一、基本介绍
1、 NIO的通道类似于流,但有些区别;
1、通道可以同时进行读写,而流只能读或者只能写
2、通道可以实现异步读写数据
3、通道可以从缓冲读数据,也可以写数据到缓冲
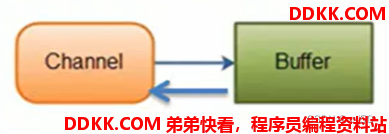
2、 BIO中的stream是单向的,例如FileInputStream对象只能进行读取数据的操作,而NIO中的通道(Channel)是双向的,可以读操作,也可以写操作;
3、 Channel在NIO中是一个接口;
public interface Channel extends Closeable
4、 常用的Channel类有:FileChannel、DatagramChannel、ServerSocketChannel(类似ServerSocket)、SocketChannel(类似Socket);
真实类型:
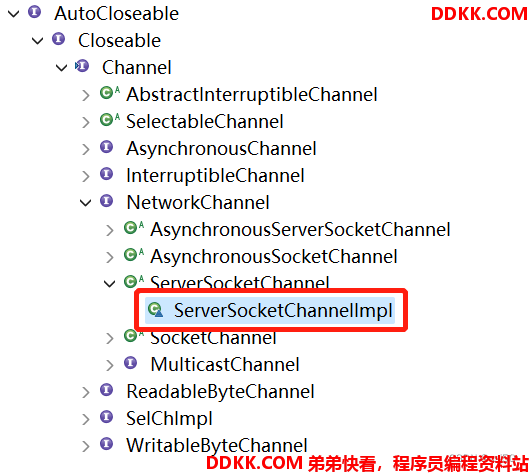
5、 FileChannel用于文件的数据读写,DatagramChannel用于UDP的数据读写,ServerSocketChannel和SocketChannel用于TCP的数据读写;
二、FileChannel类
FileChannel类主要用来对本地文件进行IO操作,常见方法有;
读和写是站在channel通道的角度
1、public abstract int read(ByteBuffer dst):从通道读取数据并放到缓冲区中
2、public abstract int write(ByteBuffer src):把缓冲区的数据写到通道中
3、public abstract long transferFrom(ReadableByteChannel src, long position, long count):从目标通道中复制数据到当前通道
4、public abstract long transferTo(long position, long count, WritableByteChannel target):把数据从当前通道复制给目标通道
三、案例1:本地文件写数据
1、 使用ByteBuffer(缓冲)和FileChannel(通道),将“hello,你好”写入到file01.txt中;
2、 文件不存在就创建;
3、 代码
![ ][nbsp2];
NIOFileChannel01.java
package netty.channel;
import java.io.FileOutputStream;
import java.nio.ByteBuffer;
import java.nio.channels.FileChannel;
public class NIOFileChannel01 {
public static void main(String[] args) throws Exception {
String str = "hello,你好";
//创建一个输出流->包装到channel中
FileOutputStream fileOutputStream = new FileOutputStream("d:\\file01.txt");
//通过fileOutputStream输出流获取对应的FileChannel
//这个fileChannel真实类型是FileChannelImpl
FileChannel fileChannel = fileOutputStream.getChannel();
//创建一个缓冲区ByteBuffer
ByteBuffer byteBuffer = ByteBuffer.allocate(1024);
//将str放入到byteBuffer中
byteBuffer.put(str.getBytes());
//对byteBuffer进行flip
byteBuffer.flip();
//将byteBuffer里的数据,写入到fileChannel
fileChannel.write(byteBuffer);
//关闭流
fileOutputStream.close();
}
}
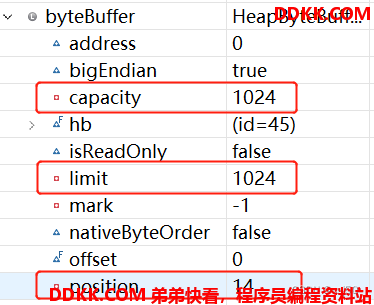
读写翻转前:
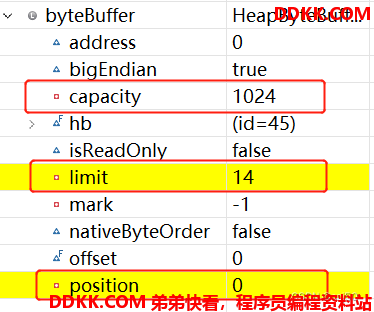
翻转后:
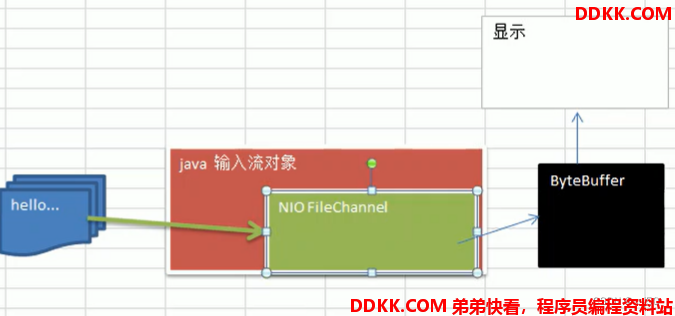
四、案例2:本地文件读数据
1、 使用ByteBuffer(缓冲)和FileChannel(通道),将file01.txt中的数据读入到程序,并显示在控制台屏幕;
2、 假定文件已经存在;
3、 代码;
NIOFileChannel02.java
package netty.channel;
