版本
基于rocketmq-all-4.3.1版本;
Remoting模块结构
1、remoting是RocketMQ的基础通信模块,阅读此模块的源码前提是对netty有一定的了解,以下是remoting模块的部分UML图;
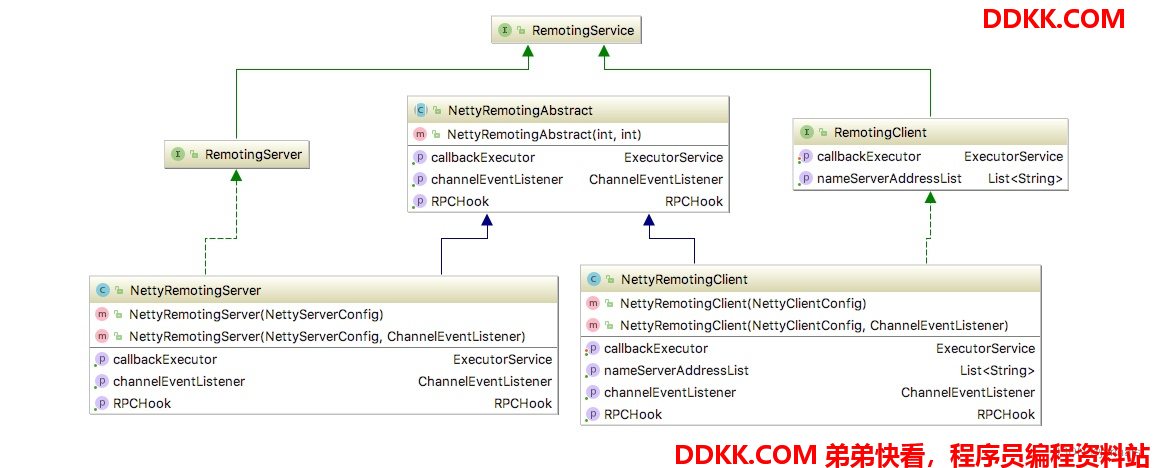
Server端关键类分析
1、NettyServerConfig:Server端配置类;
public class NettyServerConfig implements Cloneable {
private int listenPort = 8888;
private int serverWorkerThreads = 8;
private int serverCallbackExecutorThreads = 0;
private int serverSelectorThreads = 3;
private int serverOnewaySemaphoreValue = 256;
private int serverAsyncSemaphoreValue = 64;
private int serverChannelMaxIdleTimeSeconds = 120;
//发送缓冲区默认65535
private int serverSocketSndBufSize = NettySystemConfig.socketSndbufSize;
//接收缓冲区默认65535
private int serverSocketRcvBufSize = NettySystemConfig.socketRcvbufSize;
//是否使用ByteBuf内存池,netty默认使用PooledByteBufAllocator,服务端默认true
private boolean serverPooledByteBufAllocatorEnable = true;
/**
* make make install
* ../glibc-2.10.1/configure \ --prefix=/usr \ --with-headers=/usr/include \
* --host=x86_64-linux-gnu \ --build=x86_64-pc-linux-gnu \ --without-gd
*/
private boolean useEpollNativeSelector = false;
...省略getter和setter方法...
