1、SpringBoot基础配置
框架搭建:SpringBoot + HikariCP/Druid + Mybatis + Mysql+sharding-jdbc
1、POM依赖:
<dependency>
<groupId>org.apache.shardingsphere</groupId>
<artifactId>sharding-jdbc-spring-boot-starter</artifactId>
<version>4.1.1</version>
</dependency>
2、配置允许数据源覆盖
properties文件加入以下配置
# 允许数据源覆盖
spring.main.allow-bean-definition-overriding=true
3、数据源配置
数据源类型通常选择DruidDataSource或者HikariDataSource两者在配置上有所不同。
- DruidDataSource
<!-- 不能使用druid-spring-boot-starter,会导致:Property 'sqlSessionFactory' or 'sqlSessionTemplate' are required -->
<dependency>
<groupId>com.alibaba</groupId>
<artifactId>druid</artifactId>
<version>version</version>
</dependency>
com.alibaba.druid.pool.DruidDataSource
DruidDataSource需要引入druid的Jar包,使用:url
spring.shardingsphere.datasource.m1.type=com.alibaba.druid.pool.DruidDataSource
spring.shardingsphere.datasource.m1.url=
- HikariDataSource
com.zaxxer.hikari.HikariDataSource
HikariDataSource要使用:jdbc-url
spring.shardingsphere.datasource.m1.type=com.zaxxer.hikari.HikariDataSource
spring.shardingsphere.datasource.m1.jdbc-url=
2、创建表
将用户(user)表,进行水平分表,分为:user_1,user_2 .... user_6
//创建数据表
CREATE TABLE user_1/user_2/..../user_6 (
id BIGINT(20) NOT NULL COMMENT 'Id',
name VARCHAR(20) NOT NULL COMMENT '名称',
phone VARCHAR(20) NOT NULL COMMENT '电话',
email VARCHAR(20) NOT NULL COMMENT '邮箱',
PRIMARY KEY (id)
)
3、完整properties配置
server.port=9090
server.servlet.context-path=/demo
spring.application.name=sharding-jdbc-simple-demo
