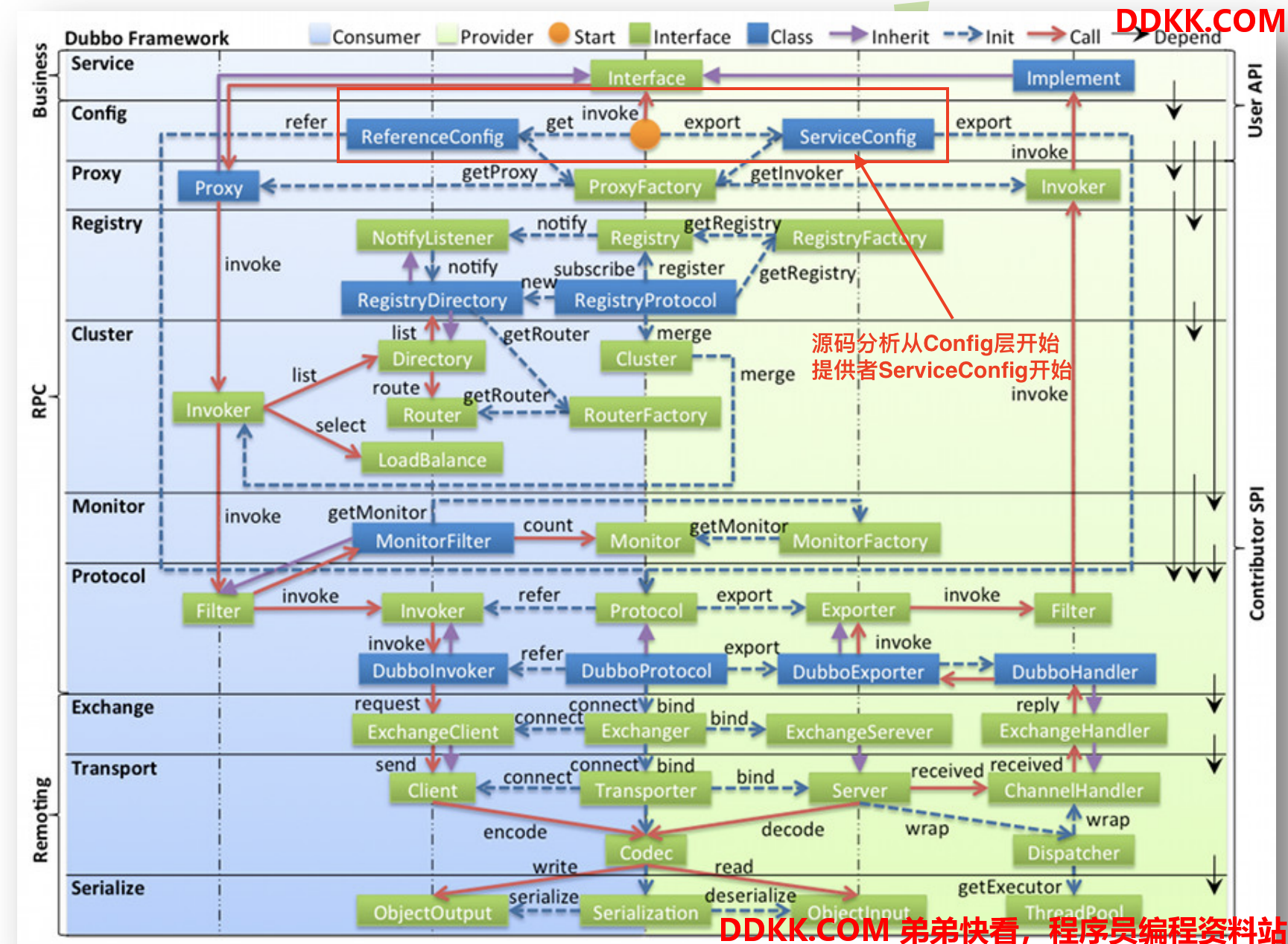
Dubbo 的源码解析
内核源码已经分析过了,接下来分析的所有Dubbo源码都是基于内核之上的。
1. Dubbo 与 Spring 整合
这里以Dubbo的org.apache.dubbo.container.Main#main开始分析:
public class Main {
...
public static final String CONTAINER_KEY = "dubbo.container";
private static final ExtensionLoader<Container> loader = ExtensionLoader.getExtensionLoader(Container.class);
...
public static void main(String[] args) {
try {
if (ArrayUtils.isEmpty(args)) {
//如果args为空,获取系统参数dubbo.container
//未指定则取Container的默认扩展类,即spring
String config = ConfigUtils.getProperty(CONTAINER_KEY, loader.getDefaultExtensionName());
args = COMMA_SPLIT_PATTERN.split(config);
}
final List<Container> containers = new ArrayList<Container>();
for (int i = 0; i < args.length; i++) {
//可以指定多个容器,不指定默认用spring容器
containers.add(loader.getExtension(args[i]));
}
logger.info("Use container type(" + Arrays.toString(args) + ") to run dubbo serivce.");
if ("true".equals(System.getProperty(SHUTDOWN_HOOK_KEY))) {
...
}
for (Container container : containers) {
//关键代码启动容器
container.start();
logger.info("Dubbo " + container.getClass().getSimpleName() + " started!");
}
System.out.println(new SimpleDateFormat("[yyyy-MM-dd HH:mm:ss]").format(new Date()) + " Dubbo service server started!");
} catch (RuntimeException e) {
logger.error(e.getMessage(), e);
System.exit(1);
}
...
}
}
主要看容器的启动方法,我们关注的是Spring容器,所以看org.apache.dubbo.container.spring.SpringContainer#start的方法:
public class SpringContainer implements Container {
public static final String SPRING_CONFIG = "dubbo.spring.config";
public static final String DEFAULT_SPRING_CONFIG = "classpath*:META-INF/spring/*.xml";
private static final Logger logger = LoggerFactory.getLogger(SpringContainer.class);
static ClassPathXmlApplicationContext context;
public static ClassPathXmlApplicationContext getContext() {
return context;
}
@Override
public void start() {
String configPath = ConfigUtils.getProperty(SPRING_CONFIG);
if (StringUtils.isEmpty(configPath)) {
configPath = DEFAULT_SPRING_CONFIG;
}
context = new ClassPathXmlApplicationContext(configPath.split("[,\\s]+"), false);
context.refresh();
context.start();
}
...
