一、Nginx代理概述
1.什么是代理?
代理一词往往并不陌生, 该服务我们常常用到如(代理理财、代理租房、代理收货等等),如下图所示
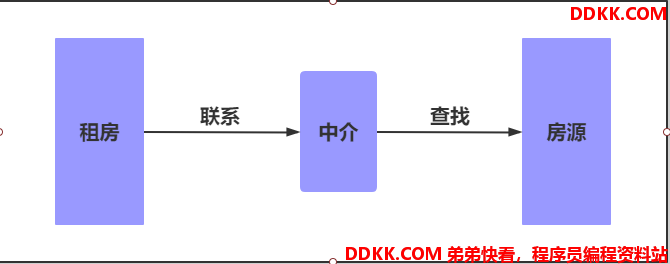
2.没有代理
在没有代理模式的情况下,客户端和Nginx服务端,都是客户端直接请求服务端,服务端直接响应客户端。

3.有代理
那么在互联网请求里面,客户端往往无法直接向服务端发起请求,那么就需要用到代理服务,来实现客户端和服务通信,如下图所示
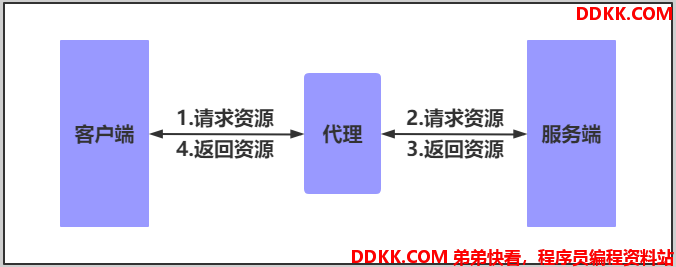
二、Nginx代理常见模式
1.常用模式
Nginx作为代理服务,按照应用场景模式进行总结,代理分为
1.正向代理
2.反向代理
2.正向代理
正向代理,(内部上网)客户端<—>代理->服务端
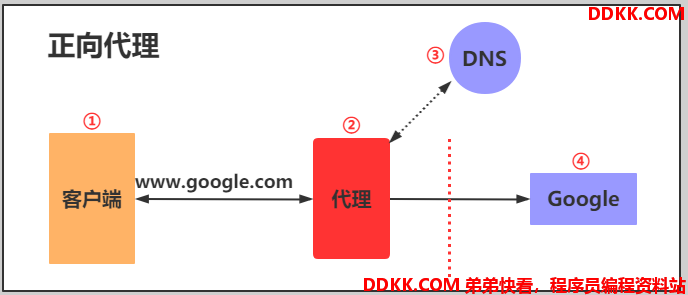
3.反向代理
反向代理,用于公司集群架构中,客户端->代理<—>服务端
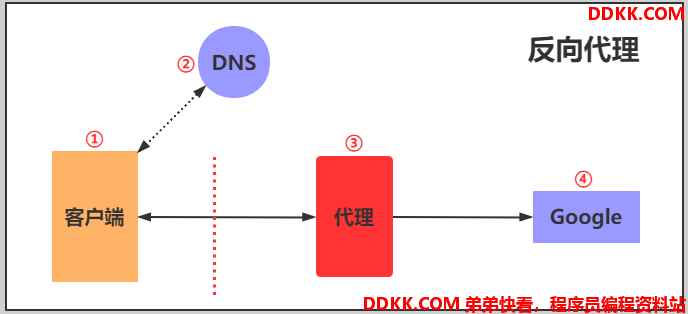
4.正向代理和反向代理的区别
1.区别在于形式上服务的"对象"不一样
2.正向代理代理的对象是客户端,为客户端服务
3.反向代理代理的对象是服务端,为服务端服务
三、Nginx代理服务支持协议
1.支持的协议
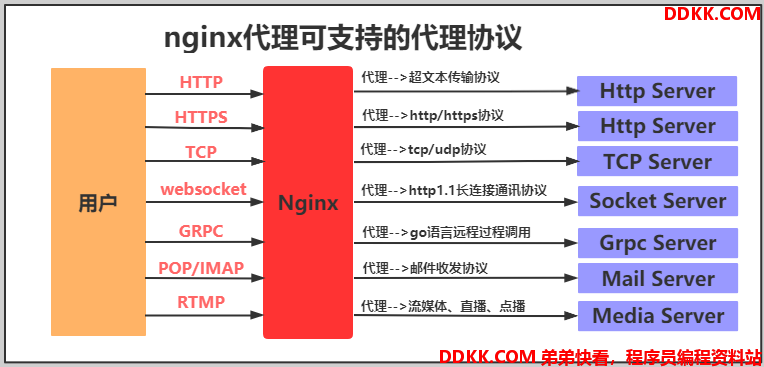
2.代理的模式
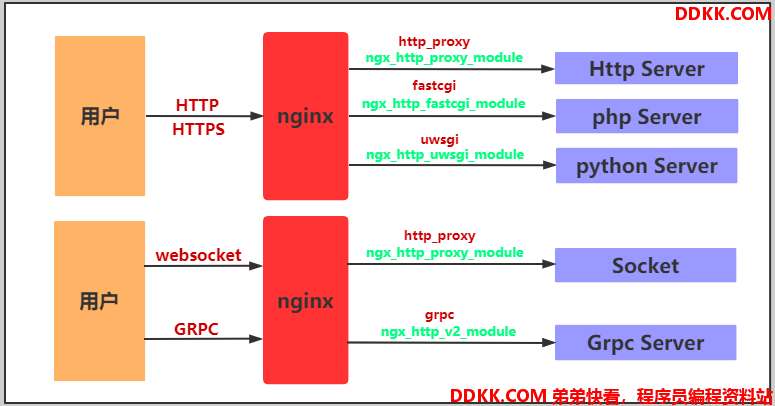
四、Nginx代理的模块
反向代理模式与Nginx代理模块总结如表格所示
| 反向代理模式 | Nginx配置模块 |
|---|---|
| http、websocket、https、tomcat(java程序) | ngx_http_proxy_module |
| fastcgi(PHP程序) | ngx_http_fastcgi_module |
| uwsgi(python程序) | ngx_http_uwsgi_module |
| grpc(go程序)(golang) | ngx_http_v2_module |
五、Nginx代理配置
1.代理语法
Syntax: proxy_pass URL;
Default: —
Context: location, if in location, limit_except
2.环境准备
| 主机 | IP | 身份 |
|---|---|---|
| lb01 | 10.0.0.4,172.16.1.4 | 代理 |
| web01 | 172.16.1.7 | 服务端 |
3.配置web01界面
[root@web01 ~]# vim /etc/nginx/conf.d/linux.proxy.com.conf
server {
listen 80;
server_name linux.proxy.com;
location / {
root /code/proxy;
index index.html;
}
}
[root@web01 ~]# systemctl restart nginx
4.编写网站
[root@web01 ~]# mkdir /code/proxy
[root@web01 ~]# vim /code/proxy/index.html
web01 .............
