源码解析 之 服务订阅
1. 查找服务订阅的入口
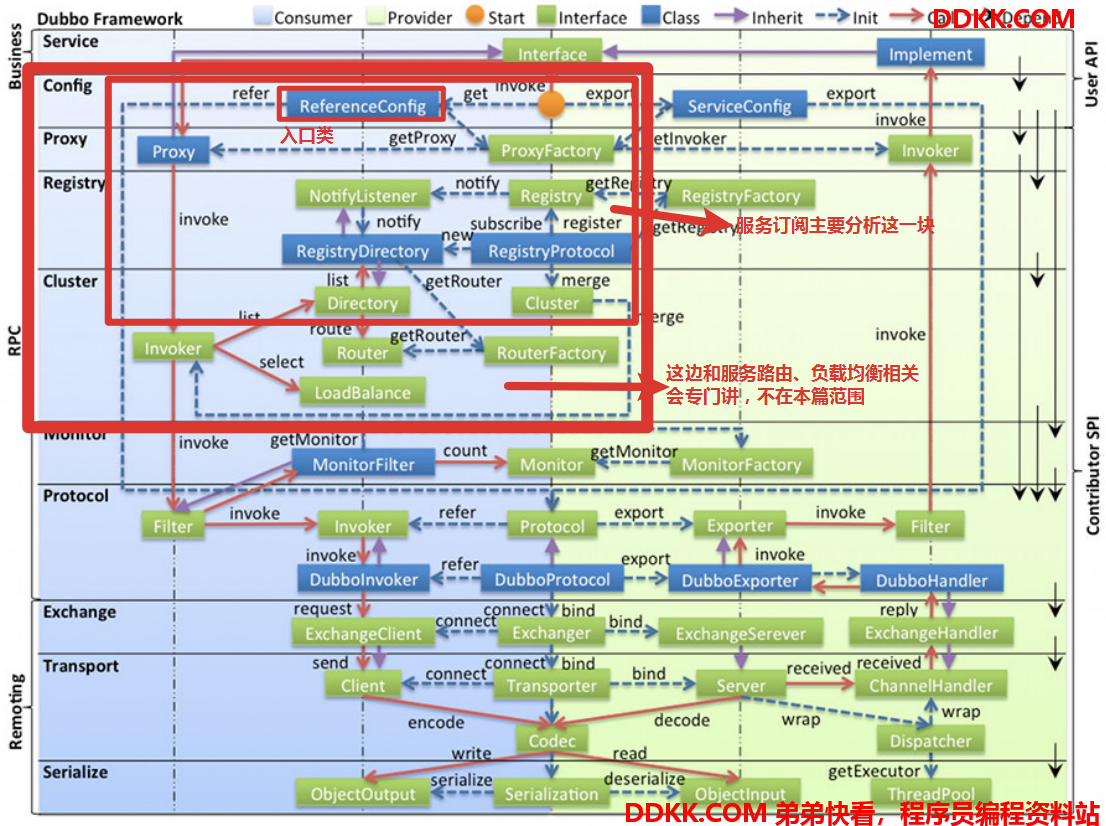
以DEMO中的启动类入口追踪流程:
public class ConsumerApplication {
public static void main(String[] args) {
ClassPathXmlApplicationContext context = new ClassPathXmlApplicationContext("spring/dubbo-consumer.xml");
context.start();
DemoService demoService = context.getBean("demoService", DemoService.class);
String hello = demoService.sayHello("world");
System.out.println("result: ========================= " + hello);
}
}
主要跟context.getBean("demoService", DemoService.class)方法(spring相关的代码不是本篇重点,只展示引用链):
org.springframework.context.support.AbstractApplicationContext#getBean(java.lang.String, java.lang.Class<T>)
org.springframework.beans.factory.support.AbstractBeanFactory#getBean(java.lang.String, java.lang.Class<T>)
org.springframework.beans.factory.support.AbstractBeanFactory#doGetBean
org.springframework.beans.factory.support.AbstractBeanFactory#getObjectForBeanInstance
org.springframework.beans.factory.support.FactoryBeanRegistrySupport#getObjectFromFactoryBean(由此可见返回的DemoService其实是一个FactoryBean)
org.springframework.beans.factory.support.FactoryBeanRegistrySupport#doGetObjectFromFactoryBean
org.springframework.beans.factory.FactoryBean#getObject
org.apache.dubbo.config.spring.ReferenceBean#getObject
public class ReferenceBean<T> extends ReferenceConfig<T> implements FactoryBean, ApplicationContextAware, InitializingBean, DisposableBean {
...
public Object getObject() {
return get();
}
...
}
继续跟get()方法就到了父类ReferenceConfig,入口就在这:
public class ReferenceBean<T> extends ReferenceConfig<T> implements FactoryBean, ApplicationContextAware, InitializingBean, DisposableBean {
...
public synchronized T get() {
checkAndUpdateSubConfigs();
//destroyed为true,表示ReferenceConfig的URL已经被销毁了
if (destroyed) {
throw new IllegalStateException("The invoker of ReferenceConfig(" + url + ") has already destroyed!");
}
//ref就是真正的代理对象
if (ref == null) {
//为空进行初始化
init();
}
return ref;
}
...
}
第一次ref肯定为null,看init()方法,该方法就是真正服务订阅的入口。
//org.apache.dubbo.config.ReferenceConfig#init
private void init() {
// 若当前代理对象已经初始化,则直接结束
if (initialized) {
return;
}
checkStubAndLocal(interfaceClass);
checkMock(interfaceClass);
// 创建并初始化用于构成url的map
Map<String, String> map = new HashMap<String, String>();
map.put(SIDE_KEY, CONSUMER_SIDE);
appendRuntimeParameters(map);
if (!isGeneric()) {
String revision = Version.getVersion(interfaceClass, version);
if (revision != null && revision.length() > 0) {
map.put(REVISION_KEY, revision);
}
String[] methods = Wrapper.getWrapper(interfaceClass).getMethodNames();
if (methods.length == 0) {
logger.warn("No method found in service interface " + interfaceClass.getName());
map.put(METHODS_KEY, ANY_VALUE);
} else {
map.put(METHODS_KEY, StringUtils.join(new HashSet<String>(Arrays.asList(methods)), COMMA_SEPARATOR));
}
}
map.put(INTERFACE_KEY, interfaceName);
appendParameters(map, metrics);
appendParameters(map, application);
appendParameters(map, module);
// remove 'default.' prefix for configs from ConsumerConfig
// appendParameters(map, consumer, Constants.DEFAULT_KEY);
appendParameters(map, consumer);
appendParameters(map, this);
Map<String, Object> attributes = null;
if (CollectionUtils.isNotEmpty(methods)) {
attributes = new HashMap<String, Object>();
for (MethodConfig methodConfig : methods) {
appendParameters(map, methodConfig, methodConfig.getName());
String retryKey = methodConfig.getName() + ".retry";
if (map.containsKey(retryKey)) {
String retryValue = map.remove(retryKey);
if ("false".equals(retryValue)) {
map.put(methodConfig.getName() + ".retries", "0");
}
}
attributes.put(methodConfig.getName(), convertMethodConfig2AyncInfo(methodConfig));
}
}
String hostToRegistry = ConfigUtils.getSystemProperty(DUBBO_IP_TO_REGISTRY);
if (StringUtils.isEmpty(hostToRegistry)) {
hostToRegistry = NetUtils.getLocalHost();
} else if (isInvalidLocalHost(hostToRegistry)) {
throw new IllegalArgumentException("Specified invalid registry ip from property:" + DUBBO_IP_TO_REGISTRY + ", value:" + hostToRegistry);
}
map.put(REGISTER_IP_KEY, hostToRegistry);
// 以上都是在处理map
// 创建代理对象(由javassist生成的动态代理对象)
ref = createProxy(map);
//初始化消费者模型
String serviceKey = URL.buildKey(interfaceName, group, version);
ApplicationModel.initConsumerModel(serviceKey, buildConsumerModel(serviceKey, attributes));
// 修改初始化标识
initialized = true;
}
这个方法主要做了三件事:
- 创建并初始化用于构成url的map
- 根据map创建代理对象
- 初始化消费者模型
之前分析服务发布,第一步和第三步都讲过,逻辑类似,没什么好分析的,重点关注第二步createProxy方法,创建代理对象。
2. 服务订阅流程概要
看createProxy方法之前,先简单概括一下服务订阅创建代理对象的流程
服务订阅创建代理对象,主要分这么几步大的流程:
-
1.首先判断是否是本地调用,还是远程调用(即订阅的服务刚好自己就是提供者)
-
1.1 本地调用
- 根据map构建URL,直接指定URL的协议是injvm
- 用injvm协议把URL构建成Invoker
-
1.2 远程调用,又分本地注册表方式、注册中心方式
-
1.2.1 本地注册表
- 解析dubbo:reference/中的url属性构建URL
- 根据URL构建Invoker
- 使用Cluster将所有Invoker伪装为一个invoker
-
1.2.2 注册中心
- 获取所有注册中心的标准化URL,并将消费者元数据信息添加到注册中心URL
- 使用RegistryProtocol注册协议把注册中心URL构建成Invoker(底层涉及很多复杂的处理)
- 使用Cluster将所有Invoker伪装为一个invoker
-
-
2.若元数据中心不为空,则将消费者元数据写入到元数据中心保存
-
3.第一步中无论什么情况,最终都会获得一个Invoker,根据该invoker创建消费者代理对象
--------- 流程分析 ---------
1. 本地调用
//org.apache.dubbo.config.ReferenceConfig#createProxy
private T createProxy(Map<String, String> map) {
// 判断是否是本地调用
if (shouldJvmRefer(map)) {
// 处理本地调用请求
URL url = new URL(LOCAL_PROTOCOL, LOCALHOST_VALUE, 0, interfaceClass.getName()).addParameters(map);
invoker = REF_PROTOCOL.refer(interfaceClass, url);
if (logger.isInfoEnabled()) {
logger.info("Using injvm service " + interfaceClass.getName());
}
} else {
// 处理远程调用
...
}
...
// create service proxy 创建消费者代理对象
return (T) PROXY_FACTORY.getProxy(invoker);
}
1.1 判断是否是本地调用
看shouldJvmRefer方法,判断是否本地调用:
//org.apache.dubbo.config.ReferenceConfig#shouldJvmRefer
protected boolean shouldJvmRefer(Map<String, String> map) {
// 创建一个临时URL(协议,地址,端口,参数)
URL tmpUrl = new URL("temp", "localhost", 0, map);
boolean isJvmRefer;
// 若<dubbo:reference/>中的injvm属性为空,则需要再判断本次调用是否是本地调用
if (isInjvm() == null) {
// 这个url就是直连的那个地址<dubbo:reference url="xxxxx"/>,如果配了肯定不是本地调用了
// if a url is specified, don't do local reference
if (url != null && url.length() > 0) {
// 若<dubbo:reference/>的url属性不为空,则一定不是本地调用
isJvmRefer = false;
} else {
// by default, reference local service if there is
isJvmRefer = InjvmProtocol.getInjvmProtocol().isInjvmRefer(tmpUrl);
}
} else {
// 获取injvm属性的值
isJvmRefer = isInjvm();
}
return isJvmRefer;
}
isInjvm就是获取dubbo:reference/中的injvm属性:
//org.apache.dubbo.config.AbstractReferenceConfig#isInjvm
public Boolean isInjvm() {
return injvm;
}
injvm属性为空,或者url属性为空,则需要执行InjvmProtocol.getInjvmProtocol().isInjvmRefer(tmpUrl)方法,判断是否是本地调用,看org.apache.dubbo.rpc.protocol.injvm.InjvmProtocol#isInjvmRefer方法:
//org.apache.dubbo.rpc.protocol.injvm.InjvmProtocol#isInjvmRefer
public boolean isInjvmRefer(URL url) {
// 获取<dubbo:reference/>的scope值
String scope = url.getParameter(SCOPE_KEY);
// Since injvm protocol is configured explicitly, we don't need to set any extra flag, use normal refer process.