import java.io.File;
import java.io.FileInputStream;
import java.nio.ByteBuffer;
import java.nio.channels.FileChannel;
public class NIOFileChannel02 {
public static void main(String[] args) throws Exception {
//创建文件的输入流
File file = new File("d:\\file01.txt");
FileInputStream fileInputStream = new FileInputStream(file);
//通过fileInputStream获取对应的FileChannel -> 实际类型FileChannelImpl
FileChannel fileChannel = fileInputStream.getChannel();
//创建缓冲区
ByteBuffer byteBuffer = ByteBuffer.allocate(1024);
//将通道的数据读入到byteBuffer中
fileChannel.read(byteBuffer);
//将byteBuffer的字节数据转成String
System.out.println(new String(byteBuffer.array())); //返回buffer中的字节数组hb
//关闭流
fileInputStream.close();
}
}
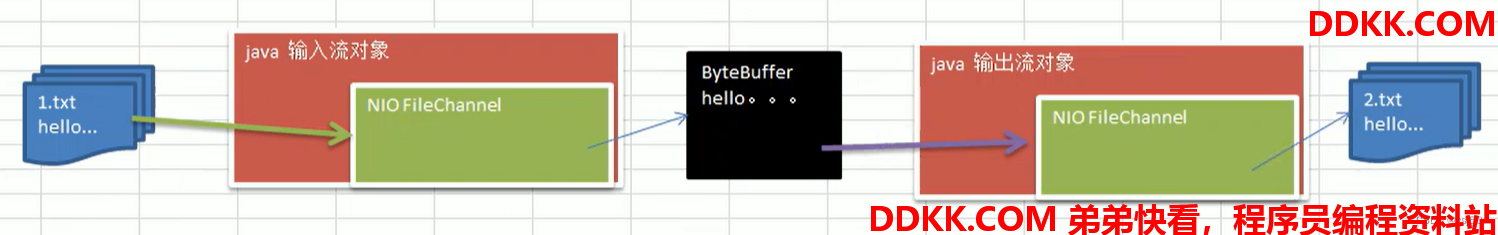
五、案例3:使用一个Buffer完成文件读取
1、 使用FileChannel(通道)和方法read、write,完成文件的拷贝;
2、 拷贝一个文本文件1.txt到2.txt,放在项目下即可;
3、 代码;
NIOFileChannel03.java
package netty.channel;
import java.io.FileInputStream;
import java.io.FileOutputStream;
import java.nio.ByteBuffer;
import java.nio.channels.FileChannel;
public class NIOFileChannel03 {
public static void main(String[] args) throws Exception {
//创建文件的输入流
FileInputStream fileInputStream = new FileInputStream("d:\\file01.txt");
//获取输入流对象的channel
FileChannel fileChannel01 = fileInputStream.getChannel();
//文件输出流对象
FileOutputStream fileOutputStream = new FileOutputStream("d:\\file02.txt");
//获取输入流对象的channel
FileChannel fileChannel02 = fileOutputStream.getChannel();
ByteBuffer byteBuffer = ByteBuffer.allocate(1024);
while(true) {
//读之前有个重要操作,一定不要忘了
byteBuffer.clear(); //复位:The position is set to zero, the limit is set to the capacity, and the mark is discarded
//循环读取
int read = fileChannel01.read(byteBuffer);
System.out.println("read = " + read);
if (read == -1) {
//表示读完
break;
}
//读写切换
byteBuffer.flip();
//将buffer中的数据写入到fileChannel02
fileChannel02.write(byteBuffer);
}
//关闭相关的流
fileInputStream.close();
fileOutputStream.close();
}
}
六、案例4:拷贝文件transferFrom方法
1、 使用FileChannel(通道)和方法transferFrom,完成文件的拷贝;
2、 拷贝一张图片;
3、 代码;
NIOFileChannel04.java
package netty.channel;
import java.io.FileInputStream;
import java.io.FileOutputStream;