# 允许数据源覆盖
spring.main.allow-bean-definition-overriding=true
# MyBatis配置
# 搜索指定包别名
mybatis.typeAliasesPackage=com.lhz.sharding.model.entity
# 配置mapper的扫描,找到所有的mapper.xml映射文件
mybatis.mapperLocations=classpath*:mybatis/**/*.xml
#数据库类型
mybatis.configuration.database-id=mysql
#自动驼峰转换
mybatis.configuration.map-underscore-to-camel-case=true
#pagehelper 分页插件
pagehelper.helper-dialect=mysql
pagehelper.reasonable=false
pagehelper.support-methods-arguments=true
pagehelper.params=count=countSql
#sharding-jdbc 水平分表规则配置,使用complex模式
# 数据源名称,多数据源逗号隔开
spring.shardingsphere.datasource.names=m1
spring.shardingsphere.datasource.m1.type=com.zaxxer.hikari.HikariDataSource
spring.shardingsphere.datasource.m1.driver-class-name=com.mysql.cj.jdbc.Driver
spring.shardingsphere.datasource.m1.jdbc-url=jdbc:mysql://127.0.0.1:3307/shardingjdbc?useUnicode=true&useSSL=false&zeroDateTimeBehavior=convertToNull&characterEncoding=UTF-8&allowMultiQueries=true&serverTimezone=Asia/Shanghai
spring.shardingsphere.datasource.m1.username=root
spring.shardingsphere.datasource.m1.password=lhzlx
# 水平分表:user_1/2/3..,多个表进行分表时,依次在tables标签后写逻辑
# user_1/2/3... 为数据库中的事实表
# user为xml编码中操作的逻辑表,sharding-jdbc会自动根据策略操作事实表
# 配置节点分布情况,表示有user_1到user_6共6张表
spring.shardingsphere.sharding.tables.user.actual-data-nodes=m1.user_$->{1..6}
# 指定user表的主键生成策略为SNOWFLAKE
spring.shardingsphere.sharding.tables.user.key-generator.column=id
spring.shardingsphere.sharding.tables.user.key-generator.type=SNOWFLAKE