// 若scope的值为local,或URL的injvm属性为true,则为本地调用
// LOCAL_PROTOCOL="injvm"
if (SCOPE_LOCAL.equals(scope) || (url.getParameter(LOCAL_PROTOCOL, false))) {
// if it's declared as local reference
// 'scope=local' is equivalent to 'injvm=true', injvm will be deprecated in the future release
return true;
} else if (SCOPE_REMOTE.equals(scope)) {
// 若scope的值为remote,则不是本地调用
// it's declared as remote reference
return false;
} else if (url.getParameter(GENERIC_KEY, false)) {
// 若当前为泛化引用,则不是本地调用
// GENERIC_KEY="generic"
// generic invocation is not local reference
return false;
} else if (getExporter(exporterMap, url) != null) {
// 若本地存在要调用的exporter,则为本地调用
// 之前跟服务发布的时候,本地暴露,就是写入到这个exporterMap的
// by default, go through local reference if there's the service exposed locally
return true;
} else {
return false;
}
}
最后一个判断最为核心,订阅的服务刚好是自己提供的,且已经本地暴露了。
1.2 injvm协议构建Invoker
//org.apache.dubbo.config.ReferenceConfig#createProxy
private T createProxy(Map<String, String> map) {
// 判断是否是本地调用
if (shouldJvmRefer(map)) {
// 处理本地调用请求
// 该url格式 injvm://127.0.0.1:0/xxx.xxx.xxxService/xxx&xxx...
URL url = new URL(LOCAL_PROTOCOL, LOCALHOST_VALUE, 0, interfaceClass.getName()).addParameters(map);
invoker = REF_PROTOCOL.refer(interfaceClass, url);
if (logger.isInfoEnabled()) {
logger.info("Using injvm service " + interfaceClass.getName());
}
} else {
// 处理远程调用
...
}
...
// create service proxy 创建消费者代理对象
return (T) PROXY_FACTORY.getProxy(invoker);
}
主要看一下REF_PROTOCOL.refer()方法,一开始走的是父类抽象类AbstractProtocol的refer方法:
//org.apache.dubbo.rpc.protocol.AbstractProtocol#refer
public <T> Invoker<T> refer(Class<T> type, URL url) throws RpcException {
return new AsyncToSyncInvoker<>(protocolBindingRefer(type, url));
}
AsyncToSyncInvoker这个类主要作用是将异步转同步,比较简单:
public class AsyncToSyncInvoker<T> implements Invoker<T> {
private Invoker<T> invoker;
public AsyncToSyncInvoker(Invoker<T> invoker) {
this.invoker = invoker;
}
@Override
public Result invoke(Invocation invocation) throws RpcException {
Result asyncResult = invoker.invoke(invocation);
try {
if (InvokeMode.SYNC == ((RpcInvocation) invocation).getInvokeMode()) {
//如果这次调用是同步模型的话,调用异步结果asyncResult的
//get方法会让线程进行阻塞,直到有结果,或者超时
asyncResult.get(Integer.MAX_VALUE, TimeUnit.MILLISECONDS);
}
} catch (InterruptedException e) {
throw new RpcException("Interrupted unexpectedly while waiting for remoting result to return! method: " + invocation.getMethodName() + ", provider: " + getUrl() + ", cause: " + e.getMessage(), e);
} catch (ExecutionException e) {
...
} catch (Throwable e) {
throw new RpcException(e.getMessage(), e);
}
return asyncResult;
}
...
}
继续看protocolBindingRefer方法,实现在子类InjvmProtocol:
//org.apache.dubbo.rpc.protocol.injvm.InjvmProtocol#protocolBindingRefer
public <T> Invoker<T> protocolBindingRefer(Class<T> serviceType, URL url) throws RpcException {
//服务发布本地暴露,就是写入到这个exporterMap的
return new InjvmInvoker<T>(serviceType, url, url.getServiceKey(), exporterMap);
}
看一下InjvmInvoker:
class InjvmInvoker<T> extends AbstractInvoker<T> {
...
@Override
public Result doInvoke(Invocation invocation) throws Throwable {
//从Injvm协议的exporterMap中获取exporter
Exporter<?> exporter = InjvmProtocol.getExporter(exporterMap, getUrl());
if (exporter == null) {
throw new RpcException("Service [" + key + "] not found.");
}
RpcContext.getContext().setRemoteAddress(LOCALHOST_VALUE, 0);
//通过exporter获取invoker,直接调用invoker
return exporter.getInvoker().invoke(invocation);
}
}
可以看到本地调用直接从本地暴露的exporter中获取invoker进行调用。
2. 远程调用本地注册表方式
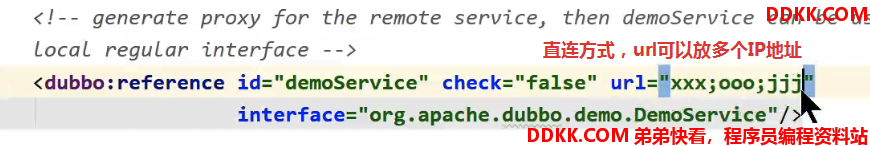
2.1 解析<dubbo:reference/>中的url属性构建URL
首先要知道什么是本地注册表方式,也可以称为直连方式:
通过dubbo:reference/的url属性可以直接配置提供者地址:
url属性有值,并且使用的是暴露协议,而不是registry协议,此时ip地址和端口号写的是提供者的地址,则属于本地注册表方式,例如:```java <!--直连式连接提供者,通过url属性配置的方式就是直连的方式,不用注册中心 --> <dubbo:reference id="someService" interface="com.abc.service.SomeService" url="dubbo://localhost:20880"/> <!-- dubbo代表用的是dubbo暴露协议 -->
>
>如果url配置的是"registry://ip:port",那么这个地址应该填的是注册中心的地址,处理的时候就和注册中心的方式一样了
>
>`即url属性允许直接配置提供者的地址,也允许配置注册中心的地址。`
先看下对<dubbo:reference/>标签url属性的处理:
```java
//org.apache.dubbo.config.ReferenceConfig#createProxy
private T createProxy(Map<String, String> map) {
// 判断是否是本地调用
if (shouldJvmRefer(map)) {
// 处理本地调用请求
...
} else {
// 处理远程调用
// urls集合中存放的是"提供者"主机的url
urls.clear(); // reference retry init will add url to urls, lead to OOM
// 若<dubbo:reference/>中的url属性不为空
// 该url属性可用于配置直连方式(本地注册表方式)
// 直连方式,则其值为使用的暴露协议+要直接调用的提供者的host与port
// 其中可以通过分号分隔,写入多个提供者主机信息
if (url != null && url.length() > 0) {
// user specified URL, could be peer-to-peer address, or register center's address.
// 使用分号分隔url的值,形成多个提供者主机地址
String[] us = SEMICOLON_SPLIT_PATTERN.split(url);
if (us != null && us.length > 0) {
// 遍历所有提供者的地址
for (String u : us) {
//地址转成URL
URL url = URL.valueOf(u);
if (StringUtils.isEmpty(url.getPath())) {
//如果path为空,设置接口名
//path就是服务名
url = url.setPath(interfaceName);
}
// 将提供者地址写入到urls集合
if (REGISTRY_PROTOCOL.equals(url.getProtocol())) {
//这里可以看到如果url配置的是registry协议
//则认为该地址是注册中心的地址,则将消费者元数据信息作为参数拼接在URL里
//后期处理和注册中心方式一样
urls.add(url.addParameterAndEncoded(REFER_KEY, StringUtils.toQueryString(map)));
} else {
urls.add(ClusterUtils.mergeUrl(url, map));
}
}
}
} else {
// assemble URL from register center's configuration
// 远程调用,注册中心的方式
...
}
// 代码运行到这里,urls中已经不为空了
// urls中的url可能是两类中的一种:
// 1)提供者主机URL
// 2)注册中心的URL(包含消费者元数据)
...//对urls的处理,根据url构建invoker
}
...
return (T) PROXY_FACTORY.getProxy(invoker);
}
上面代码中可以看出几个重要的点:
<dubbo:reference/>标签url属性既可以直接配置提供者的地址,也可以配置注册中心的地址,并且可以配置多个地址- 如果是注册中心地址,则将消费者元数据信息作为参数拼接在URL里,后期处理和注册中心方式一样
- 解析以后urls中既可能有提供者的URL,也可能有注册中心的URL
2.2 根据URL构建Invoker
上一步分析我们知道,如果是直连方式(本地注册表方式),那么urls中既可能有注册中心的URL,也可能有直接是提供者地址的URL,这里关于用URL构建Invoker,我们只考虑urls中全部是提供者地址URL的情况:
//org.apache.dubbo.config.ReferenceConfig#createProxy
private T createProxy(Map<String, String> map) {
// 判断是否是本地调用
if (shouldJvmRefer(map)) {
// 处理本地调用请求
...
} else {
// 处理远程调用
...
if (url != null && url.length() > 0) {
//直连方式处理URL
...
} else {
// assemble URL from register center's configuration
// 远程调用,注册中心的方式,处理URL
...
}
// 代码运行到这里,urls中已经不为空了
// urls中的url可能是两类中的一种:
// 1)提供者主机URL
// 2)注册中心的URL(包含消费者元数据)
if (urls.size() == 1) {
// URL只有一个的情况
// 将这个URL构建为一个invoker
invoker = REF_PROTOCOL.refer(interfaceClass, urls.get(0));
} else {
// URL有多个的情况
List<Invoker<?>> invokers = new ArrayList<Invoker<?>>();
URL registryURL = null;
// 遍历所有url
for (URL url : urls) {
// 将每个URL构建为一个invoker,并写入到invokers列表
invokers.add(REF_PROTOCOL.refer(interfaceClass, url));
// 记录最后一个注册中心地址,可以看到"registry://xxx"的地址被认为是注册中心地址
// 所有注册中心的url,除了host、port、path,及registry参数不同外,
// 其它数据都是相同的。后面的代码需要使用这些url中相同的数据部分,
// 所以只需要获取一个注册中心地址就可以了
if (REGISTRY_PROTOCOL.equals(url.getProtocol())) {
registryURL = url; // use last registry url
}
}
...//使用Cluster将所有Invoker伪装为一个invoker
}
}
...
return (T) PROXY_FACTORY.getProxy(invoker);
}
如果URL是多个,则每个URL都会创建一个Invoker,这里我们只看本地注册表的方式,例如配置文件这样的:
<!--直连式连接提供者,通过url属性配置的方式就是直连的方式,不用注册中心 -->
<dubbo:reference id="someService"
interface="com.abc.service.SomeService"
url="dubbo://localhost:20880"/>
<!-- dubbo代表用的是dubbo暴露协议 -->
那么REF_PROTOCOL.refer(interfaceClass, url)方法,通过自适应机制,最终会调用DubboProtocol:
//先会调用父类抽象类,之前看过
//org.apache.dubbo.rpc.protocol.AbstractProtocol#refer
public <T> Invoker<T> refer(Class<T> type, URL url) throws RpcException {
return new AsyncToSyncInvoker<>(protocolBindingRefer(type, url));
}
直接看org.apache.dubbo.rpc.protocol.dubbo.DubboProtocol#protocolBindingRefer
public <T> Invoker<T> protocolBindingRefer(Class<T> serviceType, URL url) throws RpcException {
optimizeSerialization(url);
// create rpc invoker.
DubboInvoker<T> invoker = new DubboInvoker<T>(serviceType, url, getClients(url), invokers);
invokers.add(invoker);
return invoker;
}
可以看到直接根据URL创建了DubboInvoker。
关于DubboInvoker,我们将在下一章《远程调用》进行详细讲解,因为这里涉及到远程调用的内容。
2.3 使用Cluster将所有Invoker伪装为一个invoker
还是这段代码:
//org.apache.dubbo.config.ReferenceConfig#createProxy
private T createProxy(Map<String, String> map) {
// 判断是否是本地调用
if (shouldJvmRefer(map)) {
// 处理本地调用请求
...
} else {
// 处理远程调用
...
if (url != null && url.length() > 0) {
//直连方式处理URL
...
} else {
// assemble URL from register center's configuration
// 远程调用,注册中心的方式,处理URL
...