}
2、RemotingServer:此接口抽象出三种调用方式,同步调用、异步调用、单程调用(不需要返回),NettyRemotingServer是RemotingServer的实现类;
public interface RemotingServer extends RemotingService {
void registerProcessor(final int requestCode, final NettyRequestProcessor processor,
final ExecutorService executor);
void registerDefaultProcessor(final NettyRequestProcessor processor, final ExecutorService executor);
int localListenPort();
Pair<NettyRequestProcessor, ExecutorService> getProcessorPair(final int requestCode);
RemotingCommand invokeSync(final Channel channel, final RemotingCommand request,
final long timeoutMillis) throws InterruptedException, RemotingSendRequestException,
RemotingTimeoutException;
void invokeAsync(final Channel channel, final RemotingCommand request, final long timeoutMillis,
final InvokeCallback invokeCallback) throws InterruptedException,
RemotingTooMuchRequestException, RemotingTimeoutException, RemotingSendRequestException;
void invokeOneway(final Channel channel, final RemotingCommand request, final long timeoutMillis)
throws InterruptedException, RemotingTooMuchRequestException, RemotingTimeoutException,
RemotingSendRequestException;
}
3、NettyRemotingServer.NettyConnectManageHandler将Netty中的事件(Close、Connect、Exception、IDLE状态)封装为NettyEvent对象,并将NettyEvent对象添加到阻塞队列中,并通过异步线程(NettyEventExecutor)进行处理(异步线程在Server启动的时候会随之启动);
4、NettyRemotingServer.NettyServerHandler是仅仅处理业务数据,请求的业务数据会被封装为RemotingCommand对象,根据RemotingCommand对象中的code(RequestCode)来找到对应的处理器进行处理(处理器在对应的线程池中异步执行业务处理);
Client关键类分析
1、NettyClientConfig:client配置类;
public class NettyClientConfig {
/**
* Worker thread number
*/
private int clientWorkerThreads = 4;
private int clientCallbackExecutorThreads = Runtime.getRuntime().availableProcessors();
//用于控制同时单程调用的请求个数,默认65535,防止调用太快
private int clientOnewaySemaphoreValue = NettySystemConfig.CLIENT_ONEWAY_SEMAPHORE_VALUE;
//用于控制同时异步调用请求个数,默认65535
private int clientAsyncSemaphoreValue = NettySystemConfig.CLIENT_ASYNC_SEMAPHORE_VALUE;
//客户端连接超时时间
private int connectTimeoutMillis = 3000;
//在当前版本没有用到这个参数?难道是忘记了?
private long channelNotActiveInterval = 1000 * 60;
/**
* IdleStateEvent will be triggered when neither read nor write was performed for
* the specified period of this time. Specify {@code 0} to disable
*/
private int clientChannelMaxIdleTimeSeconds = 120;
//客户端发送缓冲区默认65535
private int clientSocketSndBufSize = NettySystemConfig.socketSndbufSize;
//客户端接收缓冲区默认65535
private int clientSocketRcvBufSize = NettySystemConfig.socketRcvbufSize;
//是否使用ByteBuf内存池,netty默认使用PooledByteBufAllocator,客户端默认false
private boolean clientPooledByteBufAllocatorEnable = false;
//客户端同步调用超时后是否关闭Socket,默认false
private boolean clientCloseSocketIfTimeout = false;
private boolean useTLS;
...省略getter和setter方法...
}
2、ResponseFuture:remoting模块的Future并没有实现任何接口(java或者Netty的Future接口),而是直接使用一个类,此类也没有完全符合Future接口规范,而是根据自身的场景来定制的长连接通信需要客户端发送一个请求Id(唯一标识)给服务端,服务端在响应之后需要将请求id返回给客户端,客户端通过响应的请求id可以知道是哪次请求数据的响应结果一般情况下消息队列都是基于长连接通信,RocketMQ中的请求Id名叫opaque,是一个AtomicInteger,从0开始,在RemotingCommand类中获取RabbitMQ-java-client中使用的是IntAllocator,当需要产生特别多的请求id时,使用IntAllocator比使用AtomicInteger效率要高;
public class ResponseFuture {
//请求携带的id,也是响应后返回的id
private final int opaque;
private final Channel processChannel;
//响应超时时间
private final long timeoutMillis;
//回调函数
private final InvokeCallback invokeCallback;
private final long beginTimestamp = System.currentTimeMillis();
private final CountDownLatch countDownLatch = new CountDownLatch(1);
//信号量封装,确保信号量只被释放一次
private final SemaphoreReleaseOnlyOnce once;
private final AtomicBoolean executeCallbackOnlyOnce = new AtomicBoolean(false);
private volatile RemotingCommand responseCommand;
private volatile boolean sendRequestOK = true;
private volatile Throwable cause;
public ResponseFuture(Channel channel, int opaque, long timeoutMillis, InvokeCallback invokeCallback,
SemaphoreReleaseOnlyOnce once) {
this.opaque = opaque;
this.processChannel = channel;
this.timeoutMillis = timeoutMillis;
this.invokeCallback = invokeCallback;
this.once = once;
}
public void executeInvokeCallback() {
if (invokeCallback != null) {
if (this.executeCallbackOnlyOnce.compareAndSet(false, true)) {
invokeCallback.operationComplete(this);
}
}
}
public void release() {
if (this.once != null) {
this.once.release();
}
}
public boolean isTimeout() {
long diff = System.currentTimeMillis() - this.beginTimestamp;
return diff > this.timeoutMillis;
}
public RemotingCommand waitResponse(final long timeoutMillis) throws InterruptedException {
this.countDownLatch.await(timeoutMillis, TimeUnit.MILLISECONDS);
return this.responseCommand;
}
//当响应数据返回时,countDownLatch释放,此时waitResponse不再阻塞
public void putResponse(final RemotingCommand responseCommand) {
this.responseCommand = responseCommand;
this.countDownLatch.countDown();
}
... 省略其他getter和setter方法...
