一、hystrix基本介绍
Hystrix(https://github.com/Netflix/Hystrix)是Netflix(https://www.netflix.com/global)的一个开源项目,主要作用是通过控制那些访问远程系统、服务和第三方库的节点,从而对延迟和故障提供更强大的容错能力。 其可以看做是Netflix团队对分布式系统运维的各种理念和实践的总结。
二、基本用法
pom.xml加上以下依赖
<dependency>
<groupId>com.netflix.hystrix</groupId>
<artifactId>hystrix-core</artifactId>
<version>1.5.8</version>
</dependency>
基本使用
如果某程序或class要使用Hystrix,只需简单继承 HystrixCommand/HystrixObservableCommand并重写run()/construct()
然后调用程序实例化此class并执行execute()/queue()/observe()/toObservable()
例如:
public class HelloWorldHystrixCommand extends HystrixCommand<String>{
private final String name;
public HelloWorldHystrixCommand(String name) {
super(HystrixCommandGroupKey.Factory.asKey("ExampleGroup"));
this.name = name;
}
@Override
protected String run() throws Exception {
//Thread.sleep(100);
return "hello"+name;
}
}
public static void main(String[] args){
String result = new HelloWorldHystrixCommand("test").execute();
System.out.println(result);
}
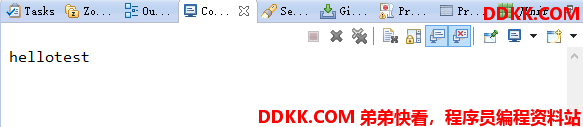
或者
public class HelloWorldHystrixObservableCommand extends HystrixObservableCommand<String>{
private final String name;
protected HelloWorldHystrixObservableCommand(String name) {
super(HystrixCommandGroupKey.Factory.asKey("ExampleGroup"));
this.name = name;
}
@Override
protected Observable<String> construct() {
System.out.println("in construct! thread:" + Thread.currentThread().getName());
return (Observable<String>) Observable.create(new Observable.OnSubscribe<String>() {
// @Override
public void call(Subscriber<? super String> observer) {
try {
System.out.println("in call of construct! thread:" + Thread.currentThread().getName());
if (!observer.isUnsubscribed()) {
// observer.onError(getExecutionException()); // 直接抛异常退出,不会往下执行
observer.onNext("Hello1" + " thread:" + Thread.currentThread().getName());
observer.onNext("Hello2" + " thread:" + Thread.currentThread().getName());
observer.onNext(name + " thread:" + Thread.currentThread().getName());
System.out.println("complete before------" + " thread:" + Thread.currentThread().getName());
observer.onCompleted(); // 不会往下执行observer的任何方法
System.out.println("complete after------" + " thread:" + Thread.currentThread().getName());
observer.onCompleted(); // 不会执行到
observer.onNext("abc"); // 不会执行到
}
} catch (Exception e) {
observer.onError(e);
}
}
});
}
}
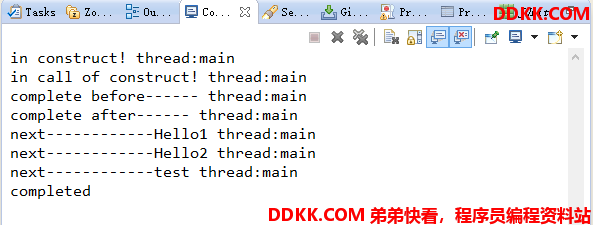
public static void main(String[] args) {
Observable<String> observable = new HelloWorldHystrixObservableCommand("test").observe();
observable.subscribe(new Subscriber<String>() {
public void onCompleted() {
System.out.println("completed");
}
public void onError(Throwable throwable) {
System.out.println("error-----------"+throwable);
}
public void onNext(String v) {
System.out.println("next------------" + v);
}
});
}
HystrixCommand 与 HystrixObservableCommand对比
要想使用hystrix,只需要继承HystrixCommand或HystrixObservableCommand,简单用法见上面例子。
两者主要区别是:
(1)前者的命令逻辑写在run();后者的命令逻辑写在construct()
(2)前者的run()是由新创建的线程执行;后者的construct()是由调用程序线程执行
(3)前者一个实例只能向调用程序发送(emit)单条数据,比如上面例子中run()只能返回一个String结果;后者一个实例可以顺序发送多条数据,比如demo中顺序调用多个onNext(),便实现了向调用程序发送多条数据;
④4个命令的执行方法对比
execute()、 queue()、 observe()、 toObservable()这4个方法用来触发执行 run()/construct(),一个实例只能执行一次这4个方法,特别说明的是 HystrixObservableCommand没有 execute()和 queue()。
4个方法的主要区别是:
