在上两篇文章中我已经将 executor 包下的其他子包核心的功能以及对应源码的实现都讲解了。
而这篇文章将会迎来大家最为期待的的 Executor 的解析,已经坚持了那么久了,越到最后就越需要毅力。坚持到 80% 很多,但是真正坚持到最后的人可能就没几个人。
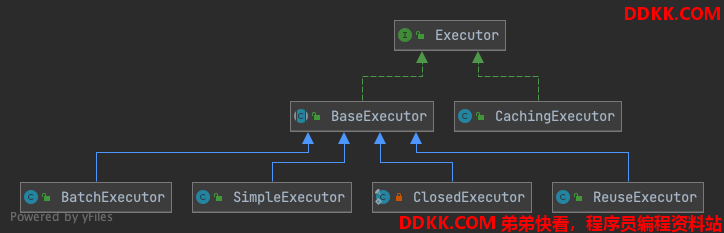
首先观察 Executor 体系,可以发现有不同的实现,并且通过实现的类名称我们已经能大概猜到它们的作用,不过还是需要深入到源码中去中去学习。
Executor
通过查看 Executor 可以发现其中定义了很多的抽象方法。我将这些抽象方法分为了几个大类。
1、 数据库操作相关;
1、 修改操作:update;
2、 返回List的查询操作:query;
3、 返回Cursor的查询操作:queryCursor;
4、 刷新语句:flushStatements;
2、 事务相关;
1、 获取事务:getTransaction;
2、 提交事务:commit;
3、 回滚事务:rollback;
3、 缓存相关;
1、 创建CacheKey:createCacheKey;
2、 本地缓存中是否缓存了语句的结果:isCached;
3、 清除本地缓存:clearLocalCache;
4、 设置执行器的包装类:setExecutorWrapper;
4、 执行期声明周期相关;
1、 关闭执行期:close;
2、 执行期是否被关闭:isClosed;
5、 其他;
1、 延迟加载:deferLoad;
BaseExecutor
它是Executor 的基类,应用了模板方法设计模式。它实现了很多公共方法,也在内部定义了一些抽象方法让子类去实现。由于方法比较多,我主要解析离我们最近的数据库操作相关的方法。
public abstract class BaseExecutor implements Executor {
@Override
public int update(MappedStatement ms, Object parameter) throws SQLException {
if (closed) {
throw new ExecutorException("Executor was closed.");
}
// 执行增删改操作前要清空本地缓存
clearLocalCache();
return doUpdate(ms, parameter);
}
@Override
public <E> List<E> query(MappedStatement ms, Object parameter, RowBounds rowBounds, ResultHandler resultHandler) throws SQLException {
// 构建 BoundSql
BoundSql boundSql = ms.getBoundSql(parameter);
// 构建 CacheKey
CacheKey key = createCacheKey(ms, parameter, rowBounds, boundSql);
return query(ms, parameter, rowBounds, resultHandler, key, boundSql);
}
@Override
public <E> List<E> query(MappedStatement ms, Object parameter, RowBounds rowBounds, ResultHandler resultHandler, CacheKey key, BoundSql boundSql) throws SQLException {
if (closed) {
throw new ExecutorException("Executor was closed.");
}
if (queryStack == 0 && ms.isFlushCacheRequired()) {
// 如果是一个新的查询并且需要清空缓存,则清空本地缓存
// 因为查询是会嵌套的,所以有一个 queryStack 变量
// 保证如果是一条语句没有完全执行结束的情况下是不会清空本地缓存的
clearLocalCache();
}
List<E> list;
try {
// 由于查询语句可能会递归执行,所以要知道当前递归的深度
queryStack++;
// 如果没有设置结果处理器,则可以从本地缓存(一级缓存)中读取结果
list = resultHandler == null ? (List<E>) localCache.getObject(key) : null;
if (list != null) {
// 从本地缓存中得到了结果
// 处理语句中的 OUT 参数
handleLocallyCachedOutputParameters(ms, key, parameter, boundSql);
} else {
// 没有从本地缓存中得到结果,从数据库中查询结果
list = queryFromDatabase(ms, parameter, rowBounds, resultHandler, key, boundSql);
}
} finally {
queryStack--;
}
private <E> List<E> queryFromDatabase(MappedStatement ms, Object parameter, RowBounds rowBounds, ResultHandler resultHandler, CacheKey key, BoundSql boundSql) throws SQLException {
List<E> list;
// 先在本地缓存中添加占位符
localCache.putObject(key, EXECUTION_PLACEHOLDER);
try {
// 执行查询
list = doQuery(ms, parameter, rowBounds, resultHandler, boundSql);
} finally {
// 去掉占位符
localCache.removeObject(key);
}
// 将查询结果放到一级缓存中
localCache.putObject(key, list);
if (ms.getStatementType() == StatementType.CALLABLE) {
// 如果语句类型为 Callable 还需要把 Output 参数缓存起来
localOutputParameterCache.putObject(key, parameter);
}
return list;
}
@Override
public <E> Cursor<E> queryCursor(MappedStatement ms, Object parameter, RowBounds rowBounds) throws SQLException {
BoundSql boundSql = ms.getBoundSql(parameter);
return doQueryCursor(ms, parameter, rowBounds, boundSql);
}
@Override
public List<BatchResult> flushStatements() throws SQLException {