}
// 代码运行到这里,urls中已经不为空了
// urls中的url可能是两类中的一种:
// 1)提供者主机URL
// 2)注册中心的URL(包含消费者元数据)
if (urls.size() == 1) {
// URL只有一个的情况
// 将这个URL构建为一个invoker
invoker = REF_PROTOCOL.refer(interfaceClass, urls.get(0));
} else {
// URL有多个的情况
List<Invoker<?>> invokers = new ArrayList<Invoker<?>>();
URL registryURL = null;
// 遍历所有url
for (URL url : urls) {
// 将每个URL构建为一个invoker,并写入到invokers列表
invokers.add(REF_PROTOCOL.refer(interfaceClass, url));
// 记录最后一个注册中心地址,可以看到"registry://xxx"的地址被认为是注册中心地址
// 所有注册中心的url,除了host、port、path,及registry参数不同外,
// 其它数据都是相同的。后面的代码需要使用这些url中相同的数据部分,
// 所以只需要获取一个注册中心地址就可以了
if (REGISTRY_PROTOCOL.equals(url.getProtocol())) {
registryURL = url; // use last registry url
}
}
if (registryURL != null) {
// registry url is available
// use RegistryAwareCluster only when register's CLUSTER is available
URL u = registryURL.addParameter(CLUSTER_KEY, RegistryAwareCluster.NAME);
// The invoker wrap relation would be: RegistryAwareClusterInvoker(StaticDirectory) -> FailoverClusterInvoker(RegistryDirectory, will execute route) -> Invoker
// 如果URL中有注册中心的地址,会对Invoker多包装一层RegistryAwareClusterInvoker
invoker = CLUSTER.join(new StaticDirectory(u, invokers));
} else {
// not a registry url, must be direct invoke.
//如果都是本地注册的,则只会用
//FailoverClusterInvoker(RegistryDirectory, will execute route) -> Invoker
invoker = CLUSTER.join(new StaticDirectory(invokers));
}
}
}
...
return (T) PROXY_FACTORY.getProxy(invoker);
}
从这段代码可以看出:
-
如果解析以后URL只有一个,那么生成的Invoker也是一个,是不需要Cluster进行包装的
-
如果URL多个,将会生成多个Invoker,此时需要用CLUSTER将多个Invoker包装成一个Invoker
-
如果URL中不包含注册中心的地址,调用程序包装关系将是
FailoverClusterInvoker(RegistryDirectory, will execute route) -> Invoker -
如果URL中包含注册中心的地址,调用程序包装关系将是
RegistryAwareClusterInvoker(StaticDirectory) -> FailoverClusterInvoker(RegistryDirectory, will execute route) -> Invoker
对比一下会发现有注册中心URL的会多包装一层RegistryAwareClusterInvoker,我们看下这个类:
public class RegistryAwareClusterInvoker<T> extends AbstractClusterInvoker<T> {
private static final Logger logger = LoggerFactory.getLogger(RegistryAwareClusterInvoker.class);
public RegistryAwareClusterInvoker(Directory<T> directory) {
super(directory);
}
@Override
@SuppressWarnings({
"unchecked", "rawtypes"})
public Result doInvoke(Invocation invocation, final List<Invoker<T>> invokers, LoadBalance loadbalance) throws RpcException {
// First, pick the invoker (XXXClusterInvoker) that comes from the local registry, distinguish by a 'default' key.
// 首先,选择来自本地注册表的调用程序(XXXClusterInvoker),通过“默认”键进行区分。
for (Invoker<T> invoker : invokers) {
if (invoker.isAvailable() && invoker.getUrl().getParameter(REGISTRY_KEY + "." + DEFAULT_KEY, false)) {
return invoker.invoke(invocation);
}
}
// If none of the invokers has a local signal, pick the first one available.
// 如果所有调用器都没有本地信号,则选择第一个可用的。
for (Invoker<T> invoker : invokers) {
if (invoker.isAvailable()) {
return invoker.invoke(invocation);
}
}
throw new RpcException("No provider available in " + invokers);
}
}
这段代码可以看出,本地注册表的Invoker优先级更高!
至与FailoverClusterInvoker这个类,我们将在《集群容错源码解析》专门讲,这个类主要负责容错功能的,这个类中还能看见路由器,具有路由的功能,因为这个时候同一个服务有多个Invoker,当然需要容错、路由、负载均衡。
3. 远程调用注册中心方式(核心)
3.1 获取所有注册中心的标准化URL,并将消费者元数据信息添加到注册中心URL
我们看下注册中心的URL处理:
//org.apache.dubbo.config.ReferenceConfig#createProxy
private T createProxy(Map<String, String> map) {
// 判断是否是本地调用
if (shouldJvmRefer(map)) {
// 处理本地调用请求
...
} else {
// 处理远程调用
urls.clear(); // reference retry init will add url to urls, lead to OOM
if (url != null && url.length() > 0) {
//直连方式处理URL
...
} else {
// assemble URL from register center's configuration
// 远程调用,注册中心的方式,处理URL
// if protocols not injvm checkRegistry
if (!LOCAL_PROTOCOL.equalsIgnoreCase(getProtocol())){
//首先判断协议是否是injvm
// 检测注册中心
checkRegistry();
// 获取所有注册中心的标准化URL,false代表当前是消费者,这个方法服务注册说过
List<URL> us = loadRegistries(false);
if (CollectionUtils.isNotEmpty(us)) {
// 遍历所有注册中心URL
for (URL u : us) {
// 获取监控中心URL
URL monitorUrl = loadMonitor(u);
if (monitorUrl != null) {
map.put(MONITOR_KEY, URL.encode(monitorUrl.toFullString()));
}
// 将消费者元数据信息(map)添加到注册中心URL
// key是"refer"
//(讲服务暴露的时候,regsitry的URL如果携带提供者信息时key是"export")
urls.add(u.addParameterAndEncoded(REFER_KEY, StringUtils.toQueryString(map)));
}
}
if (urls.isEmpty()) {
throw new IllegalStateException("No such any registry to reference " + interfaceName + " on the consumer " + NetUtils.getLocalHost() + " use dubbo version " + Version.getVersion() + ", please config <dubbo:registry address=\"...\" /> to your spring config.");
}
}
}
// 代码运行到这里,urls中已经不为空了
// 此时urls中的url只可能是注册中心的URL(包含消费者元数据)
...//对urls的处理,根据url构建invoker
}
...
return (T) PROXY_FACTORY.getProxy(invoker);
}
可以看到注册中心的方式,那么urls中全部都是注册中心的URL,在URL中通过属性refer携带消费者元数据信息。
其中检测注册中心checkRegistry方法 和 获取所有注册中心的标准化URL loadRegistries方法,在讲服务发布的时候都跟过。简单在看一下吧:
- 检测注册中心
//org.apache.dubbo.config.AbstractInterfaceConfig#checkRegistry
protected void checkRegistry() {
loadRegistriesFromBackwardConfig();
convertRegistryIdsToRegistries();
// 这里可以保证所有注册中心都是可用的
for (RegistryConfig registryConfig : registries) {
if (!registryConfig.isValid()) {
throw new IllegalStateException("No registry config found or it's not a valid config! " +
"The registry config is: " + registryConfig);
}
}
// 代码运行到这里,说明所有注册中心都是可用的
// 若没有设置配置中心,则将注册中心作为配置中心使用
useRegistryForConfigIfNecessary();
}
//org.apache.dubbo.config.AbstractInterfaceConfig#useRegistryForConfigIfNecessary
private void useRegistryForConfigIfNecessary() {
registries.stream().filter(RegistryConfig::isZookeeperProtocol).findFirst().ifPresent(rc -> {
// we use the loading status of DynamicConfiguration to decide whether ConfigCenter has been initiated.
Environment.getInstance().getDynamicConfiguration().orElseGet(() -> {
ConfigManager configManager = ConfigManager.getInstance();
ConfigCenterConfig cc = configManager.getConfigCenter().orElse(new ConfigCenterConfig());
// 若没有设置配置中心,则将注册中心作为配置中心
cc.setProtocol(rc.getProtocol());
cc.setAddress(rc.getAddress());
cc.setHighestPriority(false);
setConfigCenter(cc);
// 启动配置中心
startConfigCenter();
return null;
});
});
}
这边代码之前都跟过。
- 获取所有注册中心的标准化URL
参数provider代表当前是提供者还是消费者:
//org.apache.dubbo.config.AbstractInterfaceConfig#loadRegistries
protected List<URL> loadRegistries(boolean provider) {
// provider代表是否是提供者,之前跟服务注册的时候是true,现在为false代表消费者
// check && override if necessary
List<URL> registryList = new ArrayList<URL>();
// 若注册中心不为空
if (CollectionUtils.isNotEmpty(registries)) {
// 遍历所有注册中心
for (RegistryConfig config : registries) {
// 获取<dubbo:registry/>的address属性
String address = config.getAddress();
// 若没有设置address属性,则对所有ip均成立
if (StringUtils.isEmpty(address)) {
//0.0.0.0广播地址
address = ANYHOST_VALUE;
}
// 若当前不是直连 NO_AVAILABLE="N/A"
if (!RegistryConfig.NO_AVAILABLE.equalsIgnoreCase(address)) {
// 该map中用于存放要组装url的元数据
Map<String, String> map = new HashMap<String, String>();
// 将<dubbo:application/>中的属性写入到map
appendParameters(map, application);
// 将<dubbo:service/>中的属性写入到map
appendParameters(map, config);
// 将path写入到map
map.put(PATH_KEY, RegistryService.class.getName());
appendRuntimeParameters(map);
if (!map.containsKey(PROTOCOL_KEY)) {
map.put(PROTOCOL_KEY, DUBBO_PROTOCOL);
}
// 从一个地址解析出多个URL(处理集群情况)
List<URL> urls = UrlUtils.parseURLs(address, map);
// 将原来的类似于 zookeeper://zkOS:2181 格式的地址,格式化为
// registry://zkOS:2181?....®istry=zookeeper
for (URL url : urls) {
url = URLBuilder.from(url)
.addParameter(REGISTRY_KEY, url.getProtocol())
.setProtocol(REGISTRY_PROTOCOL)
.build();
// 若当前为提供者,且需要注册, 或 当前为消费者,且需要订阅
// 则记录下这个URL
if ((provider && url.getParameter(REGISTER_KEY, true))
|| (!provider && url.getParameter(SUBSCRIBE_KEY, true))) {
registryList.add(url);
}
}
}
}
}
return registryList;
}
这个方法将服务注册时候也跟过。
3.2 使用RegistryProtocol注册协议把注册中心URL构建成Invoker(底层涉及很多复杂的处理)
//org.apache.dubbo.config.ReferenceConfig#createProxy
private T createProxy(Map<String, String> map) {
// 判断是否是本地调用
if (shouldJvmRefer(map)) {
// 处理本地调用请求
...
} else {
// 处理远程调用
...
if (url != null && url.length() > 0) {
//直连方式处理URL
...
} else {
// 注册中心的方式,处理URL
...
}
// 代码运行到这里,urls中已经不为空了
// 此时urls中的url只可能是注册中心的URL(包含消费者元数据)
if (urls.size() == 1) {
// 注册中心只有一个的情况
// 将这个注册中心URL构建为一个invoker
// 这个invoker并不是某一个具体的提供者的代理对象,而是针对一个注册中心,一个接口(服务)
// 的invoker,这个invoker执行的时候,底层会路由、负载均衡到真正的invoker
invoker = REF_PROTOCOL.refer(interfaceClass, urls.get(0));
} else {
// 注册中心有多个的情况
List<Invoker<?>> invokers = new ArrayList<Invoker<?>>();
URL registryURL = null;
// 遍历所有注册中心url
for (URL url : urls) {
// 将每个注册中心构建为一个invoker,并写入到invokers列表
invokers.add(REF_PROTOCOL.refer(interfaceClass, url));
// 记录最后一个注册中心地址
// 所有注册中心的url,除了host、port、path,及registry参数不同外,
//(path,直连的时候是接口名,注册中心的时候是RegistryService全路径类名)
// (registry参数代表的是暴露协议)
// 其它数据都是相同的。后面的代码需要使用这些url中相同的数据部分,
// 所以只需要获取一个注册中心地址就可以了
if (REGISTRY_PROTOCOL.equals(url.getProtocol())) {
registryURL = url; // use last registry url
}
}
...//使用Cluster将所有Invoker伪装为一个invoker
}
}
...
return (T) PROXY_FACTORY.getProxy(invoker);
}
注册中心URL格式是registry://ip:port/xxx.xxx.xxService?refer=消费者元数据信息&xx=xx…
所以REF_PROTOCOL.refer通过自适应机制最终由RegistryProtocol处理
DEBUG,断点再次确认:
增强Wrapper类就不看了,直接看RegistryProtocol#refer方法:
//org.apache.dubbo.registry.integration.RegistryProtocol#refer
public <T> Invoker<T> refer(Class<T> type, URL url) throws RpcException {
//将 registry://xxxxx换成 dubbo://xxxxxx
url = URLBuilder.from(url)
.setProtocol(url.getParameter(REGISTRY_KEY, DEFAULT_REGISTRY))
.removeParameter(REGISTRY_KEY)
.build();
// 获取注册中心,以前跟过不看了,这里是zookeeper注册中心
Registry registry = registryFactory.getRegistry(url);
if (RegistryService.class.equals(type)) {
return proxyFactory.getInvoker((T) registry, type, url);
}
// group="a,b" or group="*"
Map<String, String> qs = StringUtils.parseQueryString(url.getParameterAndDecoded(REFER_KEY));
String group = qs.get(GROUP_KEY);
if (group != null && group.length() > 0) {
if ((COMMA_SPLIT_PATTERN.split(group)).length > 1 || "*".equals(group)) {
return doRefer(getMergeableCluster(), registry, type, url);
}
}
return doRefer(cluster, registry, type, url);
}
这里主要关注doRefer方法,四个核心流程:
- 将consumer注册到zk (服务注册的时候跟过类似)
- 将所有router(路由器)添加到directory (服务路由的时候专门讲)
- 订阅服务
- 将invoker列表伪装为一个invoker(和2.3,3.3类似)
//org.apache.dubbo.registry.integration.RegistryProtocol#doRefer
private <T> Invoker<T> doRefer(Cluster cluster, Registry registry, Class<T> type, URL url) {
// 生成一个动态Directory
RegistryDirectory<T> directory = new RegistryDirectory<T>(type, url);
directory.setRegistry(registry);
directory.setProtocol(protocol);
// all attributes of REFER_KEY
Map<String, String> parameters = new HashMap<String, String>(directory.getUrl().getParameters());
// 形成消费者url,CONSUMER_PROTOCOL="consumer"
// consumer://本地ip:0/服务名?xxx=xxx&xx=xxx...