# 指定user表的分片策略,分片策略包括分片键和分片算法
# 配置表的分片策略
spring.shardingsphere.sharding.tables.user.table-strategy.complex.sharding-columns=id
# 复合分片算法
spring.shardingsphere.sharding.tables.user.table-strategy.complex.algorithm-class-name=\
com.lhz.sharding.algorithm.MyComplexKeysShardingAlgorithm
# 打开sql输出日志
spring.shardingsphere.props.sql.show=true
4、分片算法
混合分片策略,支持多个分片健操作,并且集成了精确匹配与范围匹配查询,具体处理逻辑如下代码
MyComplexKeysShardingAlgorithm:
import com.google.common.collect.Range;
import org.apache.shardingsphere.api.sharding.complex.ComplexKeysShardingAlgorithm;
import org.apache.shardingsphere.api.sharding.complex.ComplexKeysShardingValue;
import java.util.ArrayList;
import java.util.Collection;
import java.util.List;
import java.util.Map;
/**
* @Description:
**/
public class MyComplexKeysShardingAlgorithm implements ComplexKeysShardingAlgorithm<Long> {
/**
* @param tbNames 数据库中所有的事实表
* @param complexKeysShardingValue 分片相关信息
* @return
*/
@Override
public Collection<String> doSharding(Collection<String> tbNames, ComplexKeysShardingValue<Long> complexKeysShardingValue) {
String logicTableName = complexKeysShardingValue.getLogicTableName();
// 获取范围查询匹配的值
Range<Long> range = this.getRangeValue(complexKeysShardingValue, "id");
if (range != null) {
// between and 的起始值,需要处理只有最大值或者只有最小值的情况
boolean hasLowerBound = range.hasLowerBound();
boolean hasUpperBound = range.hasUpperBound();
// 只有最小值,比如:id > x
if (hasLowerBound && !hasUpperBound) {
// 直接返回所有表名称
return tbNames;
}
// 只有最大值,比如:id < x
if (!hasLowerBound && hasUpperBound) {