}
接下来就是Spring的源码了,看过Spring源码的会知道,Spring启动的时候先加载并解析了Spring配置文件,将配置文件里的Bean解析成BeanDefinition存入内存,之后会对所有的单例Bean进行实例化、属性赋值、初始化,其中在解析配置文件的时候,Spring配置文件的内容分两个维度,一个是命名空间,命名空间之下再分各种标签,如果需要扩展命名空间和标签,则需要实现对应的命名空间处理器和标签解析器,Spring源码不是本篇重点,下面只列出xml方式启动容器时,解析配置文件的调用路径:
org.springframework.context.support.ClassPathXmlApplicationContext
org.springframework.context.support.AbstractApplicationContext#refresh
org.springframework.context.support.AbstractApplicationContext#obtainFreshBeanFactory
org.springframework.context.support.AbstractApplicationContext#refreshBeanFactory
org.springframework.context.support.AbstractRefreshableApplicationContext#refreshBeanFactory
org.springframework.context.support.AbstractRefreshableApplicationContext#loadBeanDefinitions
org.springframework.context.support.AbstractXmlApplicationContext#loadBeanDefinitions(org.springframework.beans.factory.support.DefaultListableBeanFactory)
org.springframework.context.support.AbstractXmlApplicationContext#loadBeanDefinitions(org.springframework.beans.factory.xml.XmlBeanDefinitionReader)
org.springframework.beans.factory.support.AbstractBeanDefinitionReader#loadBeanDefinitions(org.springframework.core.io.Resource…)
org.springframework.beans.factory.support.BeanDefinitionReader#loadBeanDefinitions(org.springframework.core.io.Resource)
org.springframework.beans.factory.xml.XmlBeanDefinitionReader#loadBeanDefinitions(org.springframework.core.io.Resource)
org.springframework.beans.factory.xml.XmlBeanDefinitionReader#loadBeanDefinitions(org.springframework.core.io.support.EncodedResource)
org.springframework.beans.factory.xml.XmlBeanDefinitionReader#doLoadBeanDefinitions
org.springframework.beans.factory.xml.XmlBeanDefinitionReader#registerBeanDefinitions
org.springframework.beans.factory.xml.BeanDefinitionDocumentReader#registerBeanDefinitions
org.springframework.beans.factory.xml.DefaultBeanDefinitionDocumentReader#doRegisterBeanDefinitions
org.springframework.beans.factory.xml.DefaultBeanDefinitionDocumentReader#parseBeanDefinitions
//org.springframework.beans.factory.xml.DefaultBeanDefinitionDocumentReader#parseBeanDefinitions
protected void parseBeanDefinitions(Element root, BeanDefinitionParserDelegate delegate) {
//判断是否是默认的命名空间
if (delegate.isDefaultNamespace(root)) {
NodeList nl = root.getChildNodes();
for(int i = 0; i < nl.getLength(); ++i) {
Node node = nl.item(i);
if (node instanceof Element) {
Element ele = (Element)node;
if (delegate.isDefaultNamespace(ele)) {
this.parseDefaultElement(ele, delegate);
} else {
delegate.parseCustomElement(ele);
}
}
}
} else {
//dubbo肯定不属于默认,走这里
delegate.parseCustomElement(root);
}
}
org.springframework.beans.factory.xml.BeanDefinitionParserDelegate#parseCustomElement(org.w3c.dom.Element)
org.springframework.beans.factory.xml.BeanDefinitionParserDelegate#parseCustomElement(org.w3c.dom.Element, org.springframework.beans.factory.config.BeanDefinition)
//org.springframework.beans.factory.xml.BeanDefinitionParserDelegate#parseCustomElement(org.w3c.dom.Element, org.springframework.beans.factory.config.BeanDefinition)
public BeanDefinition parseCustomElement(Element ele, BeanDefinition containingBd) {
String namespaceUri = this.getNamespaceURI(ele);
//关键就在这里,获取指定的名称空间处理器
NamespaceHandler handler = this.readerContext.getNamespaceHandlerResolver().resolve(namespaceUri);
if (handler == null) {
this.error("Unable to locate Spring NamespaceHandler for XML schema namespace [" + namespaceUri + "]", ele);
return null;
} else {
//使用对应的名称空间处理器解析对应的标签
return handler.parse(ele, new ParserContext(this.readerContext, this, containingBd));
}
}
这里NamespaceHandlerResolver只有一个默认实现,直接看DefaultNamespaceHandlerResolver的resolve方法:
public class DefaultNamespaceHandlerResolver implements NamespaceHandlerResolver {
public static final String DEFAULT_HANDLER_MAPPINGS_LOCATION = "META-INF/spring.handlers";
//没有特别指定的话handlerMappingsLocation值就是META-INF/spring.handlers
private final String handlerMappingsLocation;
//key为名称空间
//第一次加载配置文件的时候value是名称空间处理器类的全路径名
//当要被使用的时候会通过类全路径名 实例化,初始化,然后覆盖对应的key
private volatile Map<String, Object> handlerMappings;
public NamespaceHandler resolve(String namespaceUri) {
//名称空间和处理器之间的对应关系
Map<String, Object> handlerMappings = this.getHandlerMappings();
Object handlerOrClassName = handlerMappings.get(namespaceUri);
if (handlerOrClassName == null) {
return null;
} else if (handlerOrClassName instanceof NamespaceHandler) {
//已经初始化过了直接返回
return (NamespaceHandler)handlerOrClassName;
} else {
//否则通过类名,进行实例化、初始化
String className = (String)handlerOrClassName;
try {
Class<?> handlerClass = ClassUtils.forName(className, this.classLoader);
if (!NamespaceHandler.class.isAssignableFrom(handlerClass)) {
throw new FatalBeanException("Class [" + className + "] for namespace [" + namespaceUri + "] does not implement the [" + NamespaceHandler.class.getName() + "] interface");
} else {
NamespaceHandler namespaceHandler = (NamespaceHandler)BeanUtils.instantiateClass(handlerClass);
//初始化方法,一般是初始化当前名称空间处理器下的各个标签解析器
namespaceHandler.init();
handlerMappings.put(namespaceUri, namespaceHandler);
return namespaceHandler;
}
} catch (ClassNotFoundException var7) {
throw new FatalBeanException("NamespaceHandler class [" + className + "] for namespace [" + namespaceUri + "] not found", var7);
} catch (LinkageError var8) {
throw new FatalBeanException("Invalid NamespaceHandler class [" + className + "] for namespace [" + namespaceUri + "]: problem with handler class file or dependent class", var8);
}
}
}
private Map<String, Object> getHandlerMappings() {
if (this.handlerMappings == null) {
synchronized(this) {
if (this.handlerMappings == null) {
try {
//handlerMappingsLocation默认是META-INF/spring.handlers
Properties mappings = PropertiesLoaderUtils.loadAllProperties(this.handlerMappingsLocation, this.classLoader);
if (this.logger.isDebugEnabled()) {
this.logger.debug("Loaded NamespaceHandler mappings: " + mappings);
}
Map<String, Object> handlerMappings = new ConcurrentHashMap(mappings.size());
CollectionUtils.mergePropertiesIntoMap(mappings, handlerMappings);
this.handlerMappings = handlerMappings;
} catch (IOException var5) {
throw new IllegalStateException("Unable to load NamespaceHandler mappings from location [" + this.handlerMappingsLocation + "]", var5);
}
}
}
}
return this.handlerMappings;
}
...