URL subscribeUrl = new URL(CONSUMER_PROTOCOL, parameters.remove(REGISTER_IP_KEY), 0, type.getName(), parameters);
if (!ANY_VALUE.equals(url.getServiceInterface()) && url.getParameter(REGISTER_KEY, true)) {
directory.setRegisteredConsumerUrl(getRegisteredConsumerUrl(subscribeUrl, url));
// 将consumer注册到zk(跟服务注册的时候跟过一样)
registry.register(directory.getRegisteredConsumerUrl());
}
// 将所有router(路由器)添加到directory(后面讲路由的时候详细说)
directory.buildRouterChain(subscribeUrl);
// 订阅服务
directory.subscribe(subscribeUrl.addParameter(CATEGORY_KEY,
PROVIDERS_CATEGORY + "," + CONFIGURATORS_CATEGORY + "," + ROUTERS_CATEGORY));
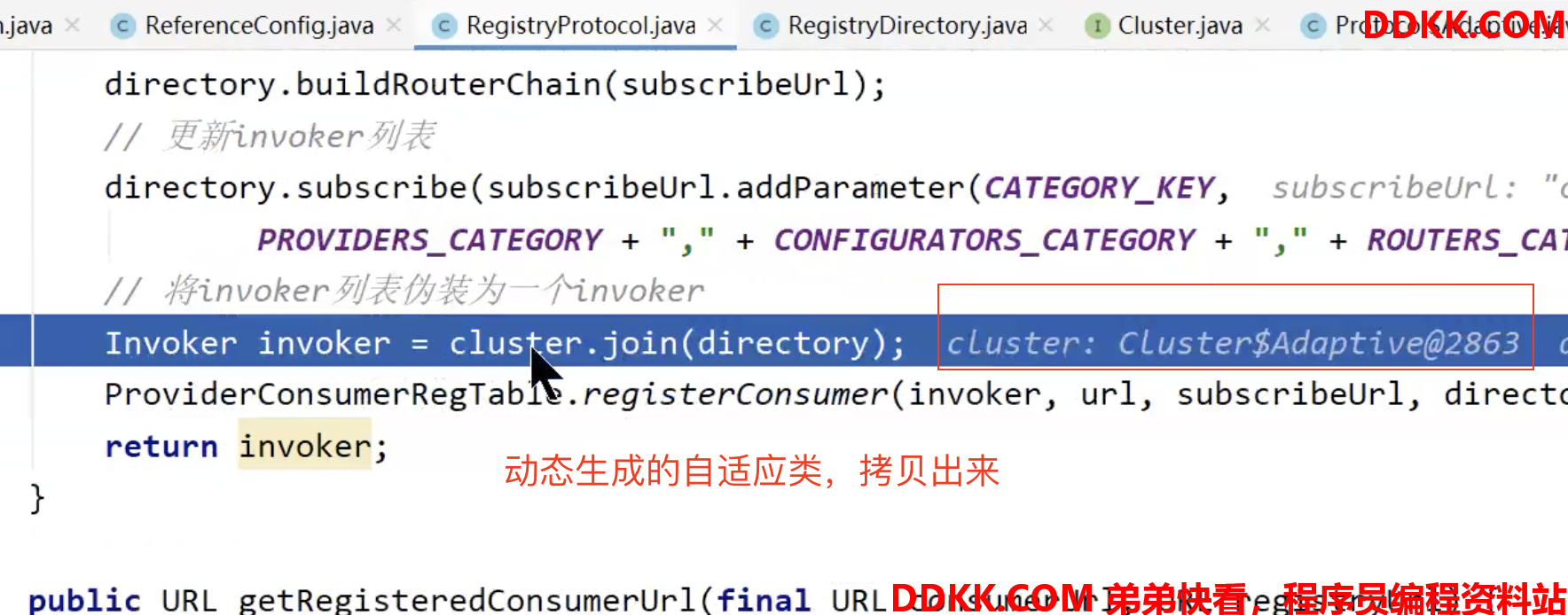
// 将invoker列表伪装为一个invoker(底层具有路由、降级、容错等功能...)
Invoker invoker = cluster.join(directory);
ProviderConsumerRegTable.registerConsumer(invoker, url, subscribeUrl, directory);
return invoker;
}
为什么consumer也要注册到到注册中心?
监控中心可以监控到consumer状态
3.2.1 订阅服务
首先从代码中可以看出subscribeUrl的格式大概是:consumer://本地ip:0/服务名?xxx=xxx&xx=xxx...
看下触发订阅服务方法时,subscribeUrl新增了什么参数:
//参数key "category",代表分类的意思
//参数value是 "providers,configurators,routers"
subscribeUrl.addParameter(CATEGORY_KEY,PROVIDERS_CATEGORY + "," + CONFIGURATORS_CATEGORY + "," + ROUTERS_CATEGORY)
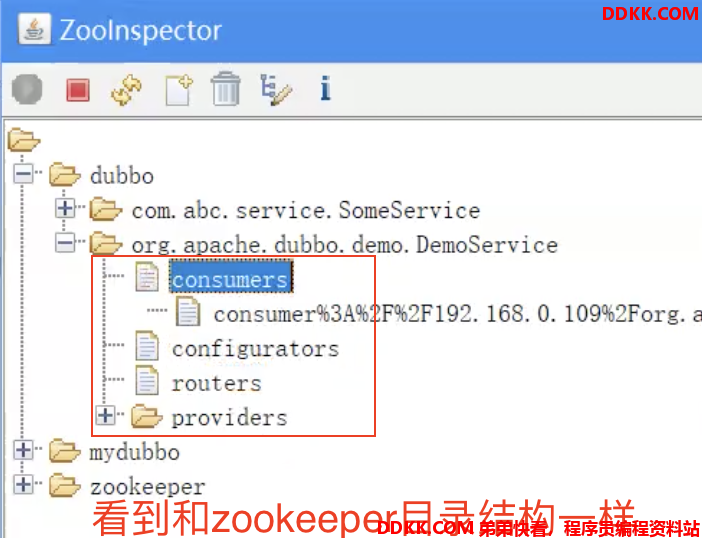
可以看到添加了category属性,值为providers,configurators,routers,代表了将订阅当前服务下这三类信息,而这三类信息对于ZK注册中心,刚好对应三个节点:
整个订阅服务方法执行成功的话,会在注册中心创建和这些类别对应的目录,
并给这些目录添加子节点列表的Watcher监听
可以看到一个服务下,有四种类别信息
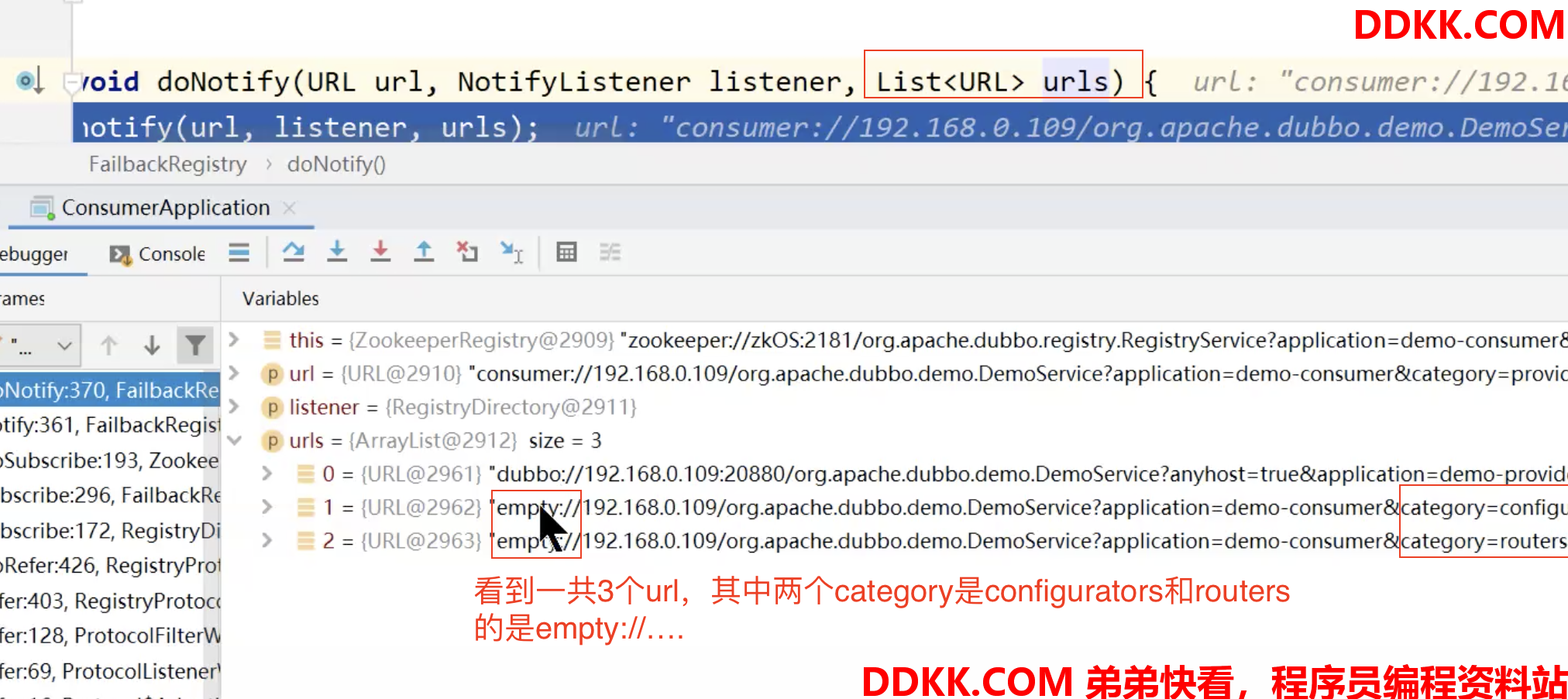
对于消费者来说,第一次启动会主动调用notify()方法,更新分类节点子节点列表,我们主要关注providers节点的子节点列表数据更新
现在我们看org.apache.dubbo.registry.integration.RegistryDirectory#subscribe方法:
//org.apache.dubbo.registry.integration.RegistryDirectory#subscribe
public void subscribe(URL url) {
setConsumerUrl(url);
CONSUMER_CONFIGURATION_LISTENER.addNotifyListener(this);
//注册配置信息监听器
serviceConfigurationListener = new ReferenceConfigurationListener(this, url);
//registry是ZookeeperRegistry
registry.subscribe(url, this);
}
直接跟subscribe方法:
org.apache.dubbo.registry.support.FailbackRegistry#subscribe
org.apache.dubbo.registry.support.FailbackRegistry#doSubscribe
org.apache.dubbo.registry.zookeeper.ZookeeperRegistry#doSubscribe方法:
- 处理interface属性为*的情况(不用关注)
- 处理interface属性为真正接口的情况(主要看这个就行了)
//org.apache.dubbo.registry.zookeeper.ZookeeperRegistry#doSubscribe
public void doSubscribe(final URL url, final NotifyListener listener) {
//注意,listener就是动态列表RegistryDirectory
try {
// ANY_VALUE = "*"
if (ANY_VALUE.equals(url.getServiceInterface())) {
// 处理interface属性为*的情况
...