5.访问测试
#配置本地hosts
网页访问linux.proxy.com
6.配置代理
#安装nginx
#配置nginx
#创建用户
#配置站点配置文件
[root@lb01 ~]# vim /etc/nginx/conf.d/daili.conf
server {
listen 80;
server_name linux.proxy.com;
location / {
proxy_pass http://172.16.1.7:80;
proxy_pass http://10.0.0.7:80; #正常情况我们使用内网IP,抓包测试使用外网
}
}
[root@lb01 ~]# systemctl start nginx
7.访问页面测试
#访问http://linux.proxy.com/返回结果不是我们要的内容
原因:
代理请求后端时,没有使用域名,是使用IP访问的,匹配的配置文件是nginx中第一个配置文件
访问页面不是域名对应的页面,是web01上面nginx第一个配置文件
使用wireshark抓包分析
可以看出,当我们只用proxy_pass代理的时候,会发现如下问题:
10.0.0.1请求10.0.0.4的时候使用的是域名
10.0.0.4请求10.0.0.7的时候使用的是IP:port
之前课程中讲到,当访问80端口的时候,没有域名的情况下,默认会去找排在最上面的那个配置文件。
所以我们需要解决这个问题,保留住最开始的请求头部信息。
proxy_set_header,这个模块可以帮我们解决这个问题
8.配置携带域名去管理
[root@lb01 ~]# vim /etc/nginx/conf.d/daili.conf
server {
listen 80;
server_name linux.proxy.com;
location / {
proxy_pass http://10.0.0.7:80;
proxy_set_header Host $http_host;
}
}
六、nginx代理常用参数
1.添加访问后端服务器的请求头信息
Syntax: proxy_set_header field value;
Default: proxy_set_header Host $proxy_host;
proxy_set_header Connection close;
Context: http, server, location
# 用户请求的时候HOST的值是www.oldboy.com, 那么代理服务会像后端传递请求的还是www.oldboy.com
proxy_set_header Host $http_host;
# 将$remote_addr的值放进变量X-Real-IP中,$remote_addr的值为客户端的ip
proxy_set_header X-Real-IP $remote_addr;
# 客户端通过代理服务访问后端服务, 后端服务通过该变量会记录真实客户端地址
proxy_set_header X-Forwarded-For $proxy_add_x_forwarded_for;
2.代理到后端的TCP连接、响应、返回等超时时间
#nginx代理与后端服务器连接超时时间(代理连接超时)
Syntax: proxy_connect_timeout time;
Default: proxy_connect_timeout 60s;
Context: http, server, location
#nginx代理等待后端服务器的响应时间
Syntax: proxy_read_timeout time;
Default: proxy_read_timeout 60s;
Context: http, server, location
#后端服务器数据回传给nginx代理超时时间
Syntax: proxy_send_timeout time;
Default: proxy_send_timeout 60s;
Context: http, server, location
3.proxy_buffer代理缓冲区
#nignx会把后端返回的内容先放到缓冲区当中,然后再返回给客户端,边收边传, 不是全部接收完再传给客户端
Syntax: proxy_buffering on | off;
Default: proxy_buffering on;
Context: http, server, location
#设置nginx代理保存用户头信息的缓冲区大小
Syntax: proxy_buffer_size size;
Default: proxy_buffer_size 4k|8k;
Context: http, server, location
#proxy_buffers 缓冲区
Syntax: proxy_buffers number size;
Default: proxy_buffers 8 4k|8k;
Context: http, server, location
4.配置代理
[root@lb01 ~]# vim /etc/nginx/conf.d/daili.conf
server {
listen 80;
server_name linux.proxy.com;
location / {
proxy_pass http://10.0.0.7:80;
include /etc/nginx/proxy_params;
}
}
5.配置优化文件
[root@lb01 ~]# vim /etc/nginx/proxy_params
proxy_set_header Host $http_host;
proxy_set_header X-Real-IP $remote_addr;
proxy_set_header X-Forwarded-For $proxy_add_x_forwarded_for;
proxy_connect_timeout 30;
proxy_send_timeout 60;
proxy_read_timeout 60;
proxy_buffering on;
proxy_buffer_size 32k;
proxy_buffers 4 128k;
七、Nginx代理实战演练
1.需求
1.恢复快照
2.搭建两台LNMP
3.数据库独立
4.文件共享
