(一)ResultSet(结果集对象)基本使用
其实结果集对象读取数据的过程就像游标一样,一行一行地读取
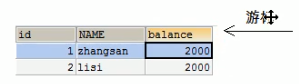
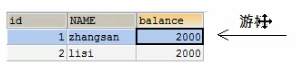
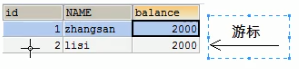
方法:
1、next():游标向下移动一行;
2、getXxx():获取数据;
注意:
Xxx代表数据类型 如:int getInt()
一次只能获取某一行某一列的一个数据
那么我们怎么才能精确地获取我们想要的数据呢?下面提供两种重载方法
参数为int的:int代表列的编号,从1开始算起,如getString(1)
参数为String的:String代表列的名称,如getDouble("balance")
(二)代码演示
首先我们加多一个全局对象
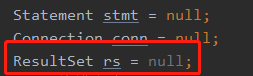
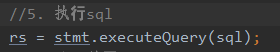
使用executeQuery去执行sql语句
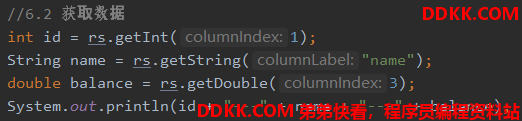
用游标去获取数据
完整代码:
public class JDBCDemo06 {
public static void main(String[] args) {
Statement stmt = null;
Connection conn = null;
ResultSet rs = null;
//1. 注册驱动
try {
Class.forName("com.mysql.cj.jdbc.Driver");
//2. 定义sql
String sql = "select * from account";
//3. 获取Connection对象
conn = DriverManager.getConnection("jdbc:mysql:///test03", "root", "root");
//4. 获取执行sql的对象 Statement
stmt = conn.createStatement();
//5. 执行sql
rs = stmt.executeQuery(sql);
//6. 处理结果
//6.1 让游标向下移动一行
rs.next();
//6.2 获取数据
int id = rs.getInt(1);
String name = rs.getString("name");
double balance = rs.getDouble(3);
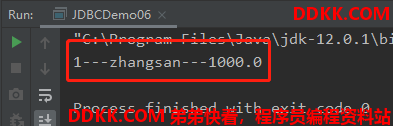
System.out.println(id + "---" + name + "---" + balance);
} catch (ClassNotFoundException e) {
e.printStackTrace();
} catch (SQLException e) {
e.printStackTrace();
} finally {
// stmt.close();
// 避免空指针异常
if (stmt != null) {
try {
stmt.close();
} catch (SQLException e) {
e.printStackTrace();
}
}
if (conn != null) {
try {
conn.close();
} catch (SQLException e) {
e.printStackTrace();
}
}
if (rs != null) {
try {
rs.close();
} catch (SQLException e) {
e.printStackTrace();
}
}
}
}
}
运行效果:
(三)ResultSet(结果集对象)正确的使用
使用步骤:
1、 游标向下移动一行;
2、 判断是否有数据:;
boolean next():游标向下移动一行,判断当前行是否为最后一行末尾(是否有数据),如果是则返回false,如果不是则返回true
3、 获取数据;
最终代码:
//6. 处理结果
if (rs.next()) {
int id = rs.getInt(1);
String name = rs.getString("name");
double balance = rs.getDouble(3);
System.out.println(id + "---" + name + "---" + balance);
}
我们可以用while循环去把所以的数据都遍历出来
while (rs.next()) {
int id = rs.getInt(1);
String name = rs.getString("name");
double balance = rs.getDouble(3);
System.out.println(id + "---" + name + "---" + balance);
}