题目地址:https://leetcode-cn.com/problems/path-with-maximum-minimum-value/
题目描述
Given a matrix of integers A with R rows and C columns, find the maximum score of a path starting at [0,0] and ending at [R-1,C-1].
Thescore of a path is the minimum value in that path. For example, the value of the path 8 → 4 → 5 → 9 is 4.
Apath moves some number of times from one visited cell to any neighbouring unvisited cell in one of the 4 cardinal directions (north, east, west, south).
Example 1:

Input: [[5,4,5],[1,2,6],[7,4,6]]
Output: 4
Explanation:
The path with the maximum score is highlighted in yellow.
Example 2:
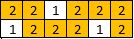
Input: [[2,2,1,2,2,2],[1,2,2,2,1,2]]
Output: 2
Example 3:
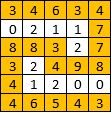
Input: [[3,4,6,3,4],[0,2,1,1,7],[8,8,3,2,7],[3,2,4,9,8],[4,1,2,0,0],[4,6,5,4,3]]
Output: 3
Note:
1、1<=R,C<=100;
2、0<=A[i][j]<=10^9;
题目大意
给你一个 R 行 C 列的整数矩阵 A。矩阵上的路径从 [0,0] 开始,在 [R-1,C-1] 结束。 路径沿四个基本方向(上、下、左、右)展开,从一个已访问单元格移动到任一相邻的未访问单元格。 路径的得分是该路径上的 最小 值。例如,路径 8 → 4 → 5 → 9 的值为 4 。 找出所有路径中得分 最高 的那条路径,返回其 得分。
解题方法
排序+并查集
参照1101. The Earliest Moment When Everyone Become Friendsopen in new window的做法,我们把图里面的每一个点按照值的大小顺序,依次遍历,如果某个点的与其四联通的某个点已经被访问过,那么把这两个点所属的子图连接成为一个图。一直遍历到左上角的位置和右下角的位置属于同一个图为止,此时就是就是题目要求的首尾相接。
帮助理解的几个点:
1、 题目的意思是路径上最小的点,并不是最短路径,所以按照值的大小进行排序;
2、 已经完成了按值的排序,所以会把图里面值最大的点优先访问;
3、 每次新遍历一个点的时候,检查周围的点是否已经访问过(值更大),把该点放入周围的图中;
4、 值最大的点不一定在一起,因此会形成多个子图;
5、 直到添加了一个较小的点时,起终两点联通了,那么这个新添加的点就是我们要求的;
C++代码如下:
class Solution {
public:
int maximumMinimumPath(vector<vector<int>>& A) {
const int M = A.size();
const int N = A[0].size();
const int X = M * N;
parent = vector<int>(X, 0);
for (int i = 0; i < parent.size(); ++i)
parent[i] = i;
vector<vector<int>> values;
for (int i = 0; i < M; ++i) {
for (int j = 0; j < N; ++j) {
values.push_back({A[i][j], i, j});
}
}
sort(values.begin(), values.end(), [](vector<int>& a, vector<int>& b) {return a[0] < b[0];});
unordered_set<int> visited;
visited.insert(0);
visited.insert(X - 1);
int res = min(A[0][0], A[M - 1][N - 1]);
while(find(0) != find(X - 1)) {
vector<int> cur = values.back(); values.pop_back();
visited.insert(cur[1] * N + cur[2]);
res = min(res, cur[0]);
for (auto& dir : dirs) {
int newx = cur[1] + dir[0];
int newy = cur[2] + dir[1];
if (newx >= 0 && newx < M && newy >= 0 && newy < N && visited.count(newx * N + newy)) {
uni(cur[1] * N + cur[2], newx * N + newy);
}
}
}
return res;
}
int find(int a) {
if (parent[a] == a)
return a;
return find(parent[a]);
}
void uni(int a, int b) {
int pa = find(a);
int pb = find(b);
if (pa == pb)
return;
parent[pa] = pb;
}
private:
vector<int> parent;
vector<vector<int>> dirs = {{0, 1}, {0, -1}, {-1, 0}, {1, 0}};
};
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 19 20 21 22 23 24 25 26 27 28 29 30 31 32 33 34 35 36 37 38 39 40 41 42 43 44 45 46 47 48 49 50
优先级队列
这个做法的思路应该更常规一点,是我想到的第一个解法,即从起点开始进行搜索,把其周围的所有点都放入大根堆中。遍历时,优先搜索值比较大的点,并把该点周围的所有点放入堆中,直至遇到了终点。
这个做法非常类似于Prim算法,Prim算法是从一个点开始,每次选择已访问过的所有点周围的没有访问过的点中距离最小的点。这个题反其道而行之,每次选择已访问过的所有点周围的没有访问过的点中值最大的点。
需要注意的是,会把每个点周围的所有点放入堆中,堆会进行排序,下次选择的仍然是到目前为止可以访问的值最大的点。举例说明:
[[6, 6, 0],
[3, 0, 0],
[3, 3, 3]]
起始时把[0,1]位置的6和[1,0]位置的3都放入堆中。
第一次会选择[0,1]位置的6,
但是由于其周围的全是0,0放入堆中排到了后面,
所以第二次访问的是[1,0]位置的3.
C++代码如下:
class Solution {
public:
int maximumMinimumPath(vector<vector<int>>& A) {
int R = A.size();
int C = A[0].size();
vector<vector<int> > visited(R, vector<int>(C, false));
visited[0][0] = true;
priority_queue<Point> pq;
pq.push(Point(0, 0, A[0][0]));
int res = min(A[0][0], A[R - 1][C - 1]);
while (!pq.empty()) {
Point p = pq.top();
pq.pop();
for (int i = 0; i < 4; ++i) {
int r = p.x + dirs[i][0];
int c = p.y + dirs[i][1];
if (r >= 0 && r < R && c >= 0 && c < C && !visited[r][c]) {
res = min(res, p.val);
if (r == R - 1 && c == C - 1) return res;
visited[r][c] = true;
pq.push(Point(r, c, A[r][c]));
}
}
}
return res;
}
private:
struct Point {
int x, y, val;
Point(int _x, int _y, int _val) : x(_x), y(_y), val(_val) {}
bool operator < (const Point& other) const {
return this->val < other.val;
}
};
int dirs[4][2] = {{-1, 0}, {1, 0}, {0, 1}, {0, -1}};
};
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 19 20 21 22 23 24 25 26 27 28 29 30 31 32 33 34 35 36 37 38
参考资料: https://leetcode-cn.com/problems/path-with-maximum-minimum-value/solution/pai-xu-bing-cha-ji-python3-by-smoon1989-2/ https://leetcode-cn.com/problems/path-with-maximum-minimum-value/solution/c-you-xian-dui-lie-by-da-li-wang-2/
2022
DDKK.COM 弟弟快看-教程,程序员编程资料站,版权归原作者所有
本文经作者:负雪明烛 授权发布,任何组织或个人未经作者授权不得转发