5.文件实时备份
6.代理一台机器
2.环境准备
| 主机 | 角色 | IP |
|---|---|---|
| webo1 | ngixn服务器 | 10.0.0.7 |
| web02 | nginx服务器 | 10.0.0.8 |
| web03 | 代理服务器 | 10.0.0.9 |
| db01 | 数据库服务器 | 10.0.0.51 |
| nfs01 | 文件共享服务器 | 10.0.0.61 |
| backup | 备份服务器 | 10.0.0.41 |
3.web01服务配置
1)搭建nginx服务
1.配置官方源
[root@web01 ~]# vim /etc/yum.repos.d/nginx.repo
[nginx-stable]
name=nginx stable repo
baseurl=http://nginx.org/packages/centos/7/$basearch/
gpgcheck=1
enabled=1
gpgkey=https://nginx.org/keys/nginx_signing.key
module_hotfixes=true
2.安装依赖
[root@web01 ~]# yum install -y gcc gcc-c++ autoconf pcre pcre-devel make automake wget httpd-tools vim tree
3.安装nginx
[root@web01 ~]# yum -y install nginx
4.配置nginx
[root@web01 ~]# vim /etc/nginx/nginx.conf
user www;
client_max_body_size 200m;
5.创建统一用户
[root@web01 ~]# groupadd -g 666 www
[root@web01 ~]# useradd www -u 666 -g 666
6.检查配置
[root@web01 ~]# nginx -t
nginx: the configuration file /etc/nginx/nginx.conf syntax is ok
nginx: configuration file /etc/nginx/nginx.conf test is successful
7.启动服务并设置开机自启
[root@web01 ~]# systemctl start nginx
[root@web01 ~]# systemctl enable nginx
Created symlink from /etc/systemd/system/multi-user.target.wants/nginx.service to /usr/lib/systemd/system/nginx.service.
2)安装PHP
1.创建目录
[root@web01 /code]# mkdir /package
2.上传源码包并解压到指定文件夹
[root@web01 ~]# rz [root@web01 ~]# ll
-rw-r--r-- 1 root root 19889622 2020-08-30 14:01 php.tar.gz
[root@web01 ~]# tar xf php.tar.gz -C /package/
3.安装PHP
[root@web01 /package]# cd /package/
[root@web01 /package]# yum -y localinstall *.rpm
4.配置PHP
[root@web01 /package]# vim /etc/php-fpm.d/www.conf
user = www
group = www
[root@web01 /package]# vim /etc/php.ini
post_max_size = 200M
upload_max_filesize = 200M
4.启动PHP并设置开机自启
[root@web01 /package]# systemctl start php-fpm.service
[root@web01 /package]# systemctl enable php-fpm.service
Created symlink from /etc/systemd/system/multi-user.target.wants/php-fpm.service to /usr/lib/systemd/system/php-fpm.service.
3)配置本地数据库
1.安装数据库
[root@web01 /package]# yum -y install mariadb-server
2.启动服务并设置开机自启
[root@web01 /package]# systemctl start mariadb.service
[root@web01 /package]# systemctl enable mariadb.service
Created symlink from /etc/systemd/system/multi-user.target.wants/mariadb.service to /usr/lib/systemd/system/mariadb.service.
3.设置数据库密码
[root@web01 /package]# mysqladmin -u root password
New password:
Confirm new password:
4.验证密码
[root@web01 /package]# mysql -uroot -p
Enter password:
Welcome to the MariaDB monitor. Commands end with ; or \g.
Your MariaDB connection id is 4
Server version: 5.5.65-MariaDB MariaDB Server
Copyright (c) 2000, 2018, Oracle, MariaDB Corporation Ab and others.
Type 'help;' or '\h' for help. Type '\c' to clear the current input statement.