} else {
// 处理interface属性为真正接口的情况
// 存放所有分类节点下的所有子节点url
List<URL> urls = new ArrayList<>();
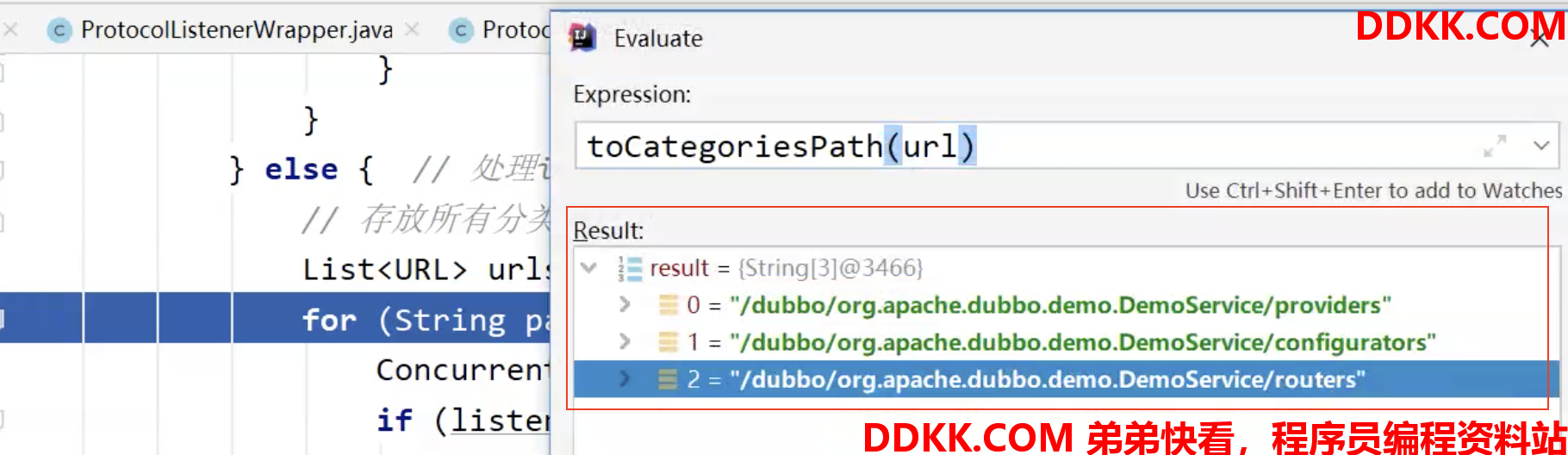
for (String path : toCategoriesPath(url)) {
//注意,toCategoriesPath转换出来的就是providers,configurators,routers
//这三个
ConcurrentMap<NotifyListener, ChildListener> listeners = zkListeners.get(url);
if (listeners == null) {
zkListeners.putIfAbsent(url, new ConcurrentHashMap<>());
listeners = zkListeners.get(url);
}
ChildListener zkListener = listeners.get(listener);
if (zkListener == null) {
listeners.putIfAbsent(listener, (parentPath, currentChilds) -> ZookeeperRegistry.this.notify(url, listener, toUrlsWithEmpty(url, parentPath, currentChilds)));
zkListener = listeners.get(listener);
}
// false创建的是持久节点
// 在zk中创建分类节点
zkClient.create(path, false);
// 为分类节点添加子节点列表变更的watcher监听
// 并返回其所有子节点列表
List<String> children = zkClient.addChildListener(path, zkListener);
if (children != null) {
// toUrlsWithEmpty()获取当前分类节点下的所有子节点url
urls.addAll(toUrlsWithEmpty(url, path, children));
}
}
// 主动调用notify()方法,更新分类节点子节点列表
notify(url, listener, urls);
}
} catch (Throwable e) {
throw new RpcException("Failed to subscribe " + url + " to zookeeper " + getUrl() + ", cause: " + e.getMessage(), e);
}
}
DEBUG,看下dubbo在Zookeeper中的三类持久节点:
3.2.2 分类节点下的所有子节点url的处理
先看下获取到各个分类节点下所有子节点列表时怎么处理的
先看toUrlsWithEmpty方法:
//org.apache.dubbo.registry.zookeeper.ZookeeperRegistry#toUrlsWithEmpty
//providers就是ZK对应category节点的子节点列表
private List<URL> toUrlsWithEmpty(URL consumer, String path, List<String> providers) {
//toUrlsWithEmpty:没有会生成一个默认的
//toUrlsWithoutEmpty:没有就没有
List<URL> urls = toUrlsWithoutEmpty(consumer, providers);
// 若当前分类节点没有子节点,则为其创建一个url,其形式为empty://...
if (urls == null || urls.isEmpty()) {
//PATH_SEPARATOR = "/"
int i = path.lastIndexOf(PATH_SEPARATOR);
String category = i < 0 ? path : path.substring(i + 1);
URL empty = URLBuilder.from(consumer)
//EMPTY_PROTOCOL="empty"
.setProtocol(EMPTY_PROTOCOL)
.addParameter(CATEGORY_KEY, category)
.build();
urls.add(empty);
}
return urls;
}
//org.apache.dubbo.registry.zookeeper.ZookeeperRegistry#toUrlsWithoutEmpty
private List<URL> toUrlsWithoutEmpty(URL consumer, List<String> providers) {
List<URL> urls = new ArrayList<>();
// 在子节点列表不为空的情况下,将所有子节点列表的url写入到urls集合
if (CollectionUtils.isNotEmpty(providers)) {
for (String provider : providers) {
//转换成URL
provider = URL.decode(provider);
//PROTOCOL_SEPARATOR = "://"
if (provider.contains(PROTOCOL_SEPARATOR)) {
URL url = URL.valueOf(provider);
if (UrlUtils.isMatch(consumer, url)) {
urls.add(url);
}
}
}
}
return urls;
}
由此可以看出如果分类节点下子节点列表是空的,那么toUrlsWithEmpty方法至少返回一个empty://的URL,不可能返回空集合。
现在看主动调用notify()方法,更新分类节点子节点列表:
//org.apache.dubbo.registry.support.FailbackRegistry#notify
protected void notify(URL url, NotifyListener listener, List<URL> urls) {
if (url == null) {
throw new IllegalArgumentException("notify url == null");
}
if (listener == null) {
throw new IllegalArgumentException("notify listener == null");
}
try {
doNotify(url, listener, urls);
} catch (Exception t) {
// Record a failed registration request to a failed list, retry regularly
addFailedNotified(url, listener, urls);
logger.error("Failed to notify for subscribe " + url + ", waiting for retry, cause: " + t.getMessage(), t);
}
}
//org.apache.dubbo.registry.support.FailbackRegistry#doNotify
protected void doNotify(URL url, NotifyListener listener, List<URL> urls) {
super.notify(url, listener, urls);
}
DEBUG,看下:
继续,看super.nofity,走父类抽象类方法:
//org.apache.dubbo.registry.support.AbstractRegistry#notify(org.apache.dubbo.common.URL, org.apache.dubbo.registry.NotifyListener, java.util.List<org.apache.dubbo.common.URL>)
protected void notify(URL url, NotifyListener listener, List<URL> urls) {
if (url == null) {
throw new IllegalArgumentException("notify url == null");
}
if (listener == null) {
throw new IllegalArgumentException("notify listener == null");
}
if ((CollectionUtils.isEmpty(urls))
&& !ANY_VALUE.equals(url.getServiceInterface())) {
logger.warn("Ignore empty notify urls for subscribe url " + url);
return;
}
if (logger.isInfoEnabled()) {
logger.info("Notify urls for subscribe url " + url + ", urls: " + urls);
}
// keep every provider's category.
// result放了什么:
// key:category
// value:为该category的所有子节点的url
Map<String, List<URL>> result = new HashMap<>();
for (URL u : urls) {
//判断url和u是否匹配
//url是消费者的URL,urls是提供者的URL
//主要判断一些属性值是否相同,例如group、version.....
if (UrlUtils.isMatch(url, u)) {
//如果匹配则
String category = u.getParameter(CATEGORY_KEY, DEFAULT_CATEGORY);
// 为每一个category创建一个List,然后将category作为key,
// 将这个创建的list作用value
List<URL> categoryList = result.computeIfAbsent(category, k -> new ArrayList<>());
// 将当前遍历的url放入到相应的category的list中
categoryList.add(u);
}
}
if (result.size() == 0) {
return;
}
// 为当前消费者url创建一个map,而这个map存的内容和上面的result一模一样
Map<String, List<URL>> categoryNotified = notified.computeIfAbsent(url, u -> new ConcurrentHashMap<>());
// 遍历所有的category
for (Map.Entry<String, List<URL>> entry : result.entrySet()) {
String category = entry.getKey();
List<URL> categoryList = entry.getValue();
//这个map存的就是前面定义的result
categoryNotified.put(category, categoryList);
// 主动调用当前遍历category的notify(),更新其子节点列表
listener.notify(categoryList);
// We will update our cache file after each notification.
// When our Registry has a subscribe failure due to network jitter, we can return at least the existing cache URL.
saveProperties(url);
}
}
result.computeIfAbsent(category, k -> new ArrayList<>()):
```java /** * ... * 等价于: * <pre> {@code * if (map.get(key) == null) { * V newValue = mappingFunction.apply(key); * if (newValue != null) * map.put(key, newValue); * } * }</pre> * */ default V computeIfAbsent(K key, Function<? super K, ? extends V> mappingFunction) { Objects.requireNonNull(mappingFunction); V v; if ((v = get(key)) == null) { V newValue; if ((newValue = mappingFunction.apply(key)) != null) { put(key, newValue); return newValue; } } return v; }
继续看listener.notify(categoryList)方法,每种category类别都会触发一次该方法,(当前有3个category),我们主要看providers的情况:
>DEBUG:![ ][nbsp 7]
listener就是动态列表RegistryDirectory,所以看RegistryDirectory.notify方法:
```java
//org.apache.dubbo.registry.integration.RegistryDirectory#notify
public synchronized void notify(List<URL> urls) {
//三类category实际上都会调用这个方法
//这里会过滤调无效的,并根据category分组,然后分别处理
Map<String, List<URL>> categoryUrls = urls.stream()
.filter(Objects::nonNull)
.filter(this::isValidCategory)
.filter(this::isNotCompatibleFor26x)
.collect(Collectors.groupingBy(url -> {
if (UrlUtils.isConfigurator(url)) {
return CONFIGURATORS_CATEGORY;
} else if (UrlUtils.isRoute(url)) {
return ROUTERS_CATEGORY;
} else if (UrlUtils.isProvider(url)) {
return PROVIDERS_CATEGORY;
}
return "";
}));
// 处理category为configurators的情况
List<URL> configuratorURLs = categoryUrls.getOrDefault(CONFIGURATORS_CATEGORY, Collections.emptyList());
this.configurators = Configurator.toConfigurators(configuratorURLs).orElse(this.configurators);
// 处理category为routers的情况
List<URL> routerURLs = categoryUrls.getOrDefault(ROUTERS_CATEGORY, Collections.emptyList());
toRouters(routerURLs).ifPresent(this::addRouters);
// providers
// 处理category为providers的情况
List<URL> providerURLs = categoryUrls.getOrDefault(PROVIDERS_CATEGORY, Collections.emptyList());
refreshOverrideAndInvoker(providerURLs);
}
这里我们只关注category为providers的情况,看refreshOverrideAndInvoker方法:
//org.apache.dubbo.registry.integration.RegistryDirectory#refreshOverrideAndInvoker
private void refreshOverrideAndInvoker(List<URL> urls) {
// mock zookeeper://xxx?mock=return null
// 记录即将被覆盖的Directory
overrideDirectoryUrl();
// 更新invoker列表
refreshInvoker(urls);
}
这里会触发最核心的方法refreshInvoker。
3.2.2 刷新Invoker列表(核心)
refreshInvoker方法的核心流程如下:
-
只有一个提供者url,且其protocol为empty
-
则说明当前没有提供者,标记为禁止远程调用,并删除所有Invokers
-
有提供者
-
标记为允许远程调用
-
更新URL列表缓存
-
将url列表转换为invokerMap(这里才是真正的更新) -
从跟新后的invokerMap中获取到最新的invokers,写入到routerChain,即写入到了Directory
-
将更新过的invoker根据group进行分组,每组合并为一个invoker
-
更新urlInvokerMap缓存
-
从老的缓存oldUrlInvokerMap中将失效的invoker销毁
//org.apache.dubbo.registry.integration.RegistryDirectory#refreshInvoker
private void refreshInvoker(List<URL> invokerUrls) {
// 参数invokerUrls是当前providers这个分类节点的所有子节点列表url
Assert.notNull(invokerUrls, "invokerUrls should not be null");
// 若只有一个提供者url,且其protocol为empty,则说明当前没有提供者
// 则本次远程调用将被禁止
if (invokerUrls.size() == 1
&& invokerUrls.get(0) != null
&& EMPTY_PROTOCOL.equals(invokerUrls.get(0).getProtocol())) {
//标记为静止远程调用
this.forbidden = true; // Forbid to access
this.invokers = Collections.emptyList();
routerChain.setInvokers(this.invokers);
destroyAllInvokers(); // Close all invokers
} else {
this.forbidden = false; // Allow to access
// 获取并记录当前旧的缓存urlInvokerMap
Map<String, Invoker<T>> oldUrlInvokerMap = this.urlInvokerMap; // local reference
if (invokerUrls == Collections.<URL>emptyList()) {
invokerUrls = new ArrayList<>();
}
if (invokerUrls.isEmpty() && this.cachedInvokerUrls != null) {
// 若providers子节点invokerUrls 为空,则用之前旧的缓存URL
invokerUrls.addAll(this.cachedInvokerUrls);
} else {
// 否则覆盖更新旧的缓存
this.cachedInvokerUrls = new HashSet<>();
this.cachedInvokerUrls.addAll(invokerUrls);//Cached invoker urls, convenient for comparison
}
if (invokerUrls.isEmpty()) {
return;
}
// 将url列表转换为invokerMap,这里才是真正的更新
// key为提供者节点的url
// value为该url对应的invoker
Map<String, Invoker<T>> newUrlInvokerMap = toInvokers(invokerUrls);// Translate url list to Invoker map
/**
* If the calculation is wrong, it is not processed.