}
由此可以看到,扩展的命名空间处理器的配置文件默认是在META-INF/spring.handlers,只有当被使用的时候才会初始化。
1.1 查找解析器
通常项目引用dubbo的时候,从 dubbo 依赖中可以看到如下的三个文件,其中就包含 spring.schemas 文件。
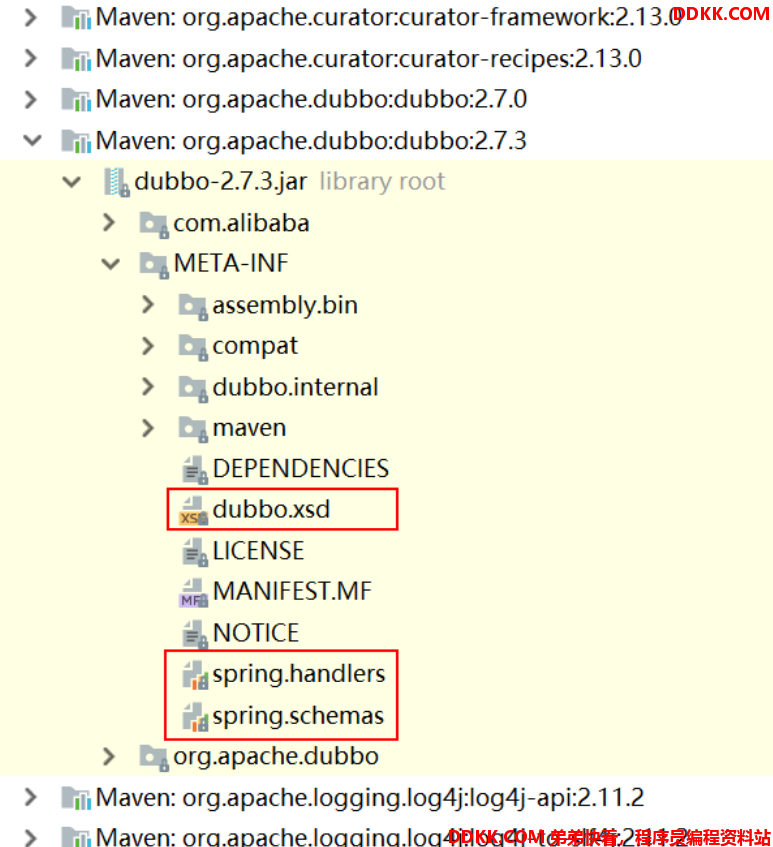
打开spring.schemas 文件,可以看到如下内容:
文件路径:META-INF/spring.schemas
http\://dubbo.apache.org/schema/dubbo/dubbo.xsd=META-INF/dubbo.xsd
http\://code.alibabatech.com/schema/dubbo/dubbo.xsd=META-INF/compat/dubbo.xsd
通过这个配置文件,指定对应的命名空间的约束文件的位置,这样就会使用本地的约束文件。
打开spring.handlers 文件,可以看到如下内容:
文件路径:META-INF/spring.handlers
http\://dubbo.apache.org/schema/dubbo=org.apache.dubbo.config.spring.schema.DubboNamespaceHandler
http\://code.alibabatech.com/schema/dubbo=org.apache.dubbo.config.spring.schema.DubboNamespaceHandler
这个文件配置的DubboNamespaceHandler 就是dubbo的命名空间处理器。
接下来我们就从org.apache.dubbo.config.spring.schema.DubboNamespaceHandler开始分析。
1.2 Dubbo 标签的解析
找到DubboNamespaceHandler类:
/**
* DubboNamespaceHandler
*
* @export
*/
public class DubboNamespaceHandler extends NamespaceHandlerSupport {
static {
Version.checkDuplicate(DubboNamespaceHandler.class);
}
@Override
public void init() {
//注册dubbo相关的标签解析器
registerBeanDefinitionParser("application", new DubboBeanDefinitionParser(ApplicationConfig.class, true));
registerBeanDefinitionParser("module", new DubboBeanDefinitionParser(ModuleConfig.class, true));
registerBeanDefinitionParser("registry", new DubboBeanDefinitionParser(RegistryConfig.class, true));
registerBeanDefinitionParser("config-center", new DubboBeanDefinitionParser(ConfigCenterBean.class, true));
registerBeanDefinitionParser("metadata-report", new DubboBeanDefinitionParser(MetadataReportConfig.class, true));
registerBeanDefinitionParser("monitor", new DubboBeanDefinitionParser(MonitorConfig.class, true));
registerBeanDefinitionParser("metrics", new DubboBeanDefinitionParser(MetricsConfig.class, true));
registerBeanDefinitionParser("provider", new DubboBeanDefinitionParser(ProviderConfig.class, true));
registerBeanDefinitionParser("consumer", new DubboBeanDefinitionParser(ConsumerConfig.class, true));
registerBeanDefinitionParser("protocol", new DubboBeanDefinitionParser(ProtocolConfig.class, true));
registerBeanDefinitionParser("service", new DubboBeanDefinitionParser(ServiceBean.class, true));
registerBeanDefinitionParser("reference", new DubboBeanDefinitionParser(ReferenceBean.class, false));
registerBeanDefinitionParser("annotation", new AnnotationBeanDefinitionParser());
}
}

这些Config封装的都是对应标签的数据(一个标签相当于一个配置对象)。
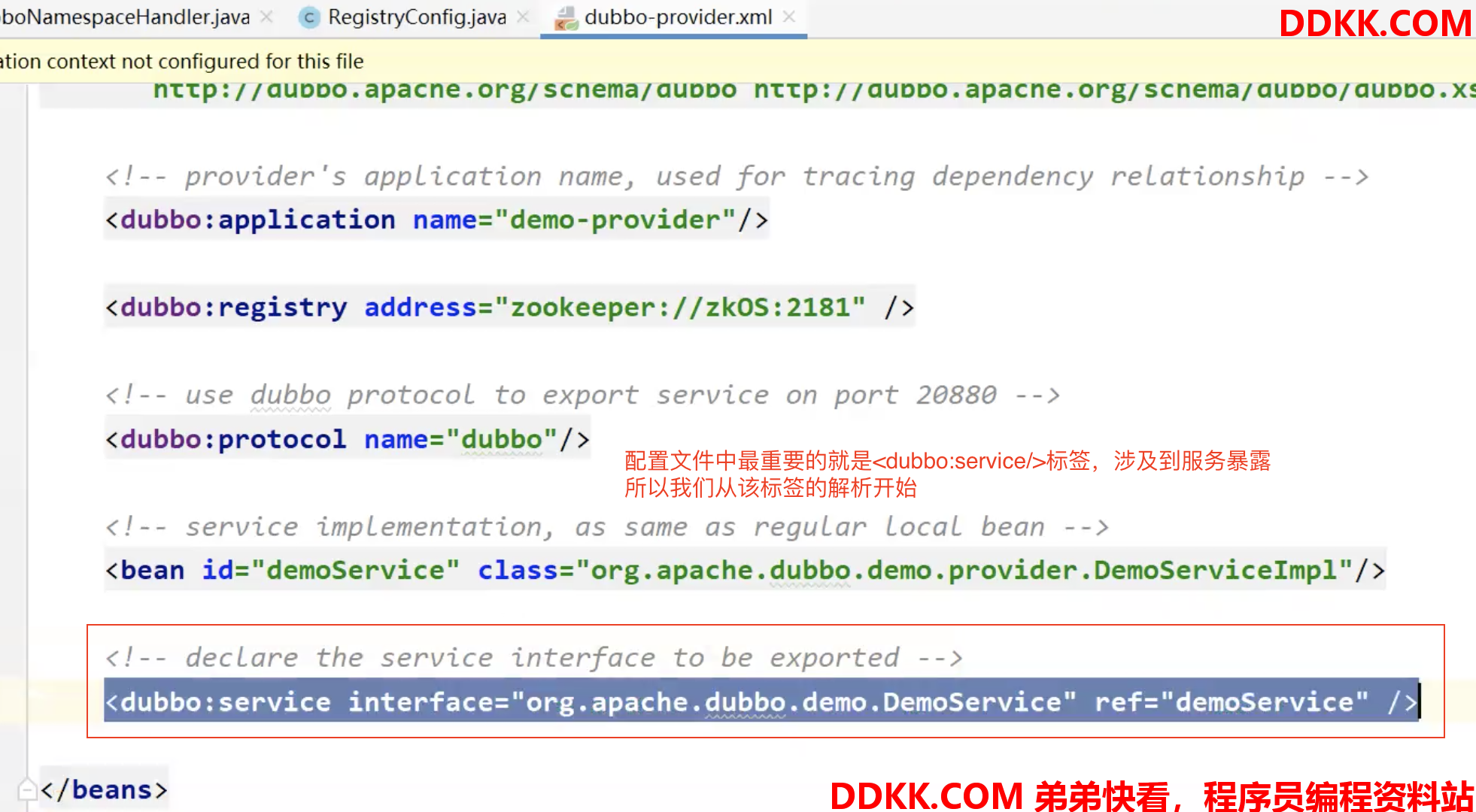

我们看下标签解析器做了哪些事,看DubboBeanDefinitionParser#parse方法,不会跟的太细,意义不大,主要分为5个流程:
-
1 创建并初始化解析对象RootBeanDefinition
-
2 解决id问题:为空 或 重复
-
3 将id属性写入解析对象
-
4 对特殊标签的特殊处理
-
处理dubbo:protocol/标签
-
处理dubbo:service/标签
-
处理dubbo:provider/标签
-
处理dubbo:consumer/标签
-
5 对所有标签的普适性处理
public class DubboBeanDefinitionParser implements BeanDefinitionParser {
...