MariaDB [(none)]>
5.创建数据库
MariaDB [(none)]> show databases;
+--------------------+
| Database |
+--------------------+
| information_schema |
| mysql |
| performance_schema |
| test |
+--------------------+
4 rows in set (0.00 sec)
MariaDB [(none)]> create database zh;
Query OK, 1 row affected (0.00 sec)
MariaDB [(none)]> create database wordpress;
Query OK, 1 row affected (0.00 sec)
4)安装知乎、wordpress
1.配置知乎站点目录
[root@web01 ~]# vim /etc/nginx/conf.d/linux.zh.com.conf
server {
listen 80;
server_name linux.zh.com;
root /code/zh;
location / {
index index.php;
}
location ~* \.php$ {
fastcgi_pass 127.0.0.1:9000;
fastcgi_param SCRIPT_FILENAME $document_root$fastcgi_script_name;
include fastcgi_params;
}
}
2.配置wordpress站点目录
[root@web01 ~]# cp /etc/nginx/conf.d/linux.zh.com.conf /etc/nginx/conf.d/linux.wordpress.com.conf
[root@web01 ~]# vim /etc/nginx/conf.d/linux.wordpress.com.conf
server {
listen 80;
server_name linux.wordpress.com;
root /code/wordpress;
location / {
index index.php;
}
location ~* \.php$ {
fastcgi_pass 127.0.0.1:9000;
fastcgi_param SCRIPT_FILENAME $document_root$fastcgi_script_name;
include fastcgi_params;
}
}
3.创建目录
[root@web01 ~]# mkdir /code
4.上传源码包并解压
[root@m01 ~]# scp ./* root@172.16.1.7:/root
[root@web01 ~]# tar xf wordpress-5.0.3-zh_CN.tar.gz -C /code/
[root@web01 ~]# unzip WeCenter_3-2-1.zip -d /code/
[root@web01 /code]# cd /code
[root@web01 /code]# ll
total 4
drwxr-xr-x 5 1006 1006 4096 2019-01-11 18:00 wordpress
drwx------ 14 root root 296 2018-06-04 14:12 zh
5.授权目录
[root@web01 /code]# chown -R www:www /code/
6.检查配置并重启配置
[root@web01 /package]# nginx -t
nginx: the configuration file /etc/nginx/nginx.conf syntax is ok
nginx: configuration file /etc/nginx/nginx.conf test is successful
[root@web01 /package]# systemctl restart nginx
7.配置本地hosts文件
C:\Windows\System32\drivers\etc
10.0.0.7 linux.wordpress.com
10.0.0.7 linux.zh.com
4.web02服务配置
1)搭建nginx服务
1.配置官方源
[root@web02 ~]# vim /etc/yum.repos.d/nginx.repo
[nginx-stable]
name=nginx stable repo
baseurl=http://nginx.org/packages/centos/7/$basearch/
gpgcheck=1
enabled=1
gpgkey=https://nginx.org/keys/nginx_signing.key
module_hotfixes=true
2.安装依赖
[root@web02 ~]# yum install -y gcc gcc-c++ autoconf pcre pcre-devel make automake wget httpd-tools vim tree
3.安装nginx
[root@web02 ~]# yum -y install nginx
4.配置nginx
[root@web02 ~]# vim /etc/nginx/nginx.conf
user www;
client_max_body_size 200m;
4.创建统一用户
[root@web02 ~]# groupadd -g 666 www
[root@web02 ~]# useradd www -u 666 -g 666
5.检查配置
[root@web02 ~]# nginx -t
nginx: the configuration file /etc/nginx/nginx.conf syntax is ok
nginx: configuration file /etc/nginx/nginx.conf test is successful
6.启动服务并设置开机自启
[root@web02 ~]# systemctl start nginx
[root@web02 ~]# systemctl enable nginx
Created symlink from /etc/systemd/system/multi-user.target.wants/nginx.service to /usr/lib/systemd/system/nginx.service.
7.配置nginx站点目录
[root@web02 /package]# scp root@172.16.1.7:/etc/nginx/conf.d/* /etc/nginx/conf.d/
The authenticity of host '172.16.1.7 (172.16.1.7)' can't be established.
ECDSA key fingerprint is SHA256:g6buQ4QMSFl+5MMAh8dTCmLtkIfdT8sgRFYc6uCzV3c.
ECDSA key fingerprint is MD5:5f:d7:ad:07:e8:fe:d2:49:ec:79:2f:d4:91:59:c5:03.
Are you sure you want to continue connecting (yes/no)? yes
Warning: Permanently added '172.16.1.7' (ECDSA) to the list of known hosts
root@172.16.1.7's password:
linux.wordpress.com.conf 100% 282 185.9KB/s 00:00
linux.zh.com.conf 100% 268 78.3KB/s 00:00
8.检查服务并重启服务
[root@web02 /package]# nginx -t
nginx: the configuration file /etc/nginx/nginx.conf syntax is ok
nginx: configuration file /etc/nginx/nginx.conf test is successful
[root@web02 /package]# systemctl restart nginx
[root@web02 /package]#
[root@web02 /package]# systemctl restart nginx
9.创建目录
[root@web02 /package]# mkdir /code
10.授权目录
[root@web02 /package]# chown -R www:www /code/
11.推送web01站点文件
[root@web02 /package]# scp -r root@172.16.1.7:/code/* /code/
12.配置本地hosts
C:\Windows\System32\drivers\etc
10.0.0.8 linux.wordpress.com
10.0.0.8 linux.zh.com
2)安装PHP
1.创建目录
[root@web02 ~]# mkdir /package
2.上传源码包并解压到指定目录
[root@web02 ~]# ll
-rw-r--r-- 1 root root 19889622 2020-08-30 15:33 php.tar.gz
[root@web02 ~]# tar xf php.tar.gz -C /package/
3.安装PHP
[root@web02 ~]# cd /package/
[root@web02 /package]# yum -y localinstall *.rpm
4.配置php
[root@web02 /package]# vim /etc/php-fpm.d/www.conf
user = www
group = www
[root@web02 /package]# vim /etc/php.ini
post_max_size = 200M
upload_max_filesize = 200M
5.启动PHP并设置开机自启
[root@web02 /package]# systemctl start php-fpm.service
[root@web02 /package]# systemctl enable php-fpm.service
Created symlink from /etc/systemd/system/multi-user.target.wants/php-fpm.service to /usr/lib/systemd/system/php-fpm.service.
5.分离数据库
1)db01安装数据库
1.安装数据库
[root@db01 ~]# yum -y install mariadb-server.x86_64
2.启动数据库并设置开机自启
[root@db01 ~]# systemctl start mariadb.service
[root@db01 systemctl enable mariadb.servicevice
Created symlink from /etc/systemd/system/multi-user.target.wants/mariadb.service to /usr/lib/systemd/system/mariadb.service.