long upper = range.upperEndpoint();
if (upper < tbNames.size()) {
// 如果最大值小于表的总数,则返回需要的表名
return matchMinAndMax(1, upper, logicTableName, tbNames);
} else {
// 如果最大值大于表的总数,则返回所有
return tbNames;
}
}
// 区间值情况
long lower = range.lowerEndpoint();
long upper = range.upperEndpoint();
// 拼接事实表名称
return matchMinAndMax(lower, upper, logicTableName, tbNames);
}
// 得到每个分片健对应的值,如果有多个则取多个实现相应逻辑即可
Collection<Long> ids = this.getShardingValue(complexKeysShardingValue, "id");
// 先按原有方式处理,注意 IN的情况,是不是返回多个对象
List<String> tableNameList = new ArrayList<>();
for (Long id : ids) {
long tableNum = id % tbNames.size();
// 事实表后缀
String suffix = String.valueOf(tableNum == 0 ? tableNum + 6 : tableNum);
String tableName = logicTableName + "_" + suffix;
if (tbNames.contains(tableName)) {
// 添加满足要求的表名称
tableNameList.add(tableName);
}
// 如果满足要求的表已经覆盖了所有表,此处处理是为了方式查询区间过大,而分表不多,导致的过度遍历
if (tableNameList.size() == tbNames.size()) {
return tableNameList;
}
}
return tableNameList;
}
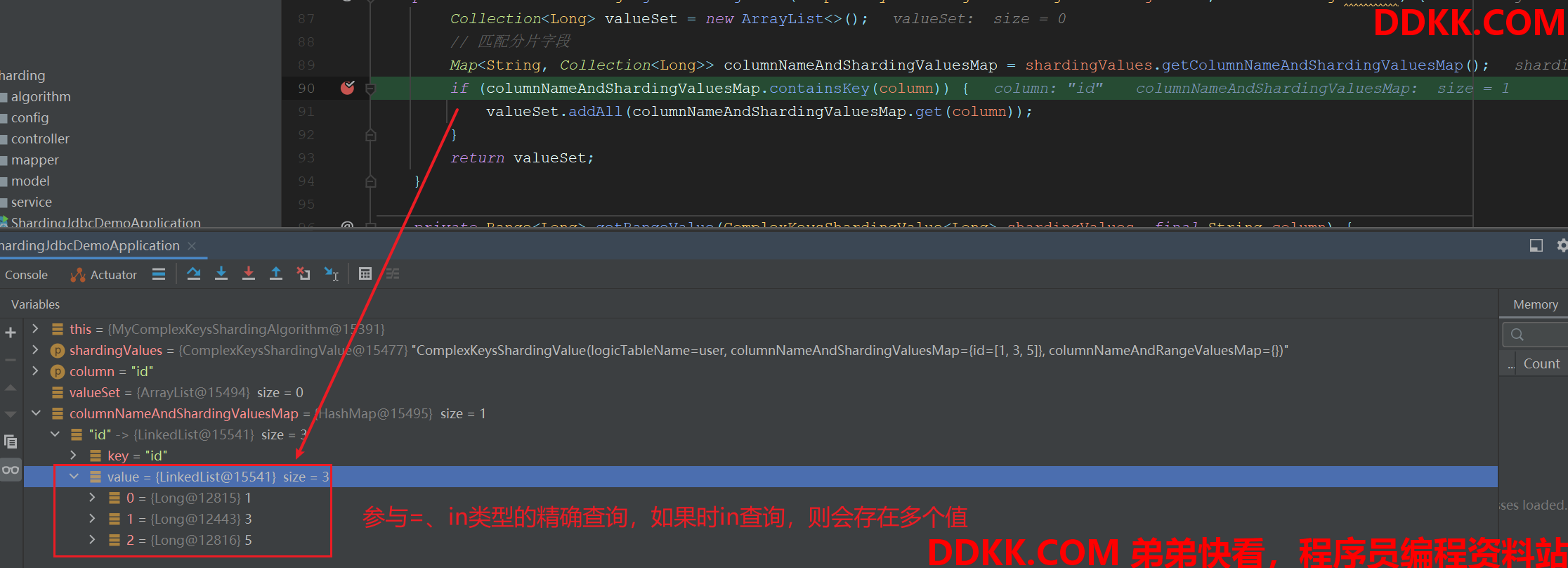
private Collection<Long> getShardingValue(ComplexKeysShardingValue<Long> shardingValues, final String column) {
Collection<Long> valueSet = new ArrayList<>();
// 匹配分片字段
Map<String, Collection<Long>> columnNameAndShardingValuesMap = shardingValues.getColumnNameAndShardingValuesMap();
if (columnNameAndShardingValuesMap.containsKey(column)) {
valueSet.addAll(columnNameAndShardingValuesMap.get(column));
}
return valueSet;
}
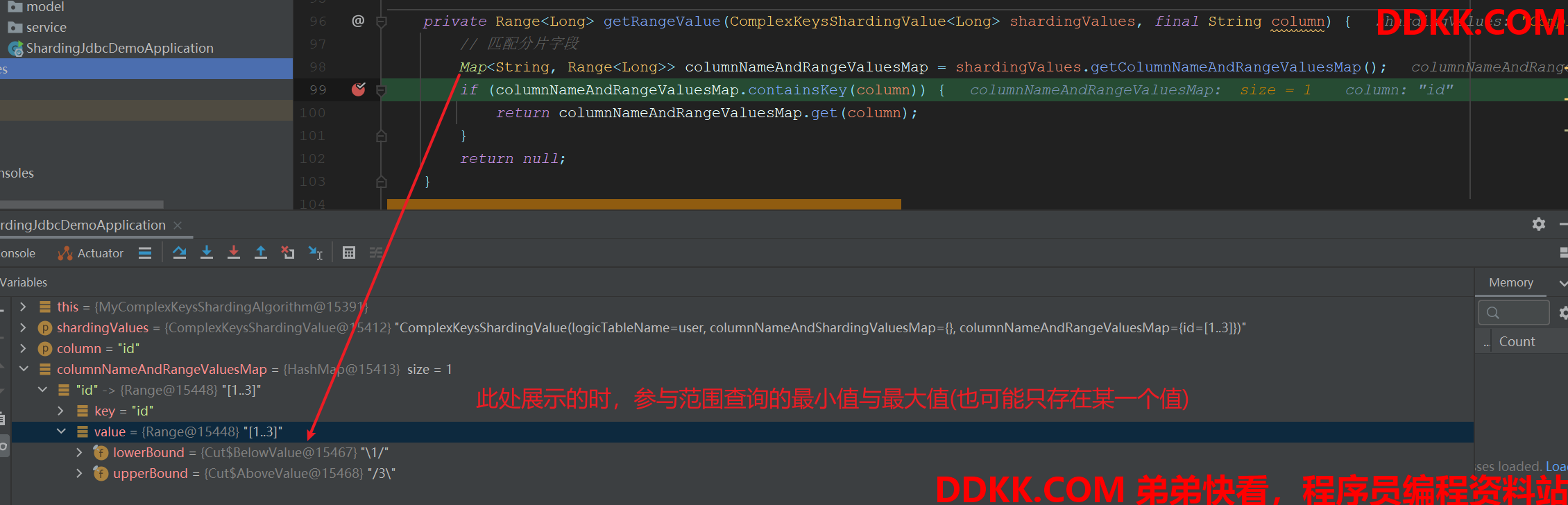