private final Class<?> beanClass;
private final boolean required;
/**
*
* @param beanClass 当前解析标签要封装的类
* @param required 用于标识当前标签是否必须具备id属性
*/
public DubboBeanDefinitionParser(Class<?> beanClass, boolean required) {
this.beanClass = beanClass;
this.required = required;
}
/**
*
* @param element 当前要解析的标签元素
* @param parserContext 这是一个典型的上下文对象,其中封装着当前应用中所有dubbo标签的信息
* @param beanClass 当前解析标签要封装的类,这个类的实例数据是原封不动的来自于标签
* @param required 用于标识当前标签是否必须具备id属性
* @return 该标签最终要形成的对象,即解析对象
*/
@SuppressWarnings("unchecked")
private static BeanDefinition parse(Element element, ParserContext parserContext, Class<?> beanClass, boolean required) {
// --------------- 1 创建并初始化解析对象 --------------
RootBeanDefinition beanDefinition = new RootBeanDefinition();
beanDefinition.setBeanClass(beanClass);
beanDefinition.setLazyInit(false);
// --------------- 2 解决id问题:为空 或 重复 --------------
// 从标签元素中获取id属性
String id = element.getAttribute("id");
// 处理 没有设置id属性,但又必须要求有id属性的 情况
if (StringUtils.isEmpty(id) && required) {
// 从标签元素中获取name属性
String generatedBeanName = element.getAttribute("name");
// 若name属性也没有设置
if (StringUtils.isEmpty(generatedBeanName)) {
// 若当前解析的是<dubbo:protocol/>标签,则name属性取值dubbo
// 若不是,则取interface属性值
if (ProtocolConfig.class.equals(beanClass)) {
generatedBeanName = "dubbo";
} else {
//只有<dubbo:reference/>和<dubbo:service/>标签有interface属性
generatedBeanName = element.getAttribute("interface");
}
}
// 若name属性仍为空,则取beanClass的类名
if (StringUtils.isEmpty(generatedBeanName)) {
generatedBeanName = beanClass.getName();
}
// 代码走到这里,name属性一定不空
id = generatedBeanName;
int counter = 2;
// 若该id重复,则在该id后添加一个数字
while (parserContext.getRegistry().containsBeanDefinition(id)) {
id = generatedBeanName + (counter++);
}
}
// --------------- 3 将id属性写入解析对象 --------------
if (id != null && id.length() > 0) {
// 这里主要用于判断自己配置的id属性是否重复(上面生成的逻辑前提是id为空)
if (parserContext.getRegistry().containsBeanDefinition(id)) {
throw new IllegalStateException("Duplicate spring bean id " + id);
}
// 将id及对应解析对象写入到上下文,并将id属性写入到解析对象
parserContext.getRegistry().registerBeanDefinition(id, beanDefinition);
beanDefinition.getPropertyValues().addPropertyValue("id", id);
}
// --------------- 4 对特殊标签的特殊处理 --------------
// 处理<dubbo:protocol/>标签
if (ProtocolConfig.class.equals(beanClass)) {
for (String name : parserContext.getRegistry().getBeanDefinitionNames()) {
BeanDefinition definition = parserContext.getRegistry().getBeanDefinition(name);
PropertyValue property = definition.getPropertyValues().getPropertyValue("protocol");
if (property != null) {
Object value = property.getValue();
if (value instanceof ProtocolConfig && id.equals(((ProtocolConfig) value).getName())) {
definition.getPropertyValues().addPropertyValue("protocol", new RuntimeBeanReference(id));
}
}
}
// 处理<dubbo:service/>标签
} else if (ServiceBean.class.equals(beanClass)) {
String className = element.getAttribute("class");
if (className != null && className.length() > 0) {
RootBeanDefinition classDefinition = new RootBeanDefinition();
classDefinition.setBeanClass(ReflectUtils.forName(className));
classDefinition.setLazyInit(false);
parseProperties(element.getChildNodes(), classDefinition);
beanDefinition.getPropertyValues().addPropertyValue("ref", new BeanDefinitionHolder(classDefinition, id + "Impl"));
}
// 处理<dubbo:provider/>标签
} else if (ProviderConfig.class.equals(beanClass)) {
// 嵌套解析 处理<dubbo:provider/>与<dubbo:service/>标签属性间的关系
parseNested(element, parserContext, ServiceBean.class, true, "service", "provider", id, beanDefinition);
// 处理<dubbo:consumer/>标签
} else if (ConsumerConfig.class.equals(beanClass)) {
// 嵌套解析 处理<dubbo:consumer/>与<dubbo:reference/>标签属性间的关系
parseNested(element, parserContext, ReferenceBean.class, false, "reference", "consumer", id, beanDefinition);
}
// --------------- 5 对所有标签的普适性处理 --------------
Set<String> props = new HashSet<>();
ManagedMap parameters = null;
for (Method setter : beanClass.getMethods()) {
String name = setter.getName();
if (name.length() > 3 && name.startsWith("set")
&& Modifier.isPublic(setter.getModifiers())
&& setter.getParameterTypes().length == 1) {
Class<?> type = setter.getParameterTypes()[0];
String beanProperty = name.substring(3, 4).toLowerCase() + name.substring(4);
String property = StringUtils.camelToSplitName(beanProperty, "-");
props.add(property);
// check the setter/getter whether match
Method getter = null;
try {
getter = beanClass.getMethod("get" + name.substring(3), new Class<?>[0]);
} catch (NoSuchMethodException e) {
try {
getter = beanClass.getMethod("is" + name.substring(3), new Class<?>[0]);
} catch (NoSuchMethodException e2) {
// ignore, there is no need any log here since some class implement the interface: EnvironmentAware,
// ApplicationAware, etc. They only have setter method, otherwise will cause the error log during application start up.