3.设置数据密码
[root@db01 ~]# mysqladmin -uroot password
New password:
Confirm new password:
4.验证密码
[root@db01 ~]# mysql -uroot -p
Enter password:
Welcome to the MariaDB monitor. Commands end with ; or \g.
Your MariaDB connection id is 3
Server version: 5.5.65-MariaDB MariaDB Server
Copyright (c) 2000, 2018, Oracle, MariaDB Corporation Ab and others.
Type 'help;' or '\h' for help. Type '\c' to clear the current input statement.
MariaDB [(none)]>
2)web01导出旧数据
1.导出web01数据
[root@web01 /code]# mysqldump -uroot -proot -B zh >/tmp/zh.sql
You have new mail in /var/spool/mail/root
[root@web01 /code]# mysqldump -uroot -proot -B wordpress >/tmp/wordpress.sql
2.推送web01数据
[root@web01 /code]# scp /tmp/zh.sql root@172.16.1.51:/tmp
The authenticity of host '172.16.1.51 (172.16.1.51)' can't be established.
ECDSA key fingerprint is SHA256:g6buQ4QMSFl+5MMAh8dTCmLtkIfdT8sgRFYc6uCzV3c.
ECDSA key fingerprint is MD5:5f:d7:ad:07:e8:fe:d2:49:ec:79:2f:d4:91:59:c5:03.
Are you sure you want to continue connecting (yes/no)? yes
Warning: Permanently added '172.16.1.51' (ECDSA) to the list of known hosts.
root@172.16.1.51's password:
zh.sql 100% 121KB 3.7MB/s 00:00
[root@web01 /code]# scp /tmp/wordpress.sql root@172.16.1.51:/tmp
root@172.16.1.51's password:
wordpress.sql 100% 868KB 7.9MB/s 00:00
[root@web01 /code]#
3.配置wordpresss连接数据库文件
[root@web01 /code]# vim /code/wordpress/wp-config.php
/** WordPress数据库的名称 */
define('DB_NAME', 'wordpress');
/** MySQL数据库用户名 */
define('DB_USER', 'wp');
/** MySQL数据库密码 */
define('DB_PASSWORD', 'wp123');
/** MySQL主机 */
define('DB_HOST', '172.16.1.51');
/** 创建数据表时默认的文字编码 */
define('DB_CHARSET', 'utf8mb4');
/** 数据库整理类型。如不确定请勿更改 */
define('DB_COLLATE', '');
4.配置知乎连接数据库文件
[root@web01 /code]# vim /code/zh/system/config/database.php
<?php
$config['charset'] = 'utf8';^M
$config['prefix'] = 'aws_';^M
$config['driver'] = 'MySQLi';^M
$config['master'] = array (
'charset' => 'utf8',
'host' => '172.16.1.51',
'username' => 'zh',
'password' => 'zh123',
'dbname' => 'zh',
);^M
$config['slave'] = false;^M
3)web02配置连接远程数据库
1.配置wordpresss连接数据库文件
[root@web01 /code]# vim /code/wordpress/wp-config.php
/** WordPress数据库的名称 */
define('DB_NAME', 'wordpress');
/** MySQL数据库用户名 */
define('DB_USER', 'wp');
/** MySQL数据库密码 */
define('DB_PASSWORD', 'wp123');
/** MySQL主机 */
define('DB_HOST', '172.16.1.51');
/** 创建数据表时默认的文字编码 */
define('DB_CHARSET', 'utf8mb4');
/** 数据库整理类型。如不确定请勿更改 */
define('DB_COLLATE', '');
2.配置知乎连接数据库文件
[root@web01 /code]# vim /code/zh/system/config/database.php
<?php
$config['charset'] = 'utf8';^M
$config['prefix'] = 'aws_';^M
$config['driver'] = 'MySQLi';^M
$config['master'] = array (
'charset' => 'utf8',
'host' => '172.16.1.51',
'username' => 'zh',
'password' => 'zh123',
'dbname' => 'zh',
);^M
$config['slave'] = false;^M
4)db01导入web01鸠数据
1.导入旧数据
[root@db01 ~]# mysql -uroot -p </tmp/zh.sql
Enter password:
[root@db01 ~]# mysql -uroot -p </tmp/wordpress.sql
Enter password:
2.检验数据库
[root@db01 ~]# mysql -uroot -p
Enter password:
Welcome to the MariaDB monitor. Commands end with ; or \g.
Your MariaDB connection id is 8
Server version: 5.5.65-MariaDB MariaDB Server
Copyright (c) 2000, 2018, Oracle, MariaDB Corporation Ab and others.
Type 'help;' or '\h' for help. Type '\c' to clear the current input statement.