}
3、NettyRemotingClient.NettyConnectManageHandler将Netty中的事件(Close、Connect、Exception、IDLE状态)封装为NettyEvent对象,并将NettyEvent对象添加到阻塞队列中,并通过异步线程(NettyEventExecutor)进行处理(异步线程在Client启动的时候会随之启动),这与Server端是一样的;
4、NettyRemotingClient.NettyClientHandler是仅仅处理业务数据,请求的业务数据会被封装为RemotingCommand对象,根据RemotingCommand对象中的code来找到对应的处理器进行处理(处理器在对应的线程池中异步执行业务处理),这与Server端是一样的;
NettyRemotingAbstract
1、 从UML图可以看出NettyRemotingAbstract是NettyRemotingServer和NettyRemotingClient的公用的抽象,NettyRemotingServer和NettyRemotingClient又分别实现自己的抽象接口主要的属性;
public abstract class NettyRemotingAbstract{
/**
* 限制单程请求的最大数量,保护系统内存占用
*/
protected final Semaphore semaphoreOneway;
/**
* 限制异步请求的最大数量,保护系统内存占用
*/
protected final Semaphore semaphoreAsync;
/**
* 保存请求id与响应Future之间的关系
*/
protected final ConcurrentMap<Integer /* opaque */, ResponseFuture> responseTable =
new ConcurrentHashMap<Integer, ResponseFuture>(256);
/**
* 请求code与请求处理器之间的关系
*/
protected final HashMap<Integer/* request code */, Pair<NettyRequestProcessor, ExecutorService>> processorTable =
new HashMap<Integer, Pair<NettyRequestProcessor, ExecutorService>>(64);
/**
*/
protected final NettyEventExecutor nettyEventExecutor = new NettyEventExecutor();
/**
* The default request processor to use in case there is no exact match in {@linkprocessorTable} per request code.
* 默认的请求处理器
*/
protected Pair<NettyRequestProcessor, ExecutorService> defaultRequestProcessor;
/**
* SSL context via which to create {@link SslHandler}.
*/
protected volatile SslContext sslContext;
...省略...
}
2、scanResponseTable:扫描所有的ResponseFuture,判断哪些是已经超时的,如果超时就移除掉,如果有单程调用的信号量也一并释放掉在client请求时会定期调用此方法扫描,避免因为超时导致内存占用以及相关资源得不到释放;
public void scanResponseTable() {
final List<ResponseFuture> rfList = new LinkedList<ResponseFuture>();
Iterator<Entry<Integer, ResponseFuture>> it = this.responseTable.entrySet().iterator();
while (it.hasNext()) {
Entry<Integer, ResponseFuture> next = it.next();
ResponseFuture rep = next.getValue();
if ((rep.getBeginTimestamp() + rep.getTimeoutMillis() + 1000) <= System.currentTimeMillis()) {
rep.release();
it.remove();
rfList.add(rep);
log.warn("remove timeout request, " + rep);
}
}
for (ResponseFuture rf : rfList) {
try {
executeInvokeCallback(rf);
} catch (Throwable e) {
log.warn("scanResponseTable, operationComplete Exception", e);
}
}
}
3、NettyRemotingAbstract.NettyEventExecutor:Netty事件执行器.当NettyHandler中的事件发生时(Close、Connect、Exception、IDLE等)会创建一个对应的NettyEvent,调用NettyEventExecutor的putNettyEvent方法将此事件添加到阻塞队列中,目前版本(rocketmq-all-4.3.1)阻塞队列在RocketMQ中是固定值10000,不可动态配置NettyRemotingAbstract.NettyEventExecutor在服务端或者客户端启动的时候启动,委托ChannelEventListener来进行相关事件的处理;
class NettyEventExecutor extends ServiceThread {
//使用阻塞队列存储NettyEvent,包括Close、Connect、Exception、IDLE
private final LinkedBlockingQueue<NettyEvent> eventQueue = new LinkedBlockingQueue<NettyEvent>();
private final int maxSize = 10000;
//事件队列大小不能根据参数调整,这里是10000
public void putNettyEvent(final NettyEvent event) {
if (this.eventQueue.size() <= maxSize) {
this.eventQueue.add(event);
} else {
log.warn("event queue size[{}] enough, so drop this event {}", this.eventQueue.size(), event.toString());
}
}
@Override