}
}
if (getter == null
|| !Modifier.isPublic(getter.getModifiers())
|| !type.equals(getter.getReturnType())) {
continue;
}
if ("parameters".equals(property)) {
parameters = parseParameters(element.getChildNodes(), beanDefinition);
} else if ("methods".equals(property)) {
parseMethods(id, element.getChildNodes(), beanDefinition, parserContext);
} else if ("arguments".equals(property)) {
parseArguments(id, element.getChildNodes(), beanDefinition, parserContext);
} else {
String value = element.getAttribute(property);
if (value != null) {
value = value.trim();
if (value.length() > 0) {
if ("registry".equals(property) && RegistryConfig.NO_AVAILABLE.equalsIgnoreCase(value)) {
RegistryConfig registryConfig = new RegistryConfig();
registryConfig.setAddress(RegistryConfig.NO_AVAILABLE);
beanDefinition.getPropertyValues().addPropertyValue(beanProperty, registryConfig);
} else if ("provider".equals(property) || "registry".equals(property) || ("protocol".equals(property) && ServiceBean.class.equals(beanClass))) {
/**
* For 'provider' 'protocol' 'registry', keep literal value (should be id/name) and set the value to 'registryIds' 'providerIds' protocolIds'
* The following process should make sure each id refers to the corresponding instance, here's how to find the instance for different use cases:
* 1. Spring, check existing bean by id, see{@link ServiceBean#afterPropertiesSet()}; then try to use id to find configs defined in remote Config Center
* 2. API, directly use id to find configs defined in remote Config Center; if all config instances are defined locally, please use {@link org.apache.dubbo.config.ServiceConfig#setRegistries(List)}
*/
beanDefinition.getPropertyValues().addPropertyValue(beanProperty + "Ids", value);