MariaDB [(none)]> show databases;
+--------------------+
| Database |
+--------------------+
| information_schema |
| mysql |
| performance_schema |
| test |
| wordpress |
| zh |
+--------------------+
6 rows in set (0.00 sec)
3.数据库授权
MariaDB [(none)]> grant all on zh.* to zh@'172.16.1.%' identified by 'zh123';
Query OK, 0 rows affected (0.00 sec)
MariaDB [(none)]> grant all on wordpress.* to wp@'172.16.1.%' identified by 'wp123';
Query OK, 0 rows affected (0.00 sec)
4.刷新数据库
MariaDB [(none)]> flush privileges;
Query OK, 0 rows affected (0.00 sec)
5.页面刷新正常登陆
6.配置nfs文件共享
1)nfs服务器安装nfs
1.安装nfs
[root@nfs ~]# yum -y install rpcbind nfs-utils
2.配置nfs
[root@nfs ~]# vim /etc/exports
/data/zh 172.16.1.0/24(rw,sync,all_squash,anonuid=666,anongid=666)
/data/wp 172.16.1.0/24(rw,sync,all_squash,anonuid=666,anongid=666)
3.创建统一用户
[root@nfs ~]# groupadd www -g 666
[root@nfs ~]# useradd www -u 666 -g 666
4.创建目录
[root@nfs ~]# mkdir -p /data/zh
[root@nfs ~]# mkdir -p /data/wp
5.授权目录
[root@nfs ~]# chown -R www:www /data/
6.启动服务并设置开机重启
[root@nfs ~]# systemctl start nfs
[root@nfs ~]# systemctl enable nfs
Created symlink from /etc/systemd/system/multi-user.target.wants/nfs-server.service to /usr/lib/systemd/system/nfs-server.service.
7.检查配置
[root@nfs ~]# cat /var/lib/nfs/etab
/data/wp 172.16.1.0/24(rw,sync,wdelay,hide,nocrossmnt,secure,root_squash,all_squash,no_subtree_check,secure_locks,acl,no_pnfs,anonuid=666,anongid=666,sec=sys,rw,secure,root_squash,all_squash)
/data/zh 172.16.1.0/24(rw,sync,wdelay,hide,nocrossmnt,secure,root_squash,all_squash,no_subtree_check,secure_locks,acl,no_pnfs,anonuid=666,anongid=666,sec=sys,rw,secure,root_squash,all_squash)
2)web01配置nfs
1.安装nfs
[root@web01 ~]# yum -y install rpcbind nfs-utils
2.启动服务并设置开机自启
[root@web01 ~]# systemctl start nfs
[root@web01 ~]# systemctl start rpcbind
[root@web01 ~]# systemctl enable nfs rpcbind
Created symlink from /etc/systemd/system/multi-user.target.wants/nfs-server.service to /usr/lib/systemd/system/nfs-server.service.
3.查看挂载点
[root@web01 ~]# showmount -e 172.16.1.31
Export list for 172.16.1.31:
/data/wp 172.16.1.0/24
/data/zh 172.16.1.0/24
4.推送源数据到挂载目录
[root@web01 ~]# scp -r /code/zh/uploads/* root@172.16.1.31:/data/zh
The authenticity of host '172.16.1.31 (172.16.1.31)' can't be established.
ECDSA key fingerprint is SHA256:g6buQ4QMSFl+5MMAh8dTCmLtkIfdT8sgRFYc6uCzV3c.
ECDSA key fingerprint is MD5:5f:d7:ad:07:e8:fe:d2:49:ec:79:2f:d4:91:59:c5:03.
Are you sure you want to continue connecting (yes/no)? yes
Warning: Permanently added '172.16.1.31' (ECDSA) to the list of known hosts.
root@172.16.1.31's password:
ffa5e93370534a62abe7746195595d5a.jpg 100% 45KB 6.0MB/s 00:00
20017b35a334e6966cd8fa21524be378.jpg 100% 443KB 7.2MB/s 00:00
170x110_20017b35a334e6966cd8fa21524be378.jpg 100% 4044 1.6MB/s 00:00
90x90_20017b35a334e6966cd8fa21524be378.jpg
[root@web01 ~]# scp -r /code/wordpress/wp-content/uploads/* root@172.16.1.31:/data/wp
root@172.16.1.31's password:
231626-156769658639a9.jpg 100% 75KB 323.6KB/s 00:00
231626-156769658639a9-150x150.jpg 100% 3516 138.1KB/s 00:00
231626-156769658639a9-300x191.jpg 100% 7046 2.6MB/s 00:00
5.挂载目录
[root@web01 ~]# mount -t nfs 172.16.1.31:/data/zh /code/zh/uploads/
[root@web01 ~]# mount -t nfs 172.16.1.31:/data/wp /code/wordpress/wp-content/uploads/
6.查看是否挂载
[root@web01 ~]# df -h
Filesystem Size Used Avail Use% Mounted on
/dev/sda3 98G 2.1G 96G 3% /
devtmpfs 980M 0 980M 0% /dev
tmpfs 991M 0 991M 0% /dev/shm
tmpfs 991M 9.6M 981M 1% /run
tmpfs 991M 0 991M 0% /sys/fs/cgroup
/dev/sda1 497M 120M 378M 25% /boot
tmpfs 199M 0 199M 0% /run/user/0
172.16.1.31:/data/zh 98G 1.7G 96G 2% /code/zh/uploads
172.16.1.31:/data/wp 98G 1.7G 96G 2% /code/wordpress/wp-content/uploads
2)web02配置nfs
1.安装nfs
[root@web02 ~]# yum -y install rpcbind nfs-utils
2.启动服务并设置开机自启
[root@web02 ~]# systemctl start rpcbind nfs-utils
[root@web02 ~]# systemctl enable rpcbind nfs-utils
3.查看挂载点
[root@web02 ~]# showmount -e 172.16.1.31
Export list for 172.16.1.31:
/data/wp 172.16.1.0/24
/data/zh 172.16.1.0/24
4.推送源数据到挂载目录
[root@web02 ~]# scp -r /code/zh/uploads/* root@172.16.1.31:/data/zh
The authenticity of host '172.16.1.31 (172.16.1.31)' can't be established.