public void run() {
log.info(this.getServiceName() + " service started");
final ChannelEventListener listener = NettyRemotingAbstract.this.getChannelEventListener();
while (!this.isStopped()) {
try {
NettyEvent event = this.eventQueue.poll(3000, TimeUnit.MILLISECONDS);
if (event != null && listener != null) {
switch (event.getType()) {
case IDLE:
listener.onChannelIdle(event.getRemoteAddr(), event.getChannel());
break;
case CLOSE:
listener.onChannelClose(event.getRemoteAddr(), event.getChannel());
break;
case CONNECT:
listener.onChannelConnect(event.getRemoteAddr(), event.getChannel());
break;
case EXCEPTION:
listener.onChannelException(event.getRemoteAddr(), event.getChannel());
break;
default:
break;
}
}
} catch (Exception e) {
log.warn(this.getServiceName() + " service has exception. ", e);
}
}
log.info(this.getServiceName() + " service end");
}
@Override
public String getServiceName() {
return NettyEventExecutor.class.getSimpleName();
}
}
4、invokeSyncImpl同步调用,invokeAsyncImpl异步调用,invokeOnewayImpl单程调用三个方法的处理方式本质都是异步处理,代码大同小异;
public void invokeAsyncImpl(final Channel channel, final RemotingCommand request, final long timeoutMillis,
final InvokeCallback invokeCallback)
throws InterruptedException, RemotingTooMuchRequestException, RemotingTimeoutException, RemotingSendRequestException {
long beginStartTime = System.currentTimeMillis();
//获取请求Id
final int opaque = request.getOpaque();
//获取信号量
boolean acquired = this.semaphoreAsync.tryAcquire(timeoutMillis, TimeUnit.MILLISECONDS);
if (acquired) {
//SemaphoreReleaseOnlyOnce 封装信号量,保证信号量仅被释放一次
final SemaphoreReleaseOnlyOnce once = new SemaphoreReleaseOnlyOnce(this.semaphoreAsync);
long costTime = System.currentTimeMillis() - beginStartTime;
if (timeoutMillis < costTime) {
throw new RemotingTooMuchRequestException("invokeAsyncImpl call timeout");
}
//创建ResponseFuture并建立opaque和ResponseFuture之间的关联
final ResponseFuture responseFuture = new ResponseFuture(channel, opaque, timeoutMillis - costTime, invokeCallback, once);
this.responseTable.put(opaque, responseFuture);
try {
//发送数据,并异步监听响应结果
channel.writeAndFlush(request).addListener(new ChannelFutureListener() {
@Override
public void operationComplete(ChannelFuture f) throws Exception {
if (f.isSuccess()) {
responseFuture.setSendRequestOK(true);
return;
}
requestFail(opaque);
log.warn("send a request command to channel <{}> failed.", RemotingHelper.parseChannelRemoteAddr(channel));
}
});
} catch (Exception e) {
responseFuture.release();
log.warn("send a request command to channel <" + RemotingHelper.parseChannelRemoteAddr(channel) + "> Exception", e);
throw new RemotingSendRequestException(RemotingHelper.parseChannelRemoteAddr(channel), e);
}
} else {
if (timeoutMillis <= 0) {
throw new RemotingTooMuchRequestException("invokeAsyncImpl invoke too fast");
} else {
String info =
String.format("invokeAsyncImpl tryAcquire semaphore timeout, %dms, waiting thread nums: %d semaphoreAsyncValue: %d",
timeoutMillis,
this.semaphoreAsync.getQueueLength(),
this.semaphoreAsync.availablePermits()
);
log.warn(info);
throw new RemotingTimeoutException(info);
}
}
}
5、 客户端与服务端异步交互流程![ ][nbsp1];