EurekaClient启动流程分析
整体流程图
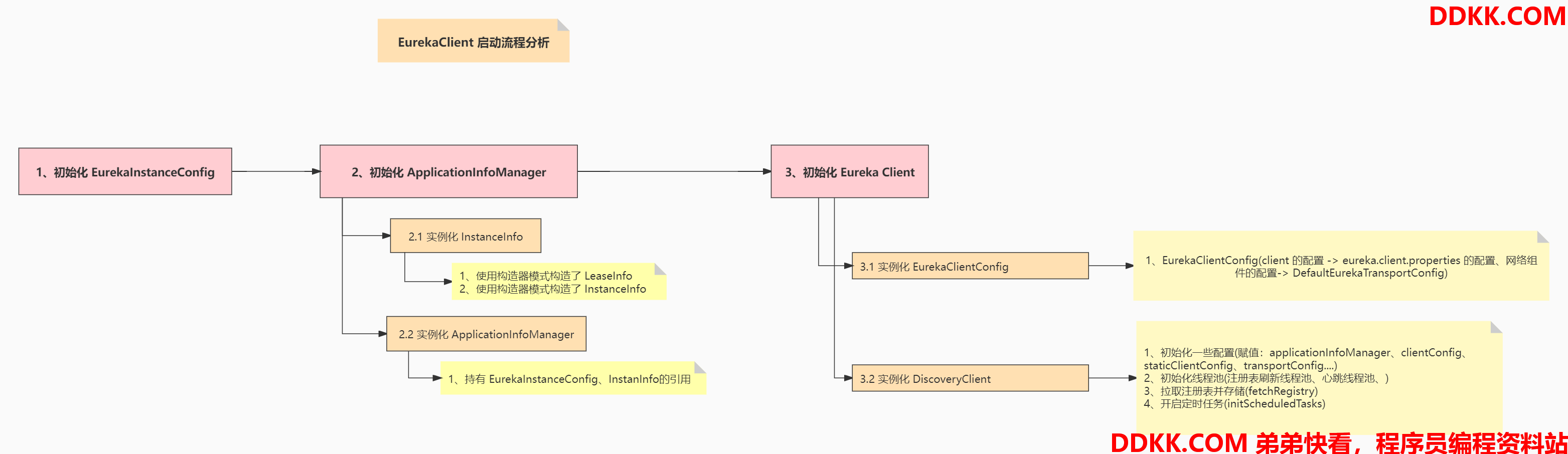
1、客户端启动源码解析
1.1、初始化线程池
// 可以看到就是使用 Executors 提供的静态方法去构造线程池,核心线程数是 2
// default size of 2 - 1 each for heartbeat and cacheRefresh
scheduler = Executors.newScheduledThreadPool(2,
new ThreadFactoryBuilder()
.setNameFormat("DiscoveryClient-%d")
.setDaemon(true)
.build());
// 自己构造线程池, coreSize 是 1, max 是5。队列使用的是 SynchronousQueue,其实是不具备队列能力的
// 下面是关于这个队列的说明。
// A blocking queue in which each insert operation must wait for a corresponding remove operation by another thread, and vice versa. A synchronous queue does not have any internal capacity, not even a capacity of one.
heartbeatExecutor = new ThreadPoolExecutor(
1, clientConfig.getHeartbeatExecutorThreadPoolSize(), 0, TimeUnit.SECONDS,
new SynchronousQueue<Runnable>(),
new ThreadFactoryBuilder()
.setNameFormat("DiscoveryClient-HeartbeatExecutor-%d")
.setDaemon(true)
.build()
); // use direct handoff
cacheRefreshExecutor = new ThreadPoolExecutor(
1, clientConfig.getCacheRefreshExecutorThreadPoolSize(), 0, TimeUnit.SECONDS,
new SynchronousQueue<Runnable>(),
new ThreadFactoryBuilder()
.setNameFormat("DiscoveryClient-CacheRefreshExecutor-%d")
.setDaemon(true)
.build()
); // use direct handoff
1.2、拉取注册表信息
1.2.1 fetchRegistry
// 如果shouldFetchRegistry 为真,则执行 fetchRegistry(false),如果返回 false,则从备份中拉取 fetchRegistryFromBackup()
if (clientConfig.shouldFetchRegistry() && !fetchRegistry(false)) {
fetchRegistryFromBackup();
}
// 拉取注册表
private boolean fetchRegistry(boolean forceFullRegistryFetch) {
Stopwatch tracer = FETCH_REGISTRY_TIMER.start();
try {
Applications applications = getApplications();
// 第 1 次注册的时候就会走这个分支
if (clientConfig.shouldDisableDelta()
|| (!Strings.isNullOrEmpty(clientConfig.getRegistryRefreshSingleVipAddress()))
|| forceFullRegistryFetch
|| (applications == null)
|| (applications.getRegisteredApplications().size() == 0)
|| (applications.getVersion() == -1)){
// 打印日志的去除了
//....