} else {
Object reference;
if (isPrimitive(type)) {
if ("async".equals(property) && "false".equals(value)
|| "timeout".equals(property) && "0".equals(value)
|| "delay".equals(property) && "0".equals(value)
|| "version".equals(property) && "0.0.0".equals(value)
|| "stat".equals(property) && "-1".equals(value)
|| "reliable".equals(property) && "false".equals(value)) {
// backward compatibility for the default value in old version's xsd
value = null;
}
reference = value;
} else if ("onreturn".equals(property)) {
int index = value.lastIndexOf(".");
String returnRef = value.substring(0, index);
String returnMethod = value.substring(index + 1);
reference = new RuntimeBeanReference(returnRef);
beanDefinition.getPropertyValues().addPropertyValue("onreturnMethod", returnMethod);
} else if ("onthrow".equals(property)) {
int index = value.lastIndexOf(".");
String throwRef = value.substring(0, index);
String throwMethod = value.substring(index + 1);
reference = new RuntimeBeanReference(throwRef);
beanDefinition.getPropertyValues().addPropertyValue("onthrowMethod", throwMethod);
} else if ("oninvoke".equals(property)) {
int index = value.lastIndexOf(".");
String invokeRef = value.substring(0, index);
String invokeRefMethod = value.substring(index + 1);
reference = new RuntimeBeanReference(invokeRef);
beanDefinition.getPropertyValues().addPropertyValue("oninvokeMethod", invokeRefMethod);
} else {
if ("ref".equals(property) && parserContext.getRegistry().containsBeanDefinition(value)) {
BeanDefinition refBean = parserContext.getRegistry().getBeanDefinition(value);
if (!refBean.isSingleton()) {
