List结构图
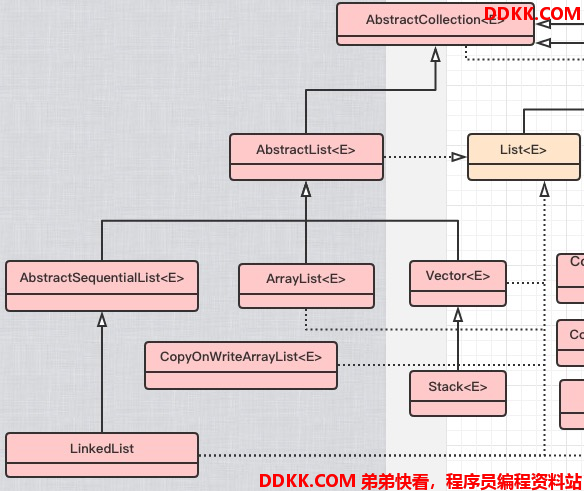
1.List
public abstract interface List extends Collection
有序、允许有重复元素、值可为NULL。用户可以根据元素的整数索引(在列表中的位置)访问元素,并搜索列表中的元素。
List 接口在 iterator、add、remove、equals 和 hashCode 方法的协定上加了一些其他约定,超过了 Collection 接口中指定的约定。
针对List的add、remove、set推荐使用Iterator进行迭代,否则稍微不注意容易导致fail-fast。
Arrays:操作数组(比如排序和搜索),集合帮助类。
2.AbstractList
publicabstract class AbstractList extends AbstractCollection implements List
提供 List 接口的骨干实现,以最大限度地减少实现“随机访问”数据存储(如数组)支持的该接口所需的工作。
支持对数据的随机访问,对于连续的访问数据(如链表),应优先使用 AbstractSequentialList,而不是此类。
AbstractList的迭代由其内部类Itr实现,其子类通过继承调用父类方法。
public Iterator<E> iterator() {
return new Itr();//Itr是其内部类
}
3.ArrayList
public class ArrayList extends AbstractList implements List
List 接口的大小可变数组的实现。默认初始容量为10,可指定大小。
有序、可重复、允许NULL值。
非同步,fail-fast。
元素以transient Object[]形式存储,适用于快速随机访问元素。
常用方法如下:
ensureCapacity(int minCapacity): 如有必要,增加此 ArrayList 实例的容量,以确保它至少能够容纳最小容量参数所指定的元素数。
public void ensureCapacity(int minCapacity) {
modCount++;
int oldCapacity = elementData.length;//获取已有元素数量
if (minCapacity > oldCapacity) {
//若最小容量大于已有数量
Object oldData[] = elementData;
int newCapacity = (oldCapacity * 3)/2 + 1;//原有容量扩大1.5倍+1
if (newCapacity < minCapacity)//扩容后的容量还小于要求的最小容量,则扩容大小为最小容量
newCapacity = minCapacity;
// minCapacity is usually close to size, so this is a win:
elementData = Arrays.copyOf(elementData, newCapacity);
}
}
add(E e): 将指定的元素添加到此列表的尾部。
public boolean add(E e) {
ensureCapacity(size + 1); // Increments modCount!!
elementData[size++] = e;
return true;
}
从源码中看出,新增步骤大致为三步:
1、 已有集合元素数量+1进行扩容,保证本次新增空间足够;
2、 将指定的元素添加到此列表的尾部;
3、 更新已有集合元素数量(+1);
remove(Object o): 移除此列表中首次出现的指定元素(如果存在)。
public boolean remove(Object o) {
if (o == null) {
for (int index = 0; index < size; index++)
if (elementData[index] == null) {
fastRemove(index);
return true;
}
} else {
for (int index = 0; index < size; index++)
if (o.equals(elementData[index])) {
fastRemove(index);
return true;
}
}
return false;
}
private void fastRemove(int index) {
//由于内部方法调用,故不做数据越界检查,默认不会越界
modCount++;
int numMoved = size - index - 1;
if (numMoved > 0)
System.arraycopy(elementData, index+1, elementData, index,
numMoved);
elementData[--size] = null; // Let gc do its work
}
从源码中看出移除Object是使用equals进行匹配,匹配成功,fastRemove匹配成功的索引对应元素。匹配不成功,则不执行faseRemove。
fastRemove大致步骤:
1、 计算需要复制的元素数量;
2、 将index+1之后的元素依次向前移动一个位置,复制完成会覆盖掉需要移除的元素,相当于删除操作;
3、 将队尾元素值设为NULL;
set(int index, E element): 用指定的元素替代此列表中指定位置上的元素。
public E set(int index, E element) {
RangeCheck(index);
E oldValue = (E) elementData[index];
elementData[index] = element;
return oldValue;
}
private void RangeCheck(int index) {
if (index >= size)
throw new IndexOutOfBoundsException(
"Index: "+index+", Size: "+size);
}
从源码中看出先进行数组越界检查,通过后,将新集合元素放置到指定索引位置,并返回对应索引的原有元素。
forEach(Consumer action): 遍历元素并进行消费–jdk1.8源码
@Override
public void forEach(Consumer<? super E> action) {
Objects.requireNonNull(action);
final int expectedModCount = modCount;
@SuppressWarnings("unchecked")
final E[] elementData = (E[]) this.elementData;
final int size = this.size;
for (int i=0; modCount == expectedModCount && i < size; i++) {
action.accept(elementData[i]);
}
if (modCount != expectedModCount) {
throw new ConcurrentModificationException();
}
}
从源码中可以看到对集合元素进行遍历,并进行消费者消费,当遍历时被外部改动过元素,消费终止并抛出ConcurrentModificationException()。