*
* 1. The protocol configured by the client is inconsistent with the protocol of the server.
* eg: consumer protocol = dubbo, provider only has other protocol services(rest).
* 2. The registration center is not robust and pushes illegal specification data.
*
*/
if (CollectionUtils.isEmptyMap(newUrlInvokerMap)) {
logger.error(new IllegalStateException("urls to invokers error .invokerUrls.size :" + invokerUrls.size() + ", invoker.size :0. urls :" + invokerUrls
.toString()));
return;
}
// 从map中获取到最新的invokers
List<Invoker<T>> newInvokers = Collections.unmodifiableList(new ArrayList<>(newUrlInvokerMap.values()));
// pre-route and build cache, notice that route cache should build on original Invoker list.
// toMergeMethodInvokerMap() will wrap some invokers having different groups, those wrapped invokers not should be routed.
// 将更新过的invokers写入到routerChain,即写入到了Directory
routerChain.setInvokers(newInvokers);
// 将更新过的invoker根据group进行分组,每组合并为一个invoker
this.invokers = multiGroup ? toMergeInvokerList(newInvokers) : newInvokers;
// 更新缓存urlInvokerMap
this.urlInvokerMap = newUrlInvokerMap;
try {
// 从老的缓存oldUrlInvokerMap中将失效的invoker销毁
destroyUnusedInvokers(oldUrlInvokerMap, newUrlInvokerMap); // Close the unused Invoker
} catch (Exception e) {
logger.warn("destroyUnusedInvokers error. ", e);
}
}
}
- 若新的map为空,则说明现在已经没有了任何提供者,所以需要将所有缓存中的invoker销毁,看destroyAllInvokers方法:
//org.apache.dubbo.registry.integration.RegistryDirectory#destroyAllInvokers
private void destroyAllInvokers() {
// 遍历缓存map,将其中的所有invoker销毁
Map<String, Invoker<T>> localUrlInvokerMap = this.urlInvokerMap; // local reference
if (localUrlInvokerMap != null) {
for (Invoker<T> invoker : new ArrayList<>(localUrlInvokerMap.values())) {
try {
invoker.destroy();
} catch (Throwable t) {
logger.warn("Failed to destroy service " + serviceKey + " to provider " + invoker.getUrl(), t);
}
}
localUrlInvokerMap.clear();
}
invokers = null;
}
- 将url列表转换为invokerMap,看最核心的Map
<String, Invoker>newUrlInvokerMap = toInvokers(invokerUrls)方法:
//org.apache.dubbo.registry.integration.RegistryDirectory#toInvokers
private Map<String, Invoker<T>> toInvokers(List<URL> urls) {
// -------------- 以下是对urls的各种检测 ----------------
Map<String, Invoker<T>> newUrlInvokerMap = new HashMap<>();
if (urls == null || urls.isEmpty()) {
return newUrlInvokerMap;
}
Set<String> keys = new HashSet<>();
String queryProtocols = this.queryMap.get(PROTOCOL_KEY);
for (URL providerUrl : urls) {
// If protocol is configured at the reference side, only the matching protocol is selected
if (queryProtocols != null && queryProtocols.length() > 0) {
boolean accept = false;
String[] acceptProtocols = queryProtocols.split(",");
for (String acceptProtocol : acceptProtocols) {
if (providerUrl.getProtocol().equals(acceptProtocol)) {
accept = true;
break;
}
}
if (!accept) {
continue;
}
}
if (EMPTY_PROTOCOL.equals(providerUrl.getProtocol())) {
continue;
}
if (!ExtensionLoader.getExtensionLoader(Protocol.class).hasExtension(providerUrl.getProtocol())) {
logger.error(new IllegalStateException("Unsupported protocol " + providerUrl.getProtocol() +
" in notified url: " + providerUrl + " from registry " + getUrl().getAddress() +
" to consumer " + NetUtils.getLocalHost() + ", supported protocol: " +
ExtensionLoader.getExtensionLoader(Protocol.class).getSupportedExtensions()));
continue;
}
// -------------- 以上是对urls的各种检测 ----------------
// 合并url(将动态配置【即ZK对应服务的configurators类别的节点的数据】、
// <dubbo:reference/>、<dubbo:consumer/>中的配置进行合并)
URL url = mergeUrl(providerUrl);
String key = url.toFullString(); // The parameter urls are sorted
if (keys.contains(key)) {
// Repeated url
continue;
}
keys.add(key);
// Cache key is url that does not merge with consumer side parameters, regardless of how the consumer combines parameters, if the server url changes, then refer again
// 从缓存中获取指定的invoker,若存在,则直接放入到map中,
// 若不存在,则创建一个新的invoker,放入到map中
Map<String, Invoker<T>> localUrlInvokerMap = this.urlInvokerMap; // local reference
Invoker<T> invoker = localUrlInvokerMap == null ? null : localUrlInvokerMap.get(key);
if (invoker == null) {
// Not in the cache, refer again
try {
boolean enabled = true;
//DISABLED_KEY = "disabled"
if (url.hasParameter(DISABLED_KEY)) {
enabled = !url.getParameter(DISABLED_KEY, false);
} else {
enabled = url.getParameter(ENABLED_KEY, true);
}
// 如果是可用的
if (enabled) {
// 创建一个invoker的委托对象invoker(将invoker和URL 信息绑定)
// protocol.refer(serviceType, url)这个方法非常重要后面
// “消费者处理提供者响应”的时候会详细讲解
// 对于消费者端来说,这个invoker属于委托对象
// 对于提供者端来说,invoker属于代理对象
invoker = new InvokerDelegate<>(protocol.refer(serviceType, url), url, providerUrl);
}
} catch (Throwable t) {
logger.error("Failed to refer invoker for interface:" + serviceType + ",url:(" + url + ")" + t.getMessage(), t);
}
if (invoker != null) {
// Put new invoker in cache
//将invoker放入新缓存,key是url
newUrlInvokerMap.put(key, invoker);
}
} else {
//如果旧缓存已经有了直接将invoker放入新缓存
newUrlInvokerMap.put(key, invoker);
}
}
keys.clear();
return newUrlInvokerMap;
}
这个方法可以看出,将URL列表转换为Invoker时,会先根据URL从缓存查询Invoker,如果不存在才会创建新的Invoker,而protocol.refer(serviceType, url)方法创建Invoker,此时url是dubbo协议,所以最终会走DubboProtocol:
org.apache.dubbo.rpc.protocol.AbstractProtocol#refer
org.apache.dubbo.rpc.protocol.dubbo.DubboProtocol#protocolBindingRefer
//org.apache.dubbo.rpc.protocol.dubbo.DubboProtocol#protocolBindingRefer
public <T> Invoker<T> protocolBindingRefer(Class<T> serviceType, URL url) throws RpcException {
optimizeSerialization(url);
// create rpc invoker.
DubboInvoker<T> invoker = new DubboInvoker<T>(serviceType, url, getClients(url), invokers);
invokers.add(invoker);
return invoker;
}
关于DubboInvoker,我们将在下一章《远程调用》进行详细讲解,因为这里涉及到远程调用的内容。
- 从老的缓存oldUrlInvokerMap中将失效的invoker销毁,destroyUnusedInvokers(oldUrlInvokerMap, newUrlInvokerMap)方法,:
//org.apache.dubbo.registry.integration.RegistryDirectory#destroyUnusedInvokers
private void destroyUnusedInvokers(Map<String, Invoker<T>> oldUrlInvokerMap, Map<String, Invoker<T>> newUrlInvokerMap) {
// 若新的map为空,则说明现在已经没有了任何提供者,所以需要将所有缓存中的invoker销毁
if (newUrlInvokerMap == null || newUrlInvokerMap.size() == 0) {
destroyAllInvokers();
return;
}
// check deleted invoker
List<String> deleted = null;
if (oldUrlInvokerMap != null) {
// 比较新老map,对于老的map中的invoker,将新的里面不存在的invoker放入到deleted集合中
Collection<Invoker<T>> newInvokers = newUrlInvokerMap.values();
for (Map.Entry<String, Invoker<T>> entry : oldUrlInvokerMap.entrySet()) {
if (!newInvokers.contains(entry.getValue())) {
if (deleted == null) {
deleted = new ArrayList<>();
}
deleted.add(entry.getKey());
}
}
}
if (deleted != null) {
// 将deleted集合中的invoker销毁
for (String url : deleted) {
if (url != null) {
Invoker<T> invoker = oldUrlInvokerMap.remove(url);
if (invoker != null) {
try {
invoker.destroy();
if (logger.isDebugEnabled()) {
logger.debug("destroy invoker[" + invoker.getUrl() + "] success. ");
}
} catch (Exception e) {
logger.warn("destroy invoker[" + invoker.getUrl() + "] failed. " + e.getMessage(), e);
}
}
}
}
}
}
3.3 使用Cluster将所有Invoker伪装为一个invoker
回到最初的方法createProxy,此时每个注册中心URL都已经创建好对应的Invoker,这个时候需要将所有的Invoker再次伪装成一个Invoker:
//org.apache.dubbo.config.ReferenceConfig#createProxy
private T createProxy(Map<String, String> map) {
// 判断是否是本地调用
if (shouldJvmRefer(map)) {
// 处理本地调用请求
...
} else {
// 处理远程调用
...
if (url != null && url.length() > 0) {
//直连方式处理URL
...
} else {
// 注册中心的方式,处理URL
...