return flushStatements(false);
}
public List<BatchResult> flushStatements(boolean isRollBack) throws SQLException {
if (closed) {
throw new ExecutorException("Executor was closed.");
}
return doFlushStatements(isRollBack);
}
}
可以发现在 update、query、queryCursor、flushStatements 中都调用了一个对应的声明的 doXXX 的抽象方法,将公共的代码提取到 BaseExecutor 中,而子类则负责具体的实现。
SimpleExecutor
简单执行器,即只有最基本的功能,本身没有其他的特性。
public class SimpleExecutor extends BaseExecutor {
@Override
public int doUpdate(MappedStatement ms, Object parameter) throws SQLException {
Statement stmt = null;
try {
Configuration configuration = ms.getConfiguration();
// 创建一个处理器
StatementHandler handler = configuration.newStatementHandler(this, ms, parameter, RowBounds.DEFAULT, null, null);
// 通过处理器得到对应的表达式
stmt = prepareStatement(handler, ms.getStatementLog());
// 执行更新操作
return handler.update(stmt);
} finally {
closeStatement(stmt);
}
}
@Override
public <E> List<E> doQuery(MappedStatement ms, Object parameter, RowBounds rowBounds, ResultHandler resultHandler, BoundSql boundSql) throws SQLException {
Statement stmt = null;
try {
Configuration configuration = ms.getConfiguration();
// 创建一个处理器
StatementHandler handler = configuration.newStatementHandler(wrapper, ms, parameter, rowBounds, resultHandler, boundSql);
// 通过处理器得到对应的表达式
stmt = prepareStatement(handler, ms.getStatementLog());
// 执行查询操作
return handler.query(stmt, resultHandler);
} finally {
closeStatement(stmt);
}
}
@Override
protected <E> Cursor<E> doQueryCursor(MappedStatement ms, Object parameter, RowBounds rowBounds, BoundSql boundSql) throws SQLException {
Configuration configuration = ms.getConfiguration();
// 创建一个处理器
StatementHandler handler = configuration.newStatementHandler(wrapper, ms, parameter, rowBounds, null, boundSql);
// 通过处理器得到对应的表达式
Statement stmt = prepareStatement(handler, ms.getStatementLog());
// 执行查询操作
Cursor<E> cursor = handler.queryCursor(stmt);
// 设置表达式自动关闭
stmt.closeOnCompletion();
return cursor;
}
@Override
public List<BatchResult> doFlushStatements(boolean isRollback) {
return Collections.emptyList();
}
private Statement prepareStatement(StatementHandler handler, Log statementLog) throws SQLException {
Statement stmt;
// 得到数据库连接
Connection connection = getConnection(statementLog);
// 得到表达式
stmt = handler.prepare(connection, transaction.getTimeout());
// 为表达式这设置值
// 1. 是为语句中的 ? 设置对应的值 (PrepareStatement、CallableStatement)
// 2. 注册 Output 参数 (CallableStatement)
handler.parameterize(stmt);
return stmt;
}
}
public class Configuration {
// 构建语句处理器
public StatementHandler newStatementHandler(Executor executor, MappedStatement mappedStatement, Object parameterObject, RowBounds rowBounds, ResultHandler resultHandler, BoundSql boundSql) {
// 构建出来的都是 RouterStatementHandler,但是在内部会选择具体的 StatementHandler
StatementHandler statementHandler = new RoutingStatementHandler(executor, mappedStatement, parameterObject, rowBounds, resultHandler, boundSql);
// 添加插件
statementHandler = (StatementHandler) interceptorChain.pluginAll(statementHandler);
return statementHandler;
}
}
ReuseExecutor
支持Statement 对象复用的执行器。其他的方法和 SimpleExecutor 类似的,唯一的区别就在于 doFlushStatements 和 prepareStatement 中的处理。
public class ReuseExecutor extends BaseExecutor {
// ...