// 获取并存储注册表信息
getAndStoreFullRegistry();
} else {
// 后期会有定时任务去拉取增量信息,就会走到这里
getAndUpdateDelta(applications);
}
// 设置 hashCode,这里增量信息获取的时候会对比其中的 hashCode,然后如果不一致会去拉取全量注册表信息
applications.setAppsHashCode(applications.getReconcileHashCode());
// 打印实例日志
logTotalInstances();
} catch (Throwable e) {
logger.error(PREFIX + appPathIdentifier + " - was unable to refresh its cache! status = " + e.getMessage(), e);
return false;
} finally {
if (tracer != null) {
tracer.stop();
}
}
// 发布缓存 refresh 的事件
onCacheRefreshed();
// 更新实例状态,跟 last 对比,不一致则替换(内部维护了上一次的信息:InstanceInfo.InstanceStatus lastRemoteInstanceStatus)
updateInstanceRemoteStatus();
// registry was fetched successfully, so return true
return true;
}
1.2.2 getAndStoreFullRegistry(第 1 次注册调用方法)
private void getAndStoreFullRegistry() throws Throwable {
long currentUpdateGeneration = fetchRegistryGeneration.get();
Applications apps = null;
EurekaHttpResponse<Applications> httpResponse = clientConfig.getRegistryRefreshSingleVipAddress() == null
// 这里会去通过 EurekaTransport 组件发起网络请求去获取 registry 信息
// 其实就是通过 jersey 客户端然后最终调用 Resources 获取。这个具体的请求其实我们没必要过多关注,就是网络请求获取数据
// 最终是会去调用 com.netflix.eureka.resources.ApplicationResource#getApplication,然后注册表信息是有 2 级缓存维护的,后面我们会专门分析一下
? eurekaTransport.queryClient.getApplications(remoteRegionsRef.get())
: eurekaTransport.queryClient.getVip(clientConfig.getRegistryRefreshSingleVipAddress(), remoteRegionsRef.get());
if (httpResponse.getStatusCode() == Status.OK.getStatusCode()) {
apps = httpResponse.getEntity();
}
logger.info("The response status is {}", httpResponse.getStatusCode());
if (apps == null) {
logger.error("The application is null for some reason. Not storing this information");
} else if (fetchRegistryGeneration.compareAndSet(currentUpdateGeneration, currentUpdateGeneration + 1)) {
// cas 操作,成功则存储获取到的注册表信息
// 过滤并乱序排除实例信息,然后存储
localRegionApps.set(this.filterAndShuffle(apps));
logger.debug("Got full registry with apps hashcode {}", apps.getAppsHashCode());
} else {
logger.warn("Not updating applications as another thread is updating it already");
}
}
1.2.2.1 shuffleAndFilterInstances(过滤并乱序方法)
private void shuffleAndFilterInstances(
Map<String, AbstractQueue<InstanceInfo>> srcMap,
Map<String, AtomicReference<List<InstanceInfo>>> destMap,
Map<String, AtomicLong> vipIndexMap, boolean filterUpInstances) {
for (Map.Entry<String, AbstractQueue<InstanceInfo>> entries : srcMap.entrySet()) {
AbstractQueue<InstanceInfo> instanceInfoQueue = entries.getValue();
List<InstanceInfo> l = new ArrayList<InstanceInfo>(instanceInfoQueue);
if (filterUpInstances) {
Iterator<InstanceInfo> it = l.iterator();
// 过滤的话,可以看到其实就是对比 InstanceStatus,如果还是 UP,则移除掉
while (it.hasNext()) {
InstanceInfo instanceInfo = it.next();
if (!InstanceStatus.UP.equals(instanceInfo.getStatus())) {
it.remove();
}
}
}
// 然后这里调用 Collections 的 shuffle 方法去打乱集合中的元素
Collections.shuffle(l);
AtomicReference<List<InstanceInfo>> instanceInfoList = destMap.get(entries.getKey());
if (instanceInfoList == null) {
instanceInfoList = new AtomicReference<List<InstanceInfo>>(l);
destMap.put(entries.getKey(), instanceInfoList);
}
instanceInfoList.set(l);
vipIndexMap.put(entries.getKey(), new AtomicLong(0));
}
// 这里就是合并一下集合,取其交集
// finally remove all vips that are completed deleted (i.e. missing) from the srcSet
Set<String> srcVips = srcMap.keySet();
Set<String> destVips = destMap.keySet();
destVips.retainAll(srcVips);
}
1.2.3 getAndUpdateDelta(applications) 后期增量获取信息时调用
private void getAndUpdateDelta(Applications applications) throws Throwable {
long currentUpdateGeneration = fetchRegistryGeneration.get();
Applications delta = null;
// 这里其实就是调用不同的方法
// 会调用到 com.netflix.eureka.resources.ApplicationsResource#getContainerDifferential 获取
EurekaHttpResponse<Applications> httpResponse = eurekaTransport.queryClient.getDelta(remoteRegionsRef.get());