}
// 代码运行到这里,urls中已经不为空了
// 此时urls中的url只可能是注册中心的URL(包含消费者元数据)
if (urls.size() == 1) {
// 注册中心只有一个的情况
// 将这个注册中心URL构建为一个invoker
// 这个invoker并不是某一个具体的提供者的代理对象,而是针对一个注册中心,一个接口(服务)
// 的invoker,这个invoker执行的时候,底层会路由、负载均衡到真正的invoker
invoker = REF_PROTOCOL.refer(interfaceClass, urls.get(0));
} else {
// 注册中心有多个的情况
List<Invoker<?>> invokers = new ArrayList<Invoker<?>>();
URL registryURL = null;
// 遍历所有注册中心url
for (URL url : urls) {
// 将每个注册中心构建为一个invoker,并写入到invokers列表
invokers.add(REF_PROTOCOL.refer(interfaceClass, url));
// 记录最后一个注册中心地址
// 所有注册中心的url,除了host、port、path,及registry参数不同外,
//(path,直连的时候是接口名,注册中心的时候是RegistryService全路径类名)
// (registry参数代表的是暴露协议)
// 其它数据都是相同的。后面的代码需要使用这些url中相同的数据部分,
// 所以只需要获取一个注册中心地址就可以了
if (REGISTRY_PROTOCOL.equals(url.getProtocol())) {
registryURL = url; // use last registry url
}
}
if (registryURL != null) {
// registry url is available
// use RegistryAwareCluster only when register's CLUSTER is available
// CLUSTER_KEY = "cluster"
// RegistryAwareCluster.NAME = "registryaware"
URL u = registryURL.addParameter(CLUSTER_KEY, RegistryAwareCluster.NAME);
// The invoker wrap relation would be: RegistryAwareClusterInvoker(StaticDirectory) -> FailoverClusterInvoker(RegistryDirectory, will execute route) -> Invoker
// 此时的invokers代表的是具有相同某个服务的所有注册中心的列表
// 它是不会变的,所以用静态列表
invoker = CLUSTER.join(new StaticDirectory(u, invokers));
} else {
// not a registry url, must be direct invoke.
invoker = CLUSTER.join(new StaticDirectory(invokers));
}
}
}
...
return (T) PROXY_FACTORY.getProxy(invoker);
}
这里Cluster的处理,和2.3中差不多,讲点没讲过的:
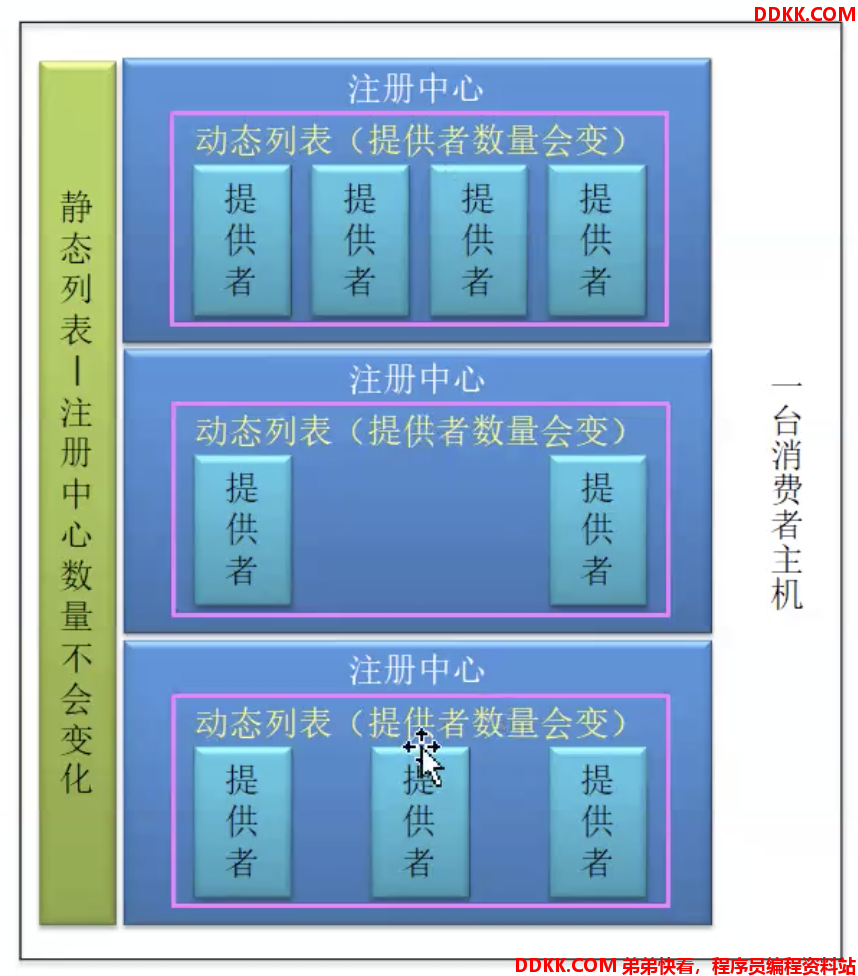
通过上一步,我们知道如果是注册中心的方式,这里的Invoker,并不是某一个具体的提供者的代理对象,而是针对一个注册中心的伪Invoker,里面封装了一个动态列表,动态列表中维护了所有真正的服务提供者代理对象。这个Invoker执行的时候,底层会进行服务路由、负载均衡,找到当前注册中心中该服务的某一个真正Invoker。
我们看invoker = CLUSTER.join(new StaticDirectory(u, invokers))方法,看到用了StaticDirectory,之前说过这个是静态列表,为什么用静态列表?
此时这里的Invoker,一个注册中心一个invoker,注册中心的数量肯定是不会动态变化的,所以用静态列表,由此可以总结出一个图:
4. 若元数据中心不为空,则将消费者元数据写入到元数据中心保存
有兴趣自己看把。
//org.apache.dubbo.config.ReferenceConfig#createProxy
private T createProxy(Map<String, String> map) {
...
// 若元数据中心不为空,则将消费者元数据写入到元数据中心保存
MetadataReportService metadataReportService = null;
if ((metadataReportService = getMetadataReportService()) != null) {
URL consumerURL = new URL(CONSUMER_PROTOCOL, map.remove(REGISTER_IP_KEY), 0, map.get(INTERFACE_KEY), map);
metadataReportService.publishConsumer(consumerURL);
}
// create service proxy 创建消费者代理对象
return (T) PROXY_FACTORY.getProxy(invoker);
}
5. 创建消费者代理对象
看createProxy方法的最后一步,此时无论前面是本地注册表方式,还是注册中心方式,最终都只会有一个Invoker,最终会对Invoker对象创建代理对象:
//org.apache.dubbo.config.ReferenceConfig#createProxy
private T createProxy(Map<String, String> map) {
...
// create service proxy 创建消费者代理对象
return (T) PROXY_FACTORY.getProxy(invoker);
}
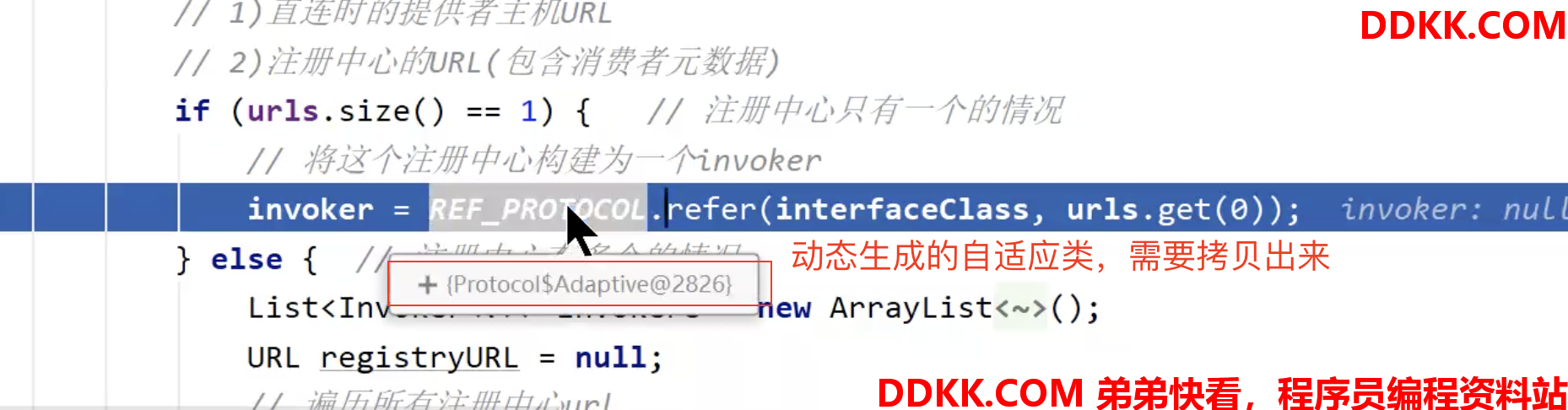
DEBUG,PROXY_FACTORY是自适应类:
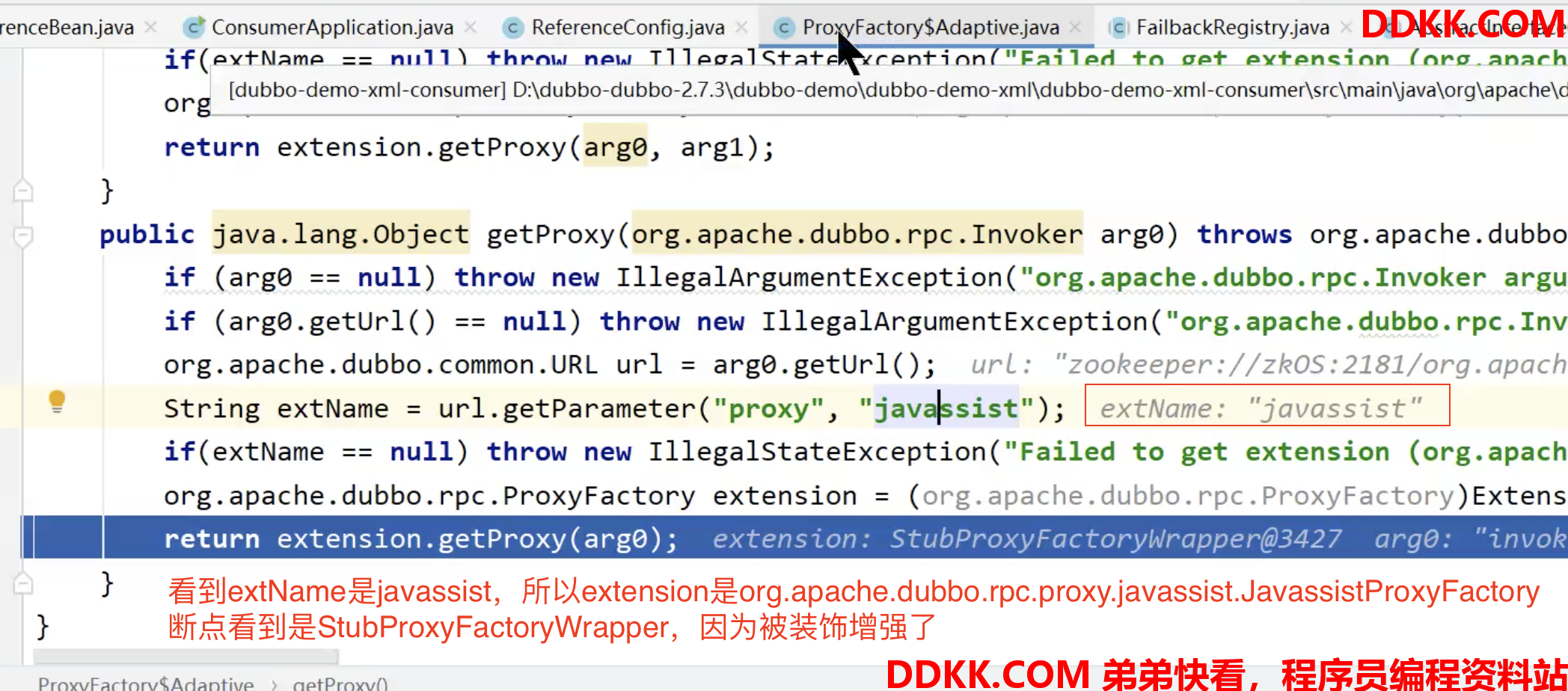
这个自适应类是动态生成的,我们拷贝出来
看到默认用JavassistProxyFactory
直接看org.apache.dubbo.rpc.proxy.javassist.JavassistProxyFactory#getProxy:
public class JavassistProxyFactory extends AbstractProxyFactory {
@Override
@SuppressWarnings("unchecked")
public <T> T getProxy(Invoker<T> invoker, Class<?>[] interfaces) {
//其实也不用跟的太细,最终这个代理对象执行任何方法都会转发到InvokerInvocationHandler的invoker方法
return (T) Proxy.getProxy(interfaces).newInstance(new InvokerInvocationHandler(invoker));
}
...