(1)execute():以同步堵塞方式执行run()。调用execute()后,hystrix先创建一个新线程运行run(),接着调用程序要在execute()调用处一直堵塞着,直到run()运行完成(2)queue():以异步非堵塞方式执行run()。一调用queue()就直接返回一个Future对象,同时hystrix创建一个新线程运行run(),调用程序通过Future.get()拿到run()的返回结果,而Future.get()是堵塞执行的。
测试代码如下:
@Test
public void testQueue() throws Exception {
// queue()是异步非堵塞性执行:直接返回,同时创建一个线程运行HelloWorldHystrixCommand.run()
// 一个对象只能queue()一次
// queue()事实上是toObservable().toBlocking().toFuture()
Future<String> future = new HelloWorldHystrixCommand("Hlx").queue();
// 使用future时会堵塞,必须等待HelloWorldHystrixCommand.run()执行完返回
String queueResult = future.get(10000, TimeUnit.MILLISECONDS);
// String queueResult = future.get();
System.out.println("queue异步结果:" + queueResult);
assertEquals("hello", queueResult.substring(0, 5));
}
(3)observe():事件注册前执行run()/construct()。第一步是事件注册前,先调用observe()自动触发执行run()/construct()(如果继承的是HystrixCommand,hystrix将创建新线程非堵塞执行run();如果继承的是HystrixObservableCommand,将以调用程序线程堵塞执行construct()),第二步是从observe()返回后调用程序调用subscribe()完成事件注册,如果run()/construct()执行成功则触发onNext()和onCompleted(),如果执行异常则触发onError()
测试代码如下:
@Test
public void testObservable() throws Exception {
// observe()是异步非堵塞性执行,同queue
Observable<String> hotObservable = new HelloWorldHystrixCommand("Hlx").observe();
// single()是堵塞的
//System.out.println("hotObservable single结果:" + hotObservable.toBlocking().single());
//System.out.println("------------------single");
// 注册观察者事件
// subscribe()是非堵塞的
hotObservable.subscribe(new Observer<String>() {
// 先执行onNext再执行onCompleted
// @Override
public void onCompleted() {
System.out.println("hotObservable completed");
}
// @Override
public void onError(Throwable e) {
e.printStackTrace();
}
// @Override
public void onNext(String v) {
System.out.println("hotObservable onNext: " + v);
}
});
// 非堵塞
// - also verbose anonymous inner-class
// - ignore errors and onCompleted signal
hotObservable.subscribe(new Action1<String>() {
// 相当于上面的onNext()
// @Override
public void call(String v) {
System.out.println("hotObservable call: " + v);
}
});
// 主线程不直接退出,在此一直等待其他线程执行
System.in.read();
}
(4)toObservable():事件注册后执行run()/construct()。第一步是事件注册前,一调用toObservable()就直接返回一个Observable<String>对象,第二步调用subscribe()完成事件注册后自动触发执行run()/construct()(如果继承的是HystrixCommand,hystrix将创建新线程非堵塞执行run(),调用程序不必等待run();如果继承的是HystrixObservableCommand,将以调用程序线程堵塞执行construct(),调用程序等待construct()执行完才能继续往下走),如果run()/construct()执行成功则触发onNext()和onCompleted(),如果执行异常则触发onError()
测试代码如下:
@Test
public void testToObservable() throws Exception {
// toObservable()是异步非堵塞性执行,同queue
Observable<String> coldObservable = new HelloWorldHystrixCommand("Hlx").toObservable();
// single()是堵塞的
//System.out.println("coldObservable single结果:" + coldObservable.toBlocking().single());
// 注册观察者事件
// subscribe()是非堵塞的
// - this is a verbose anonymous inner-class approach and doesn't do assertions
coldObservable.subscribe(new Observer<String>() {
// 先执行onNext再执行onCompleted
// @Override
public void onCompleted() {
System.out.println("coldObservable completed");
}
// @Override
public void onError(Throwable e) {
System.out.println("coldObservable error");
e.printStackTrace();
}
// @Override
public void onNext(String v) {
System.out.println("coldObservable onNext: " + v);
}
});
// 非堵塞
// - also verbose anonymous inner-class
// - ignore errors and onCompleted signal
/*coldObservable.subscribe(new Action1<String>() {
public void call(String v) {
// 相当于上面的onNext()
// @Override
System.out.println("coldObservable call: " + v);
}
});*/
// 主线程不直接退出,在此一直等待其他线程执行
System.in.read();
}