ECDSA key fingerprint is SHA256:g6buQ4QMSFl+5MMAh8dTCmLtkIfdT8sgRFYc6uCzV3c.
ECDSA key fingerprint is MD5:5f:d7:ad:07:e8:fe:d2:49:ec:79:2f:d4:91:59:c5:03.
Are you sure you want to continue connecting (yes/no)? yes
Warning: Permanently added '172.16.1.31' (ECDSA) to the list of known hosts.
root@172.16.1.31's password:
ffa5e93370534a62abe7746195595d5a.jpg 100% 45KB 6.1MB/s 00:00
20017b35a334e6966cd8fa21524be378.jpg 100% 443KB 19.8MB/s 00:00
170x110_20017b35a334e6966cd8fa21524be378.jpg 100% 4044 2.9MB/s 00:00
90x90_20017b35a334e6966cd8fa21524be378.jpg 100% 2554 1.7MB/s 00:00
[root@web02 ~]#
[root@web02 ~]# scp -r /code/wordpress/wp-content/uploads/* root@172.16.1.31:/data/wp
root@172.16.1.31's password:
231626-156769658639a9.jpg 100% 75KB 9.5MB/s 00:00
231626-156769658639a9-150x150.jpg 100% 3516 1.8MB/s 00:00
231626-156769658639a9-300x191.jpg 100% 7046 993.6KB/s 00:00
174855-1497088135bff2.jpg 100% 443KB 20.9MB/s 00:00
174855-1497088135bff2-150x150.jpg 100% 3511 1.0MB/s 00:00
174855-1497088135bff2-300x169.jpg 100% 5825 1.5MB/s 00:00
5.挂载目录
[root@web02 ~]# mount -t nfs 172.16.1.31:/data/zh /code/zh/uploads/
[root@web02 ~]# mount -t nfs 172.16.1.31:/data/wp /code/wordpress/wp-content/uploads/
6.查看是否挂载
[root@web02 ~]# df -h
Filesystem Size Used Avail Use% Mounted on
/dev/sda3 98G 1.9G 96G 2% /
devtmpfs 980M 0 980M 0% /dev
tmpfs 991M 0 991M 0% /dev/shm
tmpfs 991M 9.6M 981M 1% /run
tmpfs 991M 0 991M 0% /sys/fs/cgroup
/dev/sda1 497M 120M 378M 25% /boot
tmpfs 199M 0 199M 0% /run/user/0
172.16.1.31:/data/zh 98G 1.7G 96G 2% /code/zh/uploads
172.16.1.31:/data/wp 98G 1.7G 96G 2% /code/wordpress/wp-content/uploads
7.实现文件实时备份
1)backup服务端配置
1.安装rsync
[root@backup ~]# yum -y install rsync
2.配置rsync
[root@backup ~]# vim /etc/rsyncd.conf
uid = www
gid = www
port = 873
fake super = yes
use chroot = no
max connections =200
timeout = 600
ignore errors
read only =false
list = true
auth users = rsync_backup
secrets file = /etc/rsync.passwd
log file = /var/log/rsyncd.log
#####################################
[data]
comment = "数据备份目录"
path = /data
3.创建统一用户
[root@backup ~]# groupadd www -g 666
[root@backup ~]# useradd www -u 666 -g 666
4.创建目录并授权
[root@backup ~]# mkdir /data
[root@backup ~]# chown -R www:www /data/
5.创建密码文件并修改权限
[root@backup ~]# echo "rsync_backup:123456" >/etc/rsync.passwd
[root@backup ~]# chmod 600 /etc/rsync.passwd
6.启动服务并设置开机自启
[root@backup ~]# systemctl start rsyncd
[root@backup ~]# systemctl enable rsyncd
Created symlink from /etc/systemd/system/multi-user.target.wants/rsyncd.service to /usr/lib/systemd/system/rsyncd.service.