}
先跟Proxy.getProxy(interfaces):
//org.apache.dubbo.common.bytecode.Proxy#getProxy(java.lang.Class<?>...)
public static Proxy getProxy(Class<?>... ics) {
return getProxy(ClassUtils.getClassLoader(Proxy.class), ics);
}
继续跟org.apache.dubbo.common.bytecode.Proxy#getProxy(java.lang.ClassLoader, java.lang.Class<?>…),很长,省略了部分代码,只列我们关注的部分,其实就是用ClassGenerator(封装了javassist)生成Proxy类(Proxy类是一个抽象类,生成的是其子类),并创建了Proxy的实例:
//org.apache.dubbo.common.bytecode.Proxy#getProxy(java.lang.ClassLoader, java.lang.Class<?>...)
public static Proxy getProxy(ClassLoader cl, Class<?>... ics) {
...//一些参数校验
// use interface class name list as key.
String key = sb.toString();
// get cache by class loader.
final Map<String, Object> cache;
synchronized (PROXY_CACHE_MAP) {
cache = PROXY_CACHE_MAP.computeIfAbsent(cl, k -> new HashMap<>());
}
Proxy proxy = null;
// 缓存处理
synchronized (cache) {
do {
Object value = cache.get(key);
if (value instanceof Reference<?>) {
proxy = (Proxy) ((Reference<?>) value).get();
if (proxy != null) {
return proxy;
}
}
//处理其他线程正在处理的情况,让当前线程阻塞
//等待其他线程处理完毕后直接获取缓存结果
if (value == PENDING_GENERATION_MARKER) {
try {
cache.wait();
} catch (InterruptedException e) {
}
} else {
cache.put(key, PENDING_GENERATION_MARKER);
break;
}
}
while (true);
}
//缓存中没有数据,则且第一次创建
long id = PROXY_CLASS_COUNTER.getAndIncrement();
String pkg = null;
ClassGenerator ccp = null, ccm = null;
try {
//初始化类生成器
ccp = ClassGenerator.newInstance(cl);
Set<String> worked = new HashSet<>();
List<Method> methods = new ArrayList<>();
//处理需要实现的所有接口的方法
for (int i = 0; i < ics.length; i++) {
...
for (Method method : ics[i].getMethods()) {
...
}
}
if (pkg == null) {
pkg = PACKAGE_NAME;
}
// create ProxyInstance class.
String pcn = pkg + ".proxy" + id;
ccp.setClassName(pcn);
ccp.addField("public static java.lang.reflect.Method[] methods;");
ccp.addField("private " + InvocationHandler.class.getName() + " handler;");
ccp.addConstructor(Modifier.PUBLIC, new Class<?>[]{
InvocationHandler.class}, new Class<?>[0], "handler=$1;");
ccp.addDefaultConstructor();
Class<?> clazz = ccp.toClass();
clazz.getField("methods").set(null, methods.toArray(new Method[0]));
// create Proxy class.
String fcn = Proxy.class.getName() + id;
ccm = ClassGenerator.newInstance(cl);
ccm.setClassName(fcn);
ccm.addDefaultConstructor();
//指定父类是org.apache.dubbo.common.bytecode.Proxy
//即生成的是其子类
ccm.setSuperClass(Proxy.class);
ccm.addMethod("public Object newInstance(" + InvocationHandler.class.getName() + " h){ return new " + pcn + "($1); }");
// 生成一个代理类的class
Class<?> pc = ccm.toClass();
// 创建该class的实例
proxy = (newInstance) pc.newInstance();
} catch (RuntimeException e) {
throw e;
} catch (Exception e) {
throw new RuntimeException(e.getMessage(), e);
} finally {
...
}
return proxy;
}
接下来就要看生成的Proxy类子类的实例的newInstance方法,暂时不跟了,下一章远程调用的时候再看。
6. 关于Cluster的join方法
上面追踪源码过程中,有两个地方我们看到调用了org.apache.dubbo.rpc.cluster.Cluster#join方法:
- org.apache.dubbo.config.ReferenceConfig#createProxy
- org.apache.dubbo.registry.integration.RegistryProtocol#doRefer
Cluster主要将多个Invoker伪装成一个Invoker,但并不是简单的包装,它还提供了Mock降级功能、容错功能,先混个眼熟,之后会专门讲解降级机制、容错机制:
DEBUG,断点跟一下org.apache.dubbo.registry.integration.RegistryProtocol#doRefer:
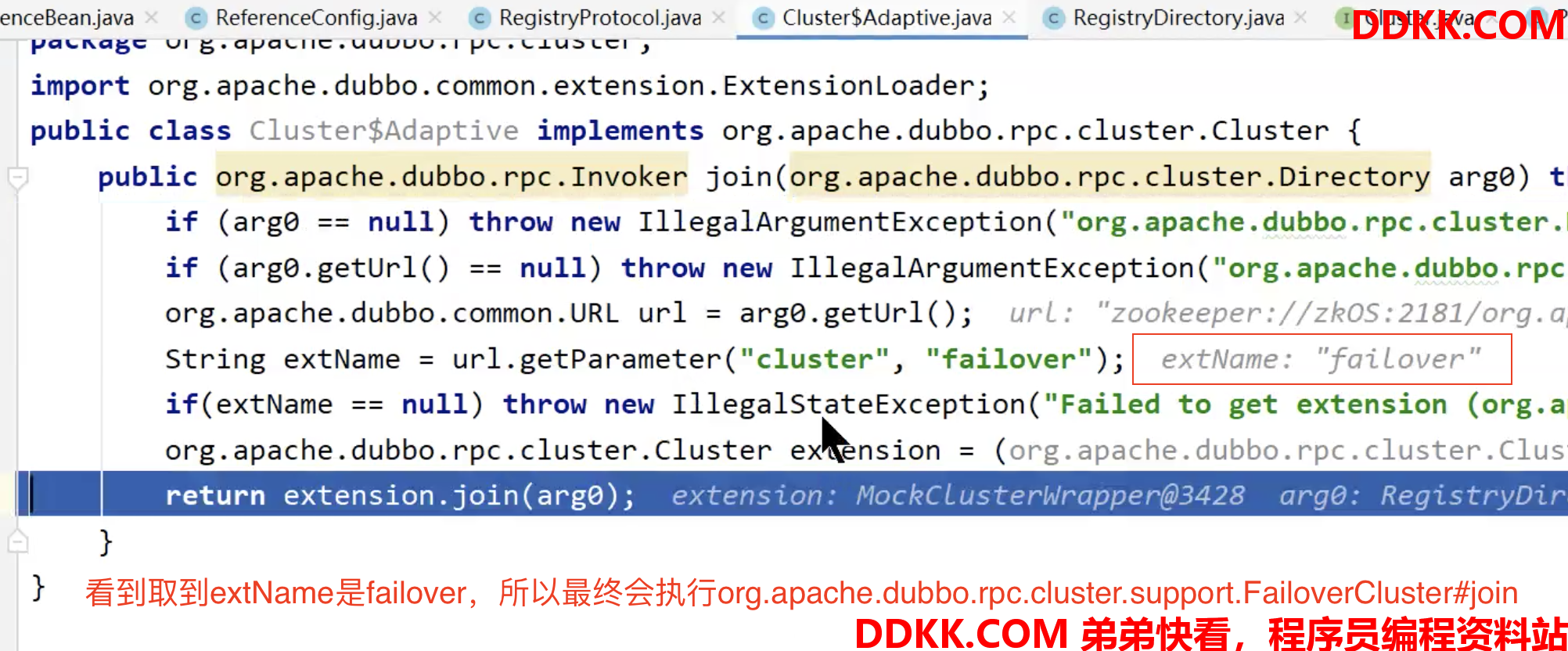
这个failover实际上是后面要说的“集群容错”相关的,等
讲容错的时候会详细说
图中可以看到extension是MockClusterWrapper,Wrapper增强类,而这个类就是提供mock降级功能的,
讲服务降级的时候详细说。先混个眼熟:```java public class MockClusterWrapper implements Cluster { private Cluster cluster; public MockClusterWrapper(Cluster cluster) { this.cluster = cluster; } @Override public <T> Invoker<T> join(Directory<T> directory) throws RpcException { return new MockClusterInvoker<T>(directory, this.cluster.join(directory)); } }
>
>MockClusterWrapper处理完就是FailoverCluster处理了:
>![ ][nbsp 13]
```java
public class FailoverCluster implements Cluster {
public final static String NAME = "failover";
@Override
public <T> Invoker<T> join(Directory<T> directory) throws RpcException {
//在这创建了具有容错功能的invoker
return new FailoverClusterInvoker<T>(directory);
}
}
我们看下FailoverClusterInvoker类,构造做了什么:
public class FailoverClusterInvoker<T> extends AbstractClusterInvoker<T> {
private static final Logger logger = LoggerFactory.getLogger(FailoverClusterInvoker.class);
public FailoverClusterInvoker(Directory<T> directory) {
super(directory);
}
...
}
看下父类构造做了什么:
public abstract class AbstractClusterInvoker<T> implements Invoker<T> {
...
protected final Directory<T> directory;
protected final boolean availablecheck;
public AbstractClusterInvoker(Directory<T> directory, URL url) {
if (directory == null) {
throw new IllegalArgumentException("service directory == null");
}
this.directory = directory;
//sticky: invoker.isAvailable() should always be checked before using when availablecheck is true.
// 粘连接,尽量让同一个客户端调用提供者服务时,用同一个提供者
// 当availablecheck为真时,再使用粘连接的这个invoker时,始终会
// 检查invoker.isavailable(),查看是否可用,可用才用,不可用用负
// 载均衡的方式选一个新的
// 该值默认为true DEFAULT_CLUSTER_AVAILABLE_CHECK=true
this.availablecheck = url.getParameter(CLUSTER_AVAILABLE_CHECK_KEY, DEFAULT_CLUSTER_AVAILABLE_CHECK);
}
...
}
通过上面分析,我们知道Invoker invoker = cluster.join(directory)方法返回的invoker,是具有降级功能,又具有容错的功能
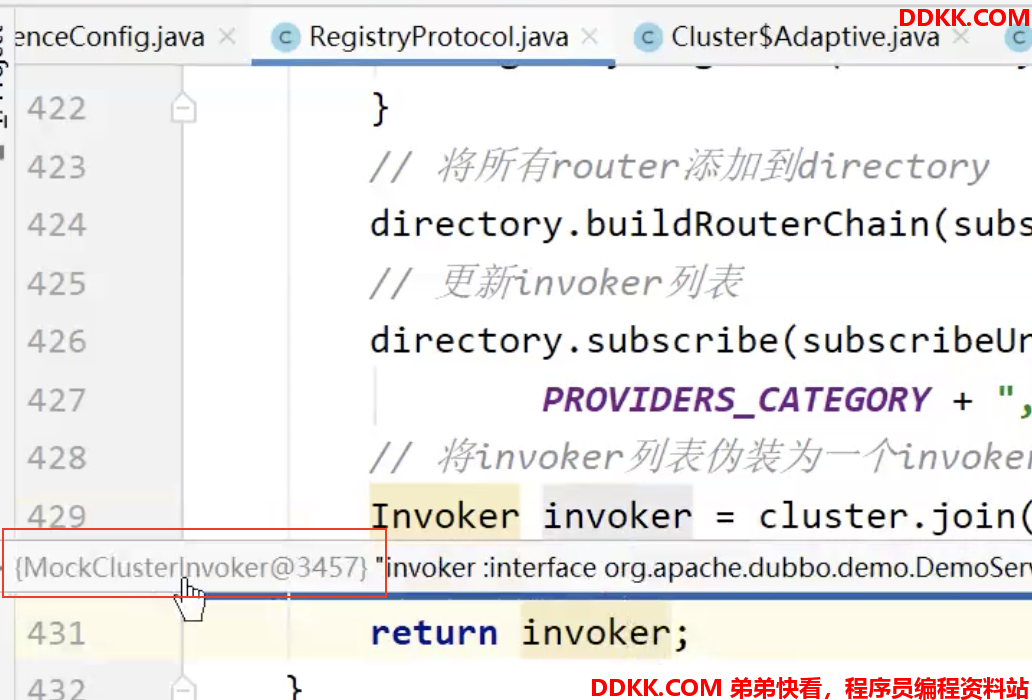
即返回的是MockClusterInvoker,里面又封装了FailoverClusterInvoker
以上服务订阅相关的内容我们就结束了。