@Override
public List<BatchResult> doFlushStatements(boolean isRollback) {
// 关闭所有暂存的语句
for (Statement stmt : statementMap.values()) {
closeStatement(stmt);
}
statementMap.clear();
return Collections.emptyList();
}
private Statement prepareStatement(StatementHandler handler, Log statementLog) throws SQLException {
Statement stmt;
BoundSql boundSql = handler.getBoundSql();
String sql = boundSql.getSql();
if (hasStatementFor(sql)) {
// 如果能通过 SQL 找到可用的语句
stmt = getStatement(sql);
applyTransactionTimeout(stmt);
} else {
// 如果不能找到
// 创建一个新的表达式,然后暂存起来
Connection connection = getConnection(statementLog);
stmt = handler.prepare(connection, transaction.getTimeout());
putStatement(sql, stmt);
}
// 设置参数的值
handler.parameterize(stmt);
return stmt;
}
// 是否暂存了 SQL 对应的语句声明
private boolean hasStatementFor(String sql) {
try {
// 通过 sql 语句找到对应的表达式
Statement statement = statementMap.get(sql);
// 如果表达式存在并且还可以被使用
return statement != null && !statement.getConnection().isClosed();
} catch (SQLException e) {
return false;
}
}
}
ClosedExecutor
它是一个特殊的执行器,可以认为是一个无效的执行器,等同于 ‘NULL’。内部的方法都会抛出异常,执行器的状态是已关闭状态。
private static final class ClosedExecutor extends BaseExecutor {
public ClosedExecutor() {
super(null, null);
}
@Override
public boolean isClosed() {
return true;
}
@Override
protected int doUpdate(MappedStatement ms, Object parameter) throws SQLException {
throw new UnsupportedOperationException("Not supported.");
}
@Override
protected List<BatchResult> doFlushStatements(boolean isRollback) throws SQLException {
throw new UnsupportedOperationException("Not supported.");
}
@Override
protected <E> List<E> doQuery(MappedStatement ms, Object parameter, RowBounds rowBounds, ResultHandler resultHandler, BoundSql boundSql) throws SQLException {
throw new UnsupportedOperationException("Not supported.");
}
@Override
protected <E> Cursor<E> doQueryCursor(MappedStatement ms, Object parameter, RowBounds rowBounds, BoundSql boundSql) throws SQLException {
throw new UnsupportedOperationException("Not supported.");
}
}
MyBatis 的一级缓存和二级缓存
MyBatis 的一级缓存
MyBatis 的一级缓存又叫本地缓存是由 BaseExecutor 实现的,是不能被关闭的,但是是可以对其进行配置的。
// BaseExecutor.java
// 查询操作的结果缓存
protected PerpetualCache localCache;
// Callable 查询的输出参数缓存
protected PerpetualCache localOutputParameterCache;
配置一:本地缓存的作用范围
- SESSION: 一次会话。(默认)
- STATEMENT: 一条语句。
配置二:在执行语句后是否清空本地缓存,通过设置 flushCache 属性实现,update 语句默认为 true。
<select id="selectById" resultType="User" flushCache="true">
...
