.getDate("joindate");
double salary = rs.getDouble("salary");
double bonus = rs.getDouble("bonus");
int dept_id = rs.getInt("dept_id");
emp = new Emp();
emp.setId(id);
emp.setEname(ename);
emp.setJob_id(job_id);
emp.setMgr(mgr);
emp.setJoindate(joindate);
emp.setSalary(salary);
emp.setBonus(bonus);
emp.setDept_id(dept_id);
return emp;
}
});
for (Emp emp : list) {
System.out.println(emp);
}
}
但是这样相当的复杂和麻烦,我们使用Spring自带的方法
/**
* 6.查询所有的记录,将其封装为Emp对象的List集合
*/
@Test
public void test6() {
String sql = "select * from emp";
List<Emp> list = template.query(sql, new BeanPropertyRowMapper<Emp>(Emp.class));
for (Emp emp : list) {
System.out.println(emp);
}
}
可以看到报错了
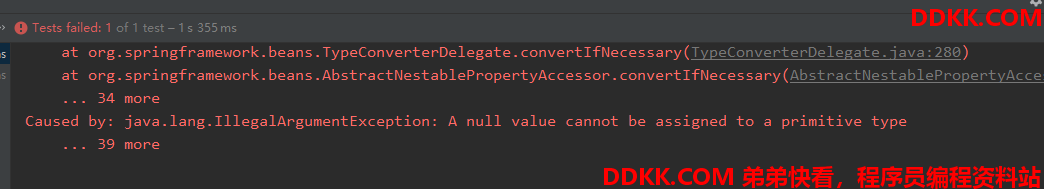
这是因为double和int等值不支持null
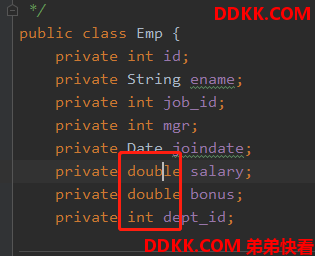
我们更改一下Emp.java,如下:
package domain;
import java.util.Date;
/**
* 封装Emp表数据的JavaBean
*/
public class Emp {
private Integer id;
private String ename;
private Integer job_id;
private Integer mgr;
private Date joindate;
private Double salary;
private Double bonus;
private Integer dept_id;
public Integer getId() {
return id;
}
public void setId(Integer id) {
this.id = id;
}
public String getEname() {
return ename;
}
public void setEname(String ename) {
this.ename = ename;
}
public Integer getJob_id() {
return job_id;
}
public void setJob_id(Integer job_id) {
this.job_id = job_id;
}
public Integer getMgr() {
return mgr;
}
public void setMgr(Integer mgr) {
this.mgr = mgr;
}
public Date getJoindate() {
return joindate;
}
public void setJoindate(Date joindate) {
this.joindate = joindate;
}
public Double getSalary() {
return salary;
}
public void setSalary(Double salary) {
this.salary = salary;
}
public Double getBonus() {
return bonus;
}
public void setBonus(Double bonus) {
this.bonus = bonus;
}
public Integer getDept_id() {
return dept_id;
}
public void setDept_id(Integer dept_id) {
this.dept_id = dept_id;
}
@Override
public String toString() {
return "Emp{" +
"id=" + id +
", ename='" + ename + '\'' +
", job_id=" + job_id +
", mgr=" + mgr +
", joindate=" + joindate +
", salary=" + salary +
", bonus=" + bonus +
", dept_id=" + dept_id +
'}';
}
}
/**
* 6.查询所有的记录,将其封装为Emp对象的List集合
*/
@Test
public void test6() {
String sql = "select * from emp";
List<Emp> list = template.query(sql, new BeanPropertyRowMapper<Emp>(Emp.class));
for (Emp emp : list) {
System.out.println(emp);
}
}
运行效果:
注意:
query的参数:RowMapper
一般我们使用BeanPropertyRowMapper实现类,可以完成JavaBean的自动封装
new BeanPropertyRowMapper<类型>(类型.class)
7.查询总记录数
/**
* 7.查询总记录数
*/
@Test
public void test7() {
String sql = "select count(id) from emp";
Long total = template.queryForObject(sql, Long.class);
System.out.println(total);
}
注意:
queryForObject:查询结果,将结果封装为对象
一般用于聚合函数的查询