throw new IllegalStateException("The exported service ref " + value + " must be singleton! Please set the " + value + " bean scope to singleton, eg: <bean id=\"" + value + "\" scope=\"singleton\" ...>");
}
}
reference = new RuntimeBeanReference(value);
}
beanDefinition.getPropertyValues().addPropertyValue(beanProperty, reference);
}
}
}
}
}
}
NamedNodeMap attributes = element.getAttributes();
int len = attributes.getLength();
for (int i = 0; i < len; i++) {
Node node = attributes.item(i);
String name = node.getLocalName();
if (!props.contains(name)) {
if (parameters == null) {
parameters = new ManagedMap();
}
String value = node.getNodeValue();
parameters.put(name, new TypedStringValue(value, String.class));
}
}
if (parameters != null) {
beanDefinition.getPropertyValues().addPropertyValue("parameters", parameters);
}
return beanDefinition;
}
...
}
以上就是dubbo和Spring整合的过程。
2. 重要接口
在讲解真正的源码流程,先了解一下Dubbo中重要的接口。
2.1 Invocation
其封装了远程调用的具体信息。
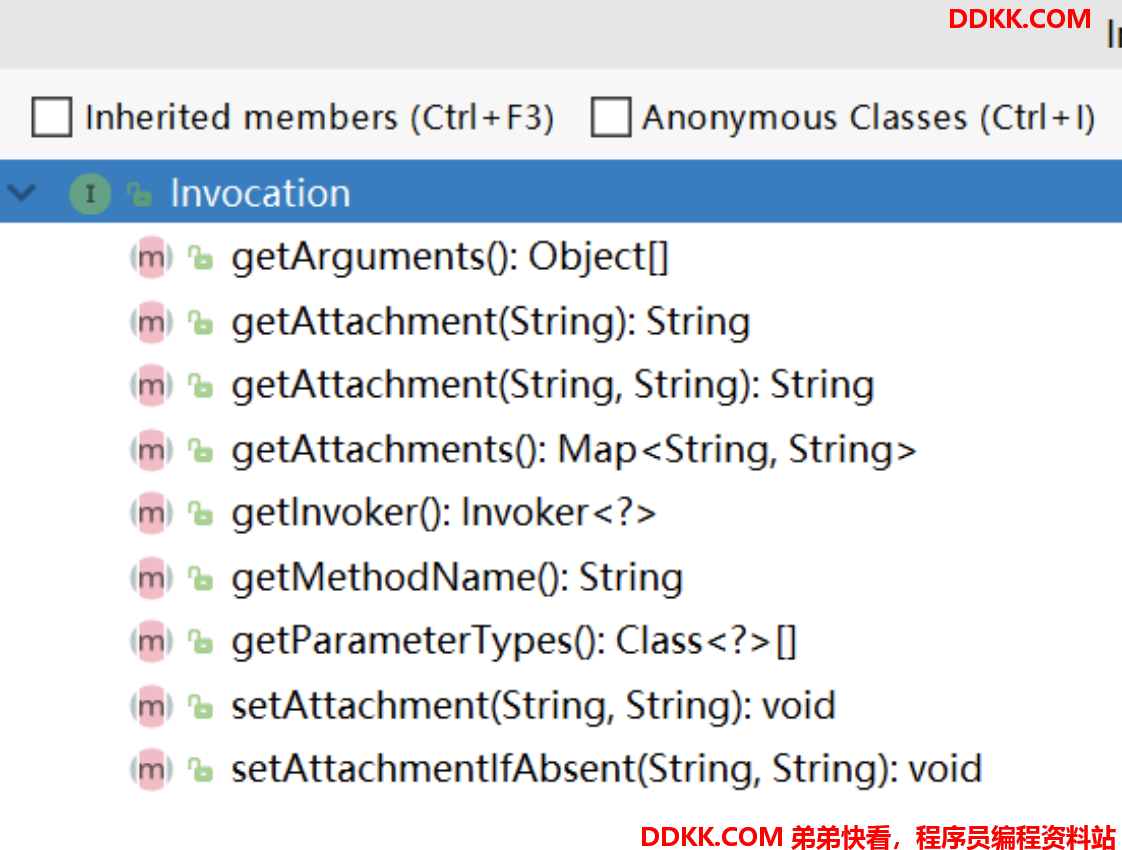
MethodName:方法名
ParameterTypes:参数类型
Arguments:真实参数
Invoker:提供者的代理对象
Attachment:附件(传输过程可以带些“私货”,key/value形式数据)
2.2 Invoker
其是提供者 provider 的代理对象,在代码中就代表提供者。特别是在消费者进行远程调用时,其通过服务路由、负载均衡、集群容错等机制要查找的就是 Invoker。找到了其需要的 Invoker 实例就可以进行远程调用了。
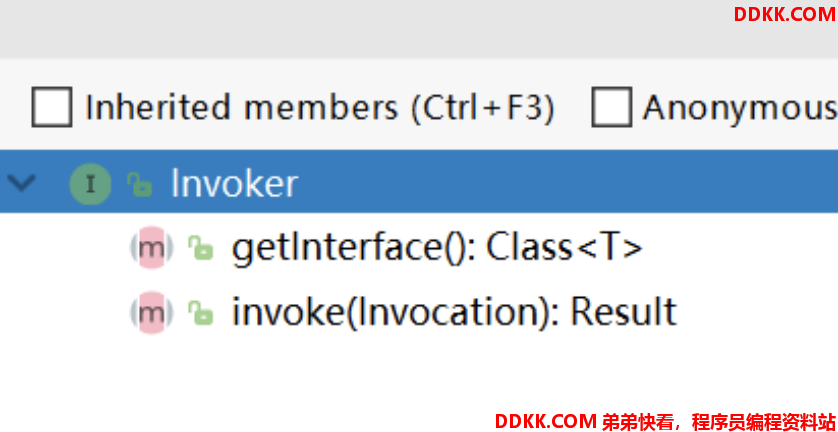
Interface:代理的接口
invoke:调用
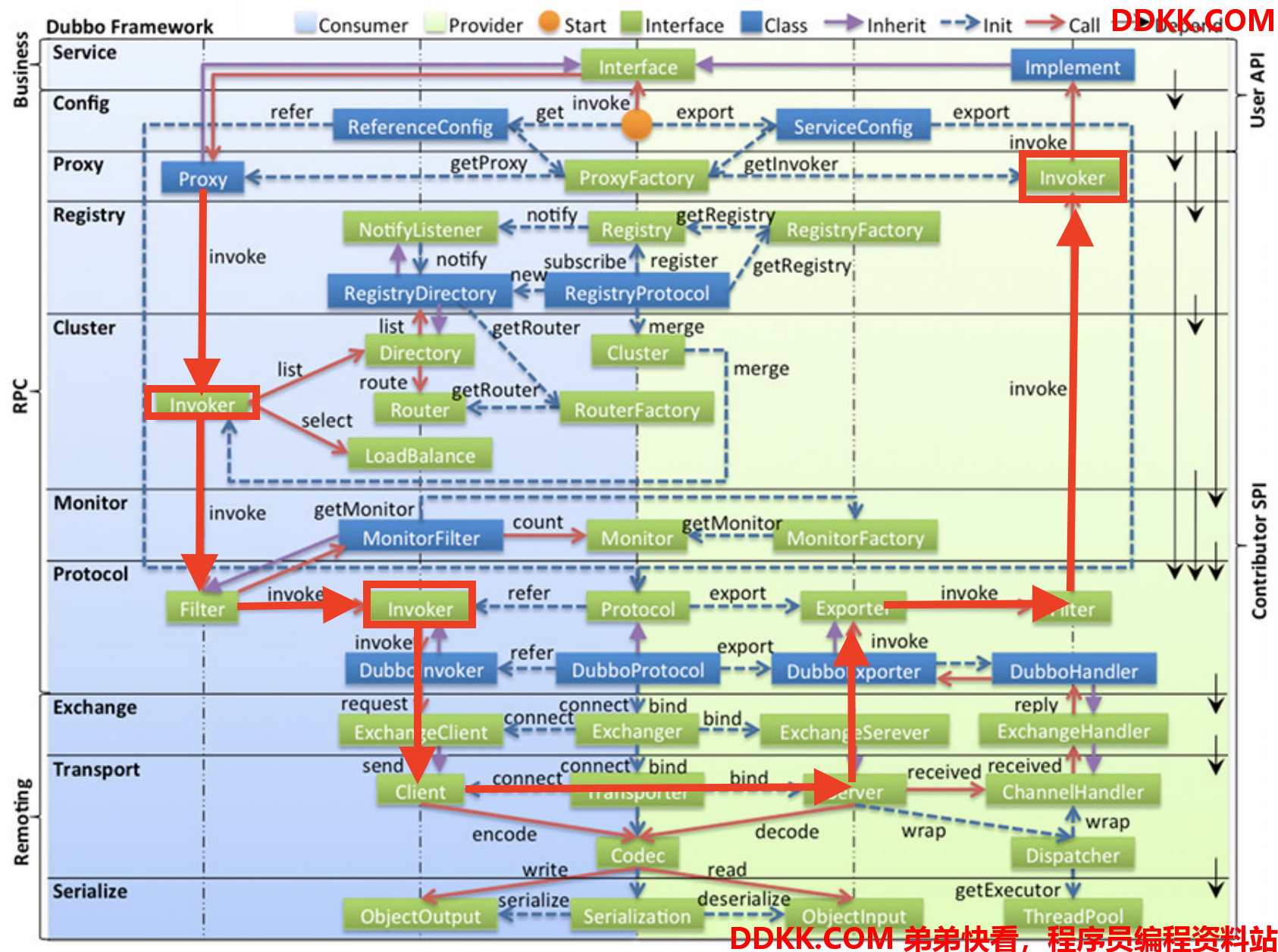
消费者端的Invoker是通过注册中心的信息生成的提供者代理对象,通过路由、负载均衡后,找到一个确定的Invoker,调用其invoker方法就会通过网络进行远程调用,最终走到提供者端的Invoker
2.3 Exporter
服务暴露对象。其包含一个很重要的方法 getInvoker(),用于获取当前服务暴露实例所包含的远程调用实例 Invoker,即可以进行的远程调用。
而unexport()方法会使服务不进行服务暴露。
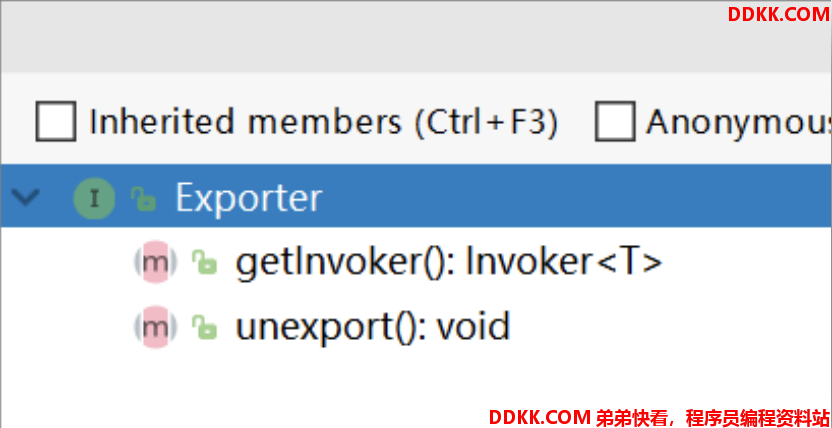
Dubbo中服务暴露分为本地暴露和远程暴露(远程暴露通常和服务注册在一起),如果服务不暴露的话,消费者是调用不了的,而一旦服务暴露,该服务对应的Invoker最终会形成一个Exporter对象,然后把该对象写入一个集合,当消费者发起远程调用后,会从这个集合找到对应的Exporter,然后通过Exporter获取到Invoker完成调用。
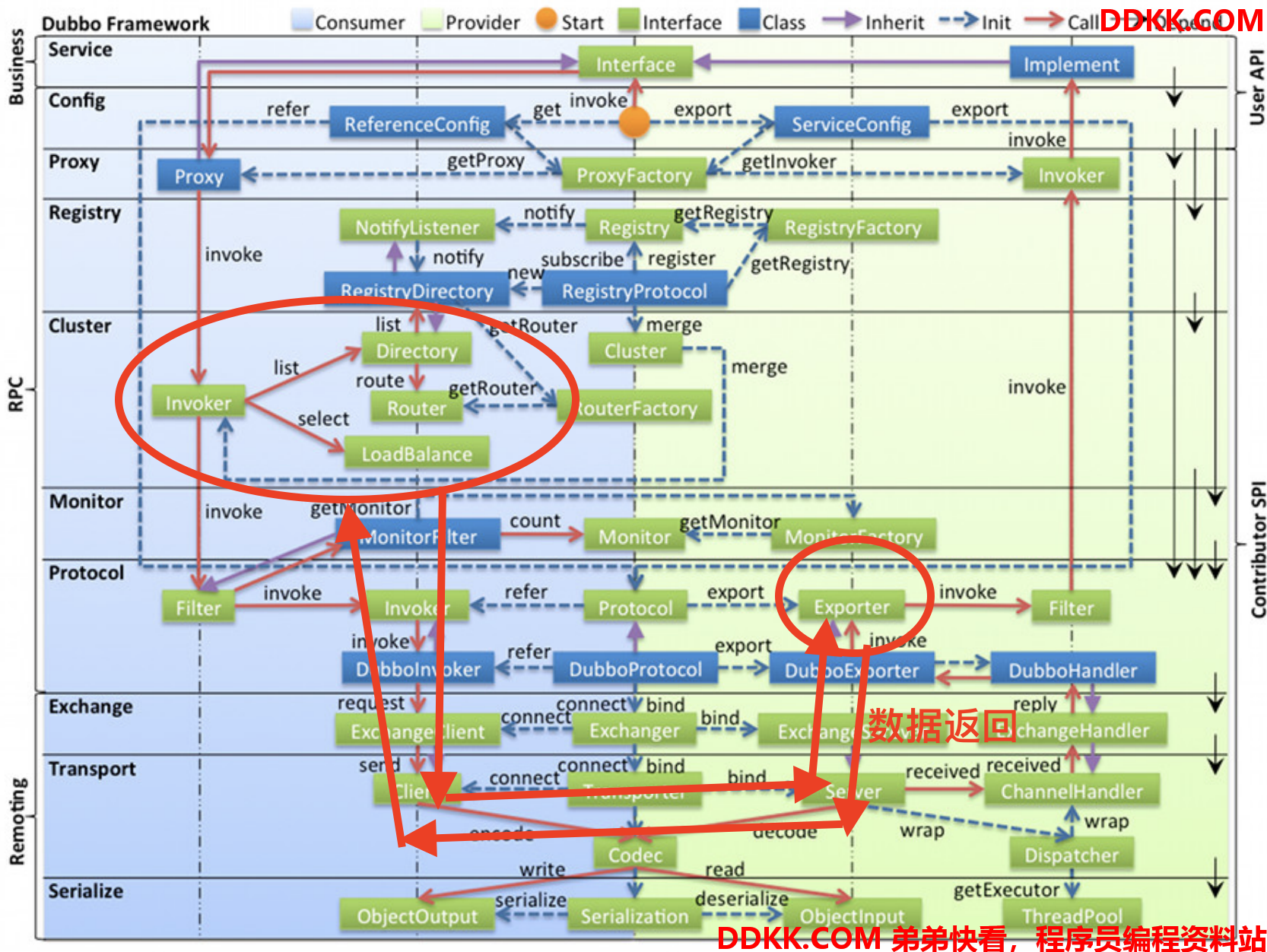
