题目地址:https://leetcode.com/problems/find-the-duplicate-number/description/
题目描述
Given an array nums containing n + 1 integers where each integer is between 1 and n (inclusive), prove that at least one duplicate number must exist. Assume that there is only one duplicate number, find the duplicate one.
Example 1:
Input: [1,3,4,2,2]
Output: 2
Example 2:
Input: [3,1,3,4,2]
Output: 3
Note:
1、 Youmustnotmodifythearray(assumethearrayisreadonly).;
2、 Youmustuseonlyconstant,O(1)extraspace.;
3、 YourruntimecomplexityshouldbelessthanO(n2).;
4、 Thereisonlyoneduplicatenumberinthearray,butitcouldberepeatedmorethanonce.;
题目大意
有一个长度是N+1的数组,数字范围是1~N,其中有个数字出现了2次,其余数字都出现了1次。求出现2次的数字是多少。
解题方法
保存已经访问过的数字
最简单的方法就是保存已经访问过哪些数字了,当我们再次访问到这个数字的时候,就直接把这个数字返回即可。这个做法使用了额外的空间。
C++代码如下:
class Solution {
public:
int findDuplicate(vector<int>& nums) {
unordered_set<int> visited;
for (int num : nums) {
if (visited.count(num))
return num;
visited.insert(num);
}
return -1;
}
};
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12
链表成环
这个题简直是神题呀,本来很简单的题目,加了一堆条件,导致很难做,考的这个算法如果不去学习的话,是不可能会做的!
把这个题的数组抽象成了Linked List Cycle IIopen in new window题。道理是因为有重复数字,那么指针在移动的过程中一定会因为这个重复的数字反复的经过某一条路径。这个路径就是我们所谓的链表的环。如果抽象到这个层面就可以使用求环的算法解析了。
如图所示,两个指针同时从直线起点开始,这个圈是顺时针方向走的,即走的顺序是S-O-x-c-O-x。
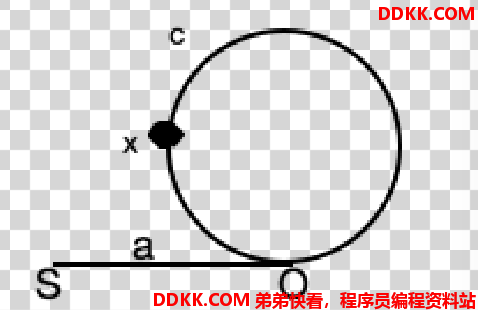
如果SO线段的长度a足够长,而圈很小的时候,当两者相遇时,快指针多走的可能不止一圈。下面要证明如果相遇之后,慢指针回到原点继续走再相遇的点在O点。
1、 首先要证明的是,两指针相遇时,慢指针还没有走完整个链表;
- 当慢指针没走完一圈时,显然成立
- 假设慢指针走完了一圈之后相遇,可以假定快指针在O的前一个位置,慢指针走一圈回到了O点,此时快指针走了两圈又回到了O的前一个位置,所以在慢指针走玩一圈之前就已经相遇。 2、 快慢指针在x处第一次汇合,xo之间距离为x,假如快指针走了n圈,快指针走过的路程为a+x+n*(c+x),慢指针走过的路程为a+x,所以a+x+n*(c+x)=2(a+x),所以a+x=n*(c+x),也就是SOx之间的距离等于n圈的长度,所以令快指针从起点开始一次一步,慢指针从x开始顺时针方向转,同时前进,则快指针走a时,慢指针走了n*(c+x)-x的长度,则必会在O处相遇!;
这个题中,一定有重复的数字,因此最少也得两个数字,故不用进行只有一个数字和是否有环的判断。
class Solution(object):
def findDuplicate(self, nums):
"""
:type nums: List[int]
:rtype: int
"""
slow = nums[0]
fast = nums[nums[0]]
while slow != fast:
fast = nums[nums[fast]]
slow = nums[slow]
fast = 0
while slow != fast:
fast = nums[fast]
slow = nums[slow]
return fast
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16
C++解法如下:
class Solution {
public:
int findDuplicate(vector<int>& nums) {
const int N = nums.size();
int slow = nums[0], fast = nums[nums[0]];
while (fast != slow) {
fast = nums[nums[fast]];
slow = nums[slow];
}
fast = 0;
while (fast != slow) {
fast = nums[fast];
slow = nums[slow];
}
return fast;
}
};
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17
二分查找
这个题还可以使用二分查找。
思路是我们在[1,N]范围内先求出mid,再统计小于等于mid的数字个数count,如果count<=mid,说明重复数字在[mid+1,N]中,否则在[1,mid)中。可能不明白为什么这么移动左右指针,所以,我做一下说明:
我们统计小于等于mid的数字个数count,当nums在[1,mid]双闭区间中的数字不存在重复时,count应该恰好等于mid;当nums在[1,mid]双闭区间中的数字存在重复时,count应该>mid;当nums在[1,mid]双闭区间中的数字存在遗漏时,count应该<mid。所以,当我们发现count <= mid时,说明重复数字在[mid + 1, N]中,否则在[1,mid)中。
class Solution {
public:
int findDuplicate(vector<int>& nums) {
const int N = nums.size();
int l = 0, r = N;
// [l, r)
while (l < r) {
int mid = l + (r - l) / 2;
int count = 0;
for (int n : nums){
if (n <= mid) {
count ++;
}
}
if (count <= mid)
l = mid + 1;
else
r = mid;
}
return r;
}
};
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 19 20 21 22
参考资料:
http://blog.csdn.net/monkeyduck/article/details/50439840 https://blog.csdn.net/l294265421/article/details/50478818
DDKK.COM 弟弟快看-教程,程序员编程资料站,版权归原作者所有
本文经作者:负雪明烛 授权发布,任何组织或个人未经作者授权不得转发