import java.nio.channels.FileChannel;
public class NIOFileChannel04 {
public static void main(String[] args) throws Exception {
//创建输入流
FileInputStream fileInputStream = new FileInputStream("d:\\a.jpg");
//创建输出流
FileOutputStream fileOutputStream = new FileOutputStream("d:\\a2.jpg");
//获取各个流对应的fileChannel
FileChannel source = fileInputStream.getChannel();
FileChannel dest = fileOutputStream.getChannel();
//使用transferFrom完成拷贝
dest.transferFrom(source, 0, source.size());
//关闭通道和流
source.close();
dest.close();
fileInputStream.close();
fileOutputStream.close();
}
}
七、ServerSocketChannel类
1、 ServerSocketChannel在服务端监听新的客户端Socket连接;
2、 相关方法;
public static ServerSocketChannel open() throws IOException:得到一个ServerSocketChannel通道
public final ServerSocketChannel bind(SocketAddress local) throws IOException:设置服务器端端口号
public final SelectableChannel configureBlocking(boolean block) throws IOException:设置阻塞或非阻塞模式,取值false表示采用非阻塞模式
public SocketChannel accept() throws IOException:接受一个连接,返回代表这个连接的通道对象
public final SelectionKey register(Selector sel, int ops) throws ClosedChannelException:注册一个选择器并设置监听事件
3、 ServerSocketChannel和SocketChannel;
ServerSocketChannel继承自AbstractSelectableChannel

SocketChannel也继承自AbstractSelectableChannel
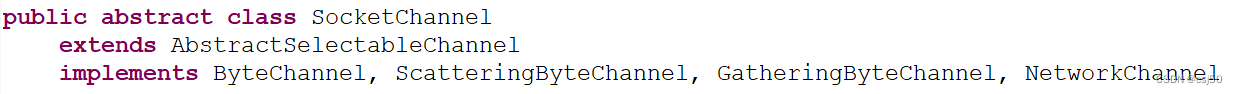
但是SocketChannel实现的接口更多,它更重要的功能是对数据的读和写
八、SocketChannel类
1、 SocketChannel,网络IO通道,具体负责进行读写操作,NIO把缓冲区的数据写入通道,或者把通道里的数据读到缓冲区;
2、 相关方法;
public static SocketChannel open() throws IOException:得到一个SocketChannel通道
public final SelectableChannel configureBlocking(boolean block) throws IOException:设置阻塞或非阻塞模式,取值false表示采用非阻塞模式
public abstract boolean connect(SocketAddress remote) throws IOException:连接服务器
public abstract boolean finishConnect() throws IOException:如果上面的方法连接失败,接下来就要通过该方法完成连接操作
public abstract int write(ByteBuffer src) throws IOException:往通道里写数据
public abstract int read(ByteBuffer dst) throws IOException:从通道里读数据
public final SelectionKey register(Selector sel, int ops, Object att) throws ClosedChannelException:注册一个选择器并设置监听事件,最后一个参数可以设置共享数据
public final void close() throws IOException:关闭通道