2.4 Directory
Directory 中包含一个很重要的方法 list(),其返回结果为一个 List
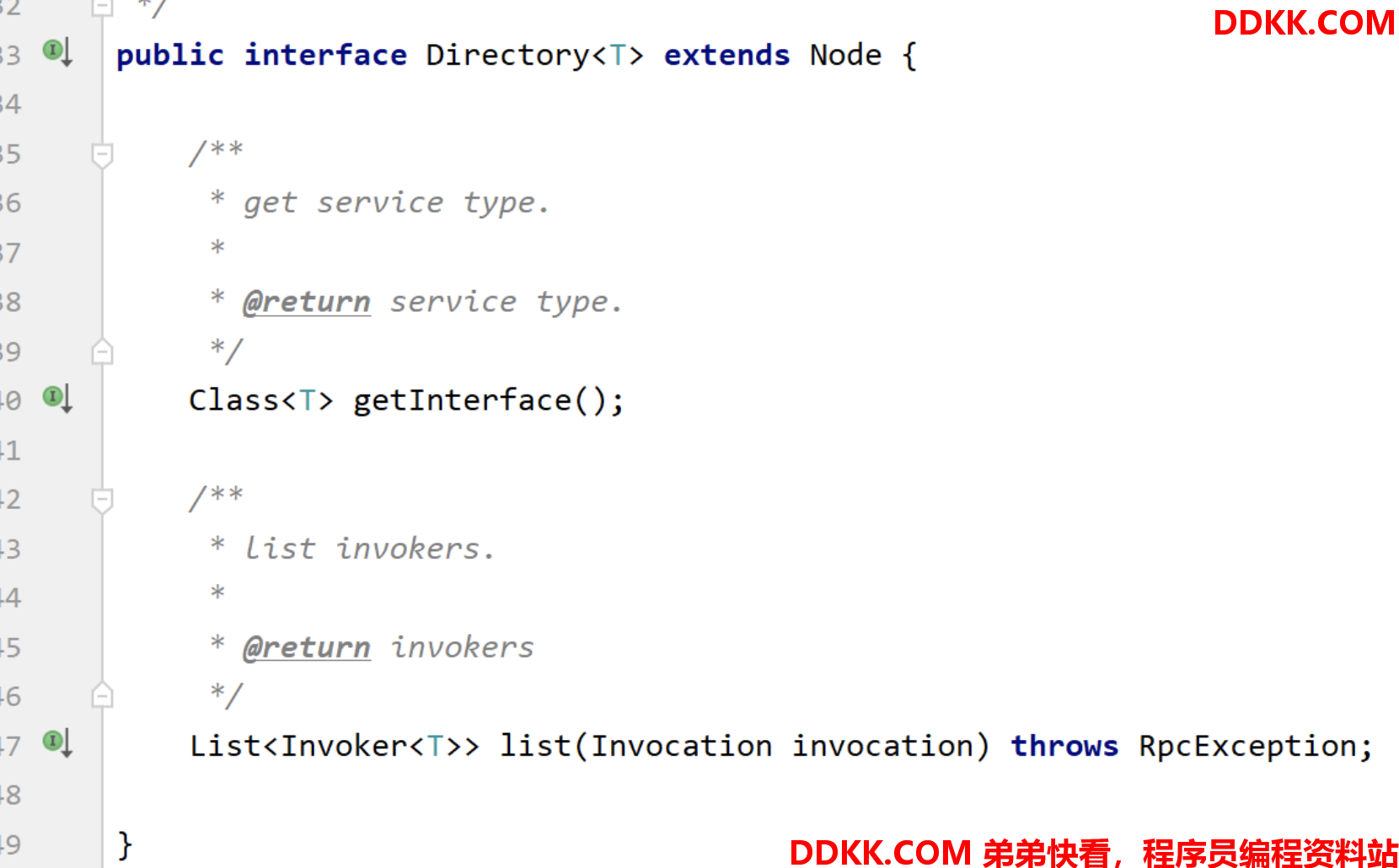
一个Directory维护了一种服务接口的所有Invoker(这句话不完全对,准确来说还有一些特殊情况)
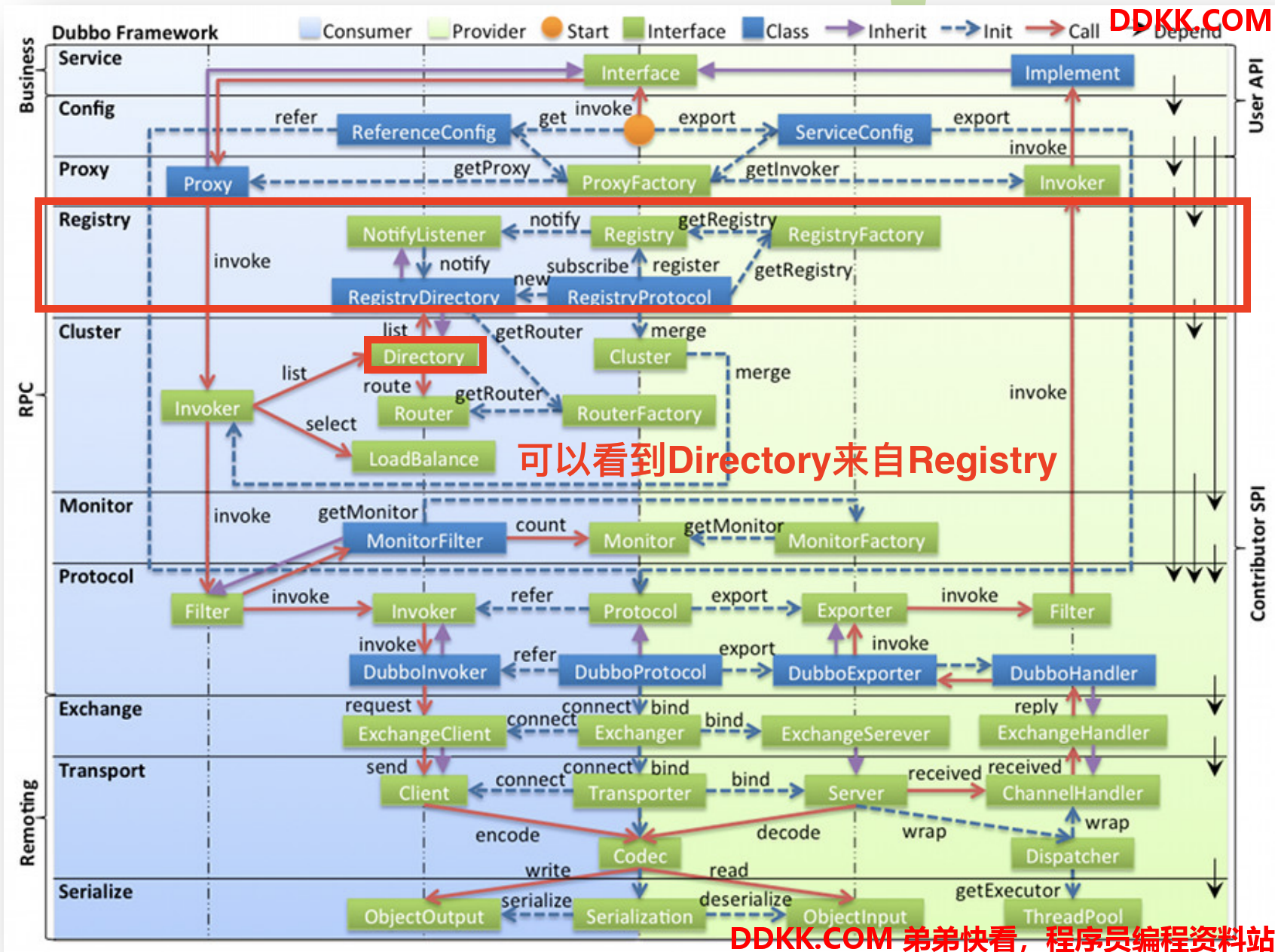
注意:可以发现Invoker和Directory都继承自org.apache.dubbo.common.Node
public interface Node {
/**
* get url.
*
* @return url.
*/
URL getUrl();
/**
* is available.
*
* @return available.
*/
boolean isAvailable();
/**
* destroy.
*/
void destroy();
}
而Node可以获取到URL!!符合Dubbo内核的Adaptive方法机制!!即Invoker和Directory可以作为参数传递实现自适应。
2.4.1 动态列表RegistryDirectory
然后看一下Directory其中的一个实现:
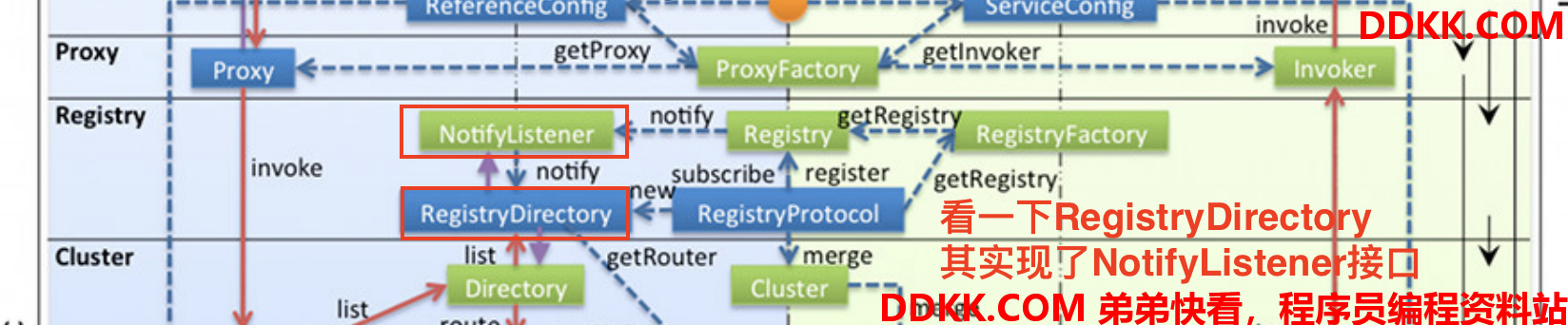
public class RegistryDirectory<T> extends AbstractDirectory<T> implements NotifyListener {
...}
public interface NotifyListener {
/**
* Triggered when a service change notification is received.
* 当收到服务更改通知时触发。
* <p>
* ...
*/
void notify(List<URL> urls);
}
可以看到RegistryDirectory实现了NotifyListener 接口,当注册中心的信息发生变化的时候就会触发notify方法,如果使用的是ZK作为注册中心,那么监听的实现用的就是ZK的Watcher监听机制,当ZK里面监听的某个服务的节点子节点列表或数据内容等发生改变,就会触发notify方法的执行。即RegistryDirectory是动态列表!
2.4.2 静态列表StaticDirectory
在看Directory另一个实现,静态列表StaticDirectory:
public class StaticDirectory<T> extends AbstractDirectory<T> {
...
}
它的应用场景是维护注册中心的,dubbo是支持多注册中心的,应用启动的时候,注册中心就已经确定并且不会变了。后面分析源码会看到。
2.4.3 MockDirectory
Directory还有第三个实现MockDirectory,继承自StaticDirectory,Mock降级机制可以定义MockClass,该Directory就是维护这些MockClass的静态列表,应用启动后这些MockClass是本地的,肯定不会变。
public class FailoverClusterInvokerTest {
...
public class MockDirectory<T> extends StaticDirectory<T> {
public MockDirectory(URL url, List<Invoker<T>> invokers) {
super(url, invokers);
}
@Override
protected List<Invoker<T>> doList(Invocation invocation) throws RpcException {
return new ArrayList<Invoker<T>>(super.doList(invocation));
}
}
}