private Range<Long> getRangeValue(ComplexKeysShardingValue<Long> shardingValues, final String column) {
// 匹配分片字段
Map<String, Range<Long>> columnNameAndRangeValuesMap = shardingValues.getColumnNameAndRangeValuesMap();
if (columnNameAndRangeValuesMap.containsKey(column)) {
return columnNameAndRangeValuesMap.get(column);
}
return null;
}
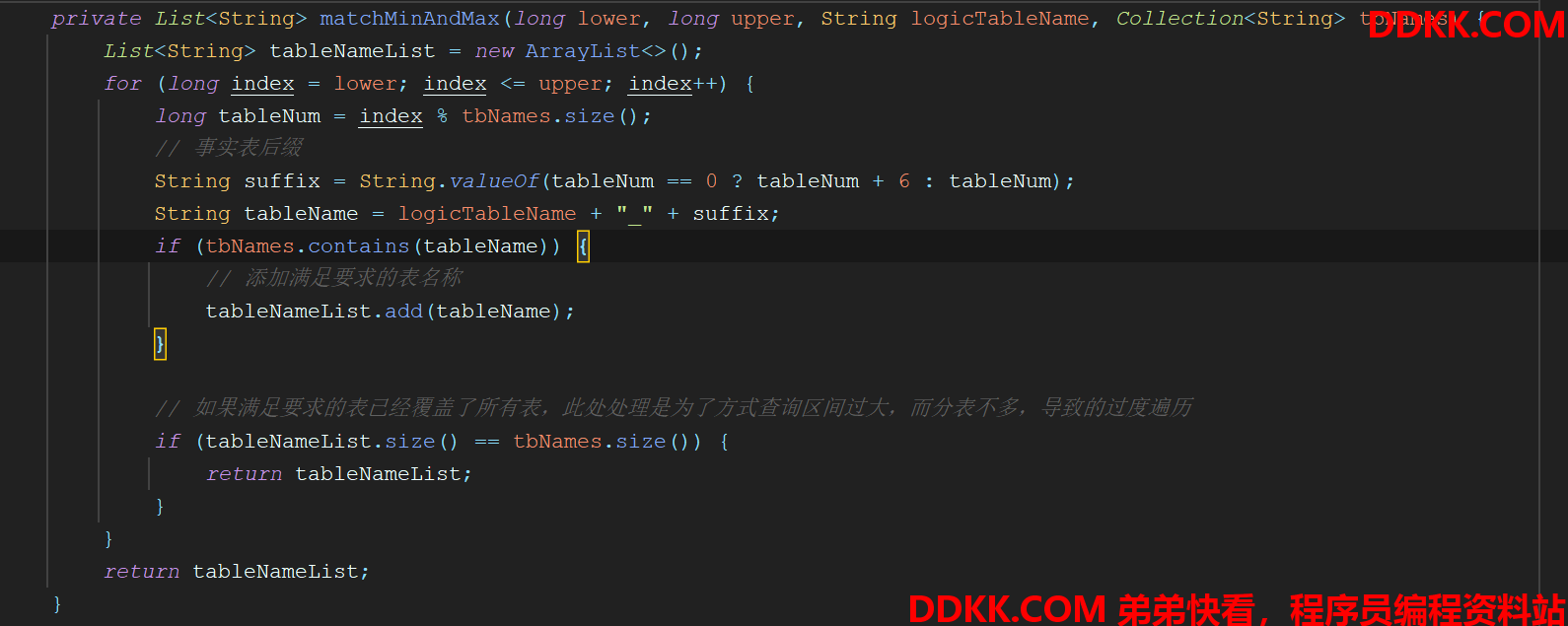
private List<String> matchMinAndMax(long lower, long upper, String logicTableName, Collection<String> tbNames) {
List<String> tableNameList = new ArrayList<>();
for (long index = lower; index <= upper; index++) {
long tableNum = index % tbNames.size();
// 事实表后缀
String suffix = String.valueOf(tableNum == 0 ? tableNum + 6 : tableNum);
String tableName = logicTableName + "_" + suffix;
if (tbNames.contains(tableName)) {
// 添加满足要求的表名称
tableNameList.add(tableName);
}
// 如果满足要求的表已经覆盖了所有表,此处处理是为了方式查询区间过大,而分表不多,导致的过度遍历
if (tableNameList.size() == tbNames.size()) {
return tableNameList;
}
}
return tableNameList;
}
}
范围查询示例:
精确查询示例:
5、实体类
User :
@Data
public class User implements Serializable {
private Long id;
private String name;
private String phone;
private String email;
}
6、Mapper类
ComplexMapper :
@Mapper
public interface ComplexMapper {
/**
* 根据ID查询
*
* @param id
* @return
*/
User selectById(@Param("id") Long id);
List<User> selectByIn(@Param("ids") List<Long> ids);
/**
* 根据ID删除
*
* @param id
* @return
*/
int deleteById(@Param("id") Long id);
/**
* 根据ID更新
*
* @param id