</select>
MyBatis 的二级缓存
MyBatis 的二级缓存是由 CachingExecutor 包装类提供的
配置一:MyBatis 的二级缓存也是可配置的,并且它是可以被关闭的。
// mybatis-config.xml
// 配置二级缓存开启或关闭
<setting name="cacheEnable" value="true"/>
配置二:然后需要指定某一个命名空间的二级缓存开启,其中的属性我们在前面 cache 包其实已经讲过了,所以这里不再重复说明了。
// XXXMapper.xml
// 设置指定命名空间开启二级缓存
<cache type="PERPETUAL" eviction="LRU" flushInterval="60000" size="512" blocking="false" readOnly="true" />
配置三:也可以多个命名空间共用一个二级缓存。
// XXXMapper.xml
<cache-ref namespace="com.yinxy.demo.UserMapper"/>
注:只有在配置一开启了二级缓存的情况下,配置二和配置三才会生效。
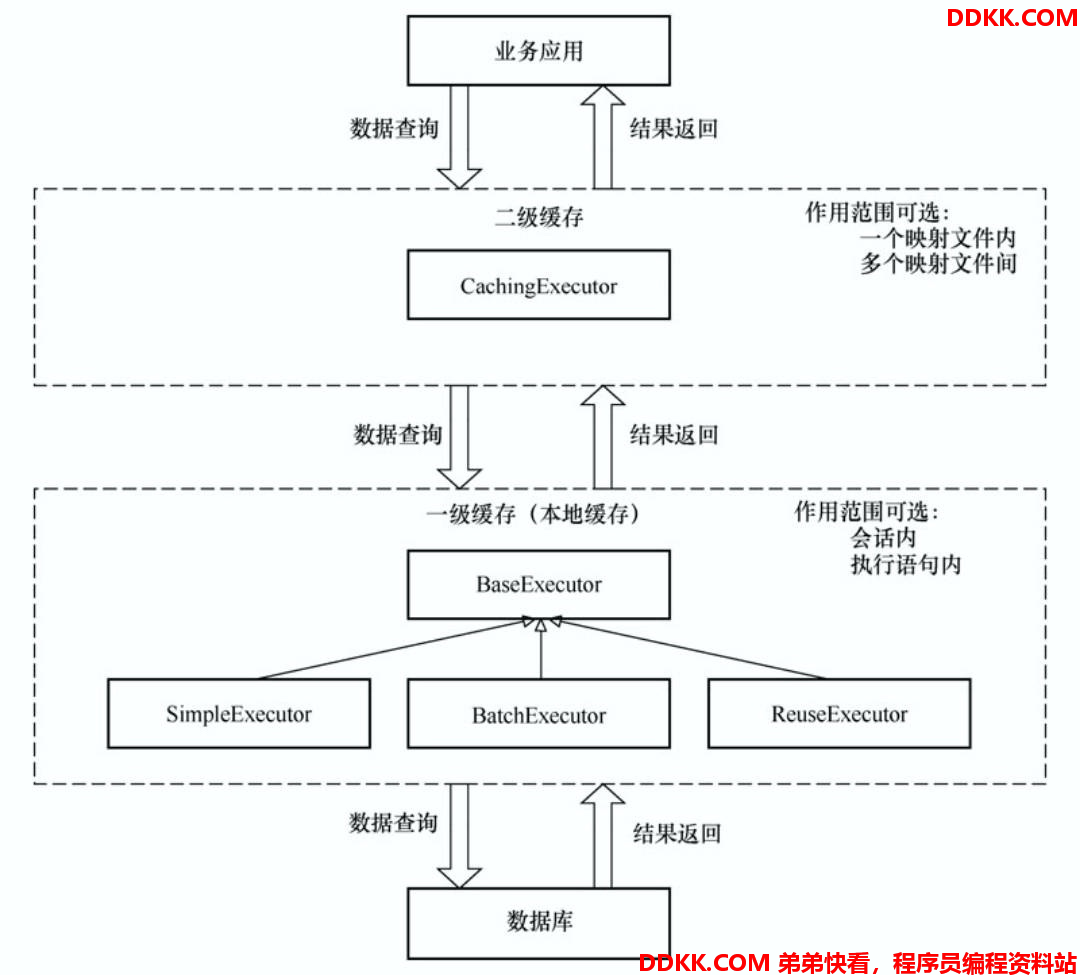
CachingExecutor
CachingExecutor 利用了装饰者模式,装饰的正是 Executor,而它的作用就是实现二级缓存。并且也引入了事务缓存管理器保证事务之间的隔离型。
public class CachingExecutor implements Executor {
// 被修饰的执行器,可以是 SimpleExecutor、ReuseExecutor
private final Executor delegate;
// 事务缓存管理器
private final TransactionalCacheManager tcm = new TransactionalCacheManager();
public CachingExecutor(Executor delegate) {
this.delegate = delegate;
// 保证被代理对象中的执行也需要使用 CachingExecutor
delegate.setExecutorWrapper(this);
}
@Override
public void close(boolean forceRollback) {
try {
if (forceRollback) {
// 在关闭连接时事务进行回滚
tcm.rollback();
} else {
// 在关闭连接时事务进行提交
tcm.commit();
}
} finally {
delegate.close(forceRollback);// 关闭连接的地方
}
}
@Override
public boolean isClosed() {
return delegate.isClosed();
}
@Override
public int update(MappedStatement ms, Object parameterObject) throws SQLException {
flushCacheIfRequired(ms);// 在执行语句前,如果需要清除缓存的话,会清除缓存
return delegate.update(ms, parameterObject);
}
@Override
public <E> Cursor<E> queryCursor(MappedStatement ms, Object parameter, RowBounds rowBounds) throws SQLException {
flushCacheIfRequired(ms);// 在执行语句前,如果需要清除缓存的话,会清除缓存
// 返回游标的这种形式是没有走二级缓存的
return delegate.queryCursor(ms, parameter, rowBounds);
}
@Override