7.检查服务
[root@backup ~]# netstat -lntp
Active Internet connections (only servers)
Proto Recv-Q Send-Q Local Address Foreign Address State PID/Program name
tcp 0 0 0.0.0.0:873 0.0.0.0:* LISTEN 29190/rsync
tcp 0 0 0.0.0.0:111 0.0.0.0:* LISTEN 6135/rpcbind
tcp 0 0 0.0.0.0:22 0.0.0.0:* LISTEN 7151/sshd
tcp 0 0 127.0.0.1:25 0.0.0.0:* LISTEN 7291/master
tcp6 0 0 :::873 :::* LISTEN 29190/rsync
tcp6 0 0 :::111 :::* LISTEN 6135/rpcbind
tcp6 0 0 :::22 :::* LISTEN 7151/sshd
tcp6 0 0 ::1:25 :::* LISTEN 7291/master
2)nfs客户端配置
1.安装rsync和inotify
[root@nfs ~]# yum install rsync inotify-tools -y
2.上传源码包
[root@m01 ~]# scp sersync2.5.4_64bit_binary_stable_final.tar.gz root@172.16.1.31:/root
sersync2.5.4_64bit_binary_stable_final.tar.gz 100% 710KB 18.9MB/s 00:00
3.解压安装包
[root@nfs ~]# tar xf sersync2.5.4_64bit_binary_stable_final.tar.gz
4.移动并重名
[root@nfs ~]# mv GNU-Linux-x86/ /usr/local/sersync
5.修改配置文件
[root@nfs ~]# vim /usr/local/sersync/confxml.xml
<?xml version="1.0" encoding="ISO-8859-1"?>
<head version="2.5">
<host hostip="localhost" port="8008"></host>
<debug start="false"/>
<fileSystem xfs="false"/>
<filter start="false">
<exclude expression="(.*)\.svn"></exclude>
<exclude expression="(.*)\.gz"></exclude>
<exclude expression="^info/*"></exclude>
<exclude expression="^static/*"></exclude>
</filter>
<inotify>
<delete start="true"/>
<createFolder start="true"/>
<createFile start="true"/>
<closeWrite start="true"/>
<moveFrom start="true"/>
<moveTo start="true"/>
<attrib start="true"/>
<modify start="true"/>
</inotify>
<sersync>
<localpath watch="/data">
<remote ip="172.16.1.41" name="data"/>
</localpath>
<rsync>
<commonParams params="-artuz"/>
<auth start="true" users="rsync_backup" passwordfile="/etc/rsync.password"/>
<userDefinedPort start="false" port="874"/><!-- port=874 -->
<timeout start="false" time="100"/><!-- timeout=100 -->
<ssh start="false"/>
6.创建密码文件并修改权限
[root@nfs ~]# echo "123456" >/etc/rsync.password
[root@nfs ~]# chmod 600 /etc/rsync.password
7.启动服务实现数据实时备份
[root@nfs ~]# /usr/local/sersync/sersync2 -dro /usr/local/sersync/confxml.xml
set the system param
execute:echo 50000000 > /proc/sys/fs/inotify/max_user_watches
execute:echo 327679 > /proc/sys/fs/inotify/max_queued_events
parse the command param
option: -d run as a daemon
option: -r rsync all the local files to the remote servers before the sersync work
option: -o config xml name: /usr/local/sersync/confxml.xml
daemon thread num: 10
parse xml config file
host ip : localhost host port: 8008
will ignore the inotify createFile event
daemon start,sersync run behind the console
use rsync password-file :
user is rsync_backup
passwordfile is /etc/rsync.password
config xml parse success
please set /etc/rsyncd.conf max connections=0 Manually
sersync working thread 12 = 1(primary thread) + 1(fail retry thread) + 10(daemon sub threads)
Max threads numbers is: 22 = 12(Thread pool nums) + 10(Sub threads)
please according your cpu ,use -n param to adjust the cpu rate
------------------------------------------
rsync the directory recursivly to the remote servers once
working please wait...
execute command: cd /data && rsync -artuz -R --delete ./ rsync_backup@172.16.1.41::data --password-file=/etc/rsync.password >/dev/null 2>&1
run the sersync:
watch path is: /data
8.实现web01代理
1)web01相关配置
1.配置nginx站点目录
[root@web01 ~]# vim /etc/nginx/conf.d/linux.proxy.com.conf
server {
listen 80;
server_name linux.proxy.com;
location / {
root /code/proxy;
index index.html;
}
}
2.检查配置并重启服务
[root@web01 ~]# nginx -t
nginx: the configuration file /etc/nginx/nginx.conf syntax is ok
nginx: configuration file /etc/nginx/nginx.conf test is successful
[root@web01 ~]# systemctl restart nginx
3.创建index文件
[root@web01 ~]# cd /code/
[root@web01 /code]#
[root@web01 /code]#
[root@web01 /code]# mkdir /code/proxy
[root@web01 /code]# vim /code/proxy/index.html
检查配置并重启服务
nginx -t
nginx: the configuration file /etc/nginx/nginx.conf syntax is ok
nginx: configuration file /etc/nginx/nginx.conf test is successful
ystemctl restart nginx
4.配置本地hosts
C:\Windows\System32\drivers\etc
10.0.0.7 linux.proxy.com
2)web03配置代理
1.配置官方源
[root@web03 ~]# vim /etc/yum.repos.d/nginx.repo
[nginx-stable]
name=nginx stable repo
baseurl=http://nginx.org/packages/centos/7/$basearch/
gpgcheck=1
enabled=1
gpgkey=https://nginx.org/keys/nginx_signing.key
module_hotfixes=true
2.安装依赖
[root@web03 ~]# yum install -y gcc gcc-c++ autoconf pcre pcre-devel make automake wget httpd-tools vim tree
3.安装nginx
[root@web03 ~]# yum -y install nginx
4.配置nginx
[root@web03 ~]# vim /etc/nginx/nginx.conf
user www;
5.创建统一用户
[root@web03 ~]# groupadd -g 666 www
[root@web03 ~]# useradd www -u 666 -g 666
6.配置nginx代理站点文件
[root@web03 ~]# vim /etc/nginx/conf.d/daili.conf
server {
listen 80;
server_name linux.proxy.com;
location / {
proxy_pass http://172.16.1.7:80;
proxy_pass http://10.0.0.7:80;
proxy_set_header Host $http_host;
}
}
7.检查配置
[root@web03 ~]# nginx -t
nginx: the configuration file /etc/nginx/nginx.conf syntax is ok
nginx: configuration file /etc/nginx/nginx.conf test is successful
8.启动服务并设置开机自启
[root@web03 ~]# systemctl start nginx
[root@web03 ~]# systemctl enable nginx
Created symlink from /etc/systemd/system/multi-user.target.wants/nginx.service to /usr/lib/systemd/system/nginx.service.