if (httpResponse.getStatusCode() == Status.OK.getStatusCode()) {
delta = httpResponse.getEntity();
}
//如果 delta 为空,则全量存储
if (delta == null) {
logger.warn("The server does not allow the delta revision to be applied because it is not safe. "
+ "Hence got the full registry.");
getAndStoreFullRegistry();
} else if (fetchRegistryGeneration.compareAndSet(currentUpdateGeneration, currentUpdateGeneration + 1)) {
//cas 操作成功
logger.debug("Got delta update with apps hashcode {}", delta.getAppsHashCode());
// 然后加锁,去更新 delta 信息,
String reconcileHashCode = "";
if (fetchRegistryUpdateLock.tryLock()) {
try {
// 基于 delta 信息和原有的信息去合并注册表
updateDelta(delta);
// 获取 applications 的 hashCode
reconcileHashCode = getReconcileHashCode(applications);
} finally {
fetchRegistryUpdateLock.unlock();
}
} else {
logger.warn("Cannot acquire update lock, aborting getAndUpdateDelta");
}
// There is a diff in number of instances for some reason
if (!reconcileHashCode.equals(delta.getAppsHashCode()) || clientConfig.shouldLogDeltaDiff()) {
// 对比 hashCode 打印不同的
reconcileAndLogDifference(delta, reconcileHashCode); // this makes a remoteCall
}
} else {
logger.warn("Not updating application delta as another thread is updating it already");
logger.debug("Ignoring delta update with apps hashcode {}, as another thread is updating it already", delta.getAppsHashCode());
}
}
1.2.3.1 updateDelta(更新增量信息)
private void updateDelta(Applications delta) {
int deltaCount = 0;
// 双层 for 循环
// 外层 增量的 Appllications -> List<Application>、内层 Instances -> List<InstanceInfo>
for (Application app : delta.getRegisteredApplications()) {
for (InstanceInfo instance : app.getInstances()) {
Applications applications = getApplications();
String instanceRegion = instanceRegionChecker.getInstanceRegion(instance);
if (!instanceRegionChecker.isLocalRegion(instanceRegion)) {
Applications remoteApps = remoteRegionVsApps.get(instanceRegion);
if (null == remoteApps) {
remoteApps = new Appl1ications();
remoteRegionVsApps.put(instanceRegion, remoteApps);
}
applications = remoteApps;
}
++deltaCount;
// 根据 ActionType 去做不同的操作 ADDED、MODIFIED、DELETED
if (ActionType.ADDED.equals(instance.getActionType())) {
Application existingApp = applications.getRegisteredApplications(instance.getAppName());
if (existingApp == null) {
applications.addApplication(app);
}
logger.debug("Added instance {} to the existing apps in region {}", instance.getId(), instanceRegion);
applications.getRegisteredApplications(instance.getAppName()).addInstance(instance);
} else if (ActionType.MODIFIED.equals(instance.getActionType())) {
Application existingApp = applications.getRegisteredApplications(instance.getAppName());
if (existingApp == null) {
applications.addApplication(app);
}
logger.debug("Modified instance {} to the existing apps ", instance.getId());
applications.getRegisteredApplications(instance.getAppName()).addInstance(instance);
} else if (ActionType.DELETED.equals(instance.getActionType())) {
Application existingApp = applications.getRegisteredApplications(instance.getAppName());
if (existingApp == null) {
applications.addApplication(app);
}
logger.debug("Deleted instance {} to the existing apps ", instance.getId());
// 从 application 中移除 Instance
applications.getRegisteredApplications(instance.getAppName()).removeInstance(instance);
}
}
}
logger.debug("The total number of instances fetched by the delta processor : {}", deltaCount);
getApplications().setVersion(delta.getVersion());
getApplications().shuffleInstances(clientConfig.shouldFilterOnlyUpInstances());
for (Applications applications : remoteRegionVsApps.values()) {
applications.setVersion(delta.getVersion());
applications.shuffleInstances(clientConfig.shouldFilterOnlyUpInstances());
}
}
2、注册逻辑
客户端启动的时候会去服务端注册,这个逻辑放到下一篇来分析
版权声明:「DDKK.COM 弟弟快看,程序员编程资料站」本站文章,版权归原作者所有