public <E> List<E> query(MappedStatement ms, Object parameterObject, RowBounds rowBounds, ResultHandler resultHandler) throws SQLException {
BoundSql boundSql = ms.getBoundSql(parameterObject);
CacheKey key = createCacheKey(ms, parameterObject, rowBounds, boundSql);
return query(ms, parameterObject, rowBounds, resultHandler, key, boundSql);
}
@Override
public <E> List<E> query(MappedStatement ms, Object parameterObject, RowBounds rowBounds, ResultHandler resultHandler, CacheKey key, BoundSql boundSql)
throws SQLException {
Cache cache = ms.getCache();
if (cache != null) {
// 如果当前映射语句开启了二级缓存
flushCacheIfRequired(ms);
if (ms.isUseCache() && resultHandler == null) {
// 如果当前语句需要使用缓存,则会去二级缓存中查找
ensureNoOutParams(ms, boundSql);
@SuppressWarnings("unchecked")
List<E> list = (List<E>) tcm.getObject(cache, key);
if (list == null) {
// 如果二级缓存中没有,则会去一级缓存中拿,然后再放到二级缓存中
list = delegate.query(ms, parameterObject, rowBounds, resultHandler, key, boundSql);
tcm.putObject(cache, key, list);
}
return list;
}
}
return delegate.query(ms, parameterObject, rowBounds, resultHandler, key, boundSql);
}
@Override
public void commit(boolean required) throws SQLException {
delegate.commit(required);
tcm.commit();
}
@Override
public void rollback(boolean required) throws SQLException {
try {
delegate.rollback(required);
} finally {
if (required) {
tcm.rollback();
}
}
}
private void ensureNoOutParams(MappedStatement ms, BoundSql boundSql) {
if (ms.getStatementType() == StatementType.CALLABLE) {
for (ParameterMapping parameterMapping : boundSql.getParameterMappings()) {
if (parameterMapping.getMode() != ParameterMode.IN) {
throw new ExecutorException("");
}
}
}
}
private void flushCacheIfRequired(MappedStatement ms) {
Cache cache = ms.getCache();
if (cache != null && ms.isFlushCacheRequired()) {
tcm.clear(cache);
}
}
}
参考文献
1、 《通用源码阅读指导书:Mybatis源码阅读详解》——易哥;