* @return
*/
int updateById(@Param("id") Long id);
/**
* 新增数据
*
* @param min
* @param max
* @return
*/
List<User> listByRange(@Param("min") Long min, @Param("max") Long max);
int insert(User user);
int insertBatch(List<User> list);
}
StandardMapper.xml:
<?xml version="1.0" encoding="UTF-8"?>
<!DOCTYPE mapper PUBLIC "-//mybatis.org//DTD Mapper 3.0//EN" "http://mybatis.org/dtd/mybatis-3-mapper.dtd">
<mapper namespace="com.lhz.sharding.mapper.ComplexMapper">
<select id="selectById" parameterType="java.lang.Long"
resultType="com.lhz.sharding.model.entity.User">
select a.*
from user a
where a.id ={id}
</select>
<select id="selectByIn" parameterType="java.lang.Long"
resultType="com.lhz.sharding.model.entity.User">
select a.*
from user a
where a.id IN
<foreach collection="ids" item="id" open="(" close=")" separator=",">
{id}
</foreach>
</select>
<select id="listByRange"
resultType="com.lhz.sharding.model.entity.User">
select a.*
from user a
<!--where a.id >{min}-->
<!--where a.id <{max}-->
where a.id >={min} and a.id <={max}
<!-- where a.id between{min} and{max}-->
</select>
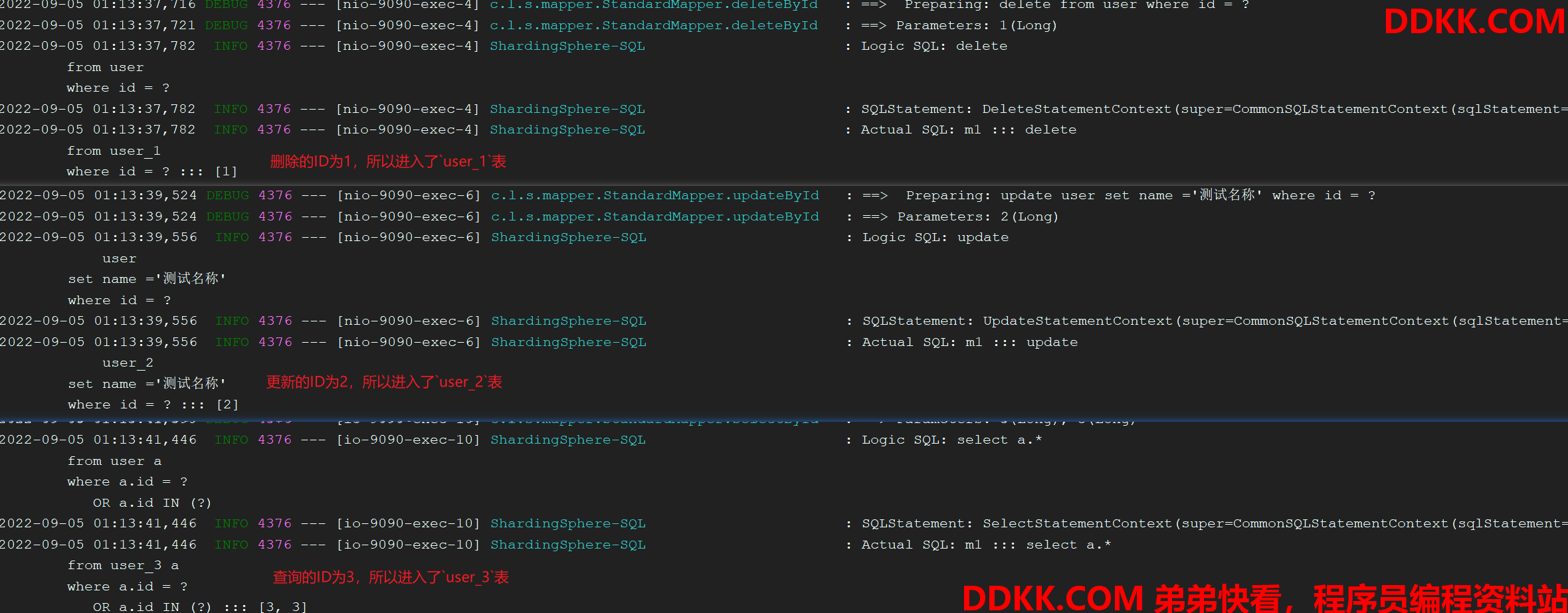
<update id="updateById" parameterType="java.lang.Long">
update
user
set name ='测试名称'
where id ={id}
</update>
<delete id="deleteById" parameterType="java.lang.Long">
delete
from user
where id ={id}
</delete>
<insert id="insert" parameterType="com.lhz.sharding.model.entity.User">
insert into user(id, name, phone, email)
values (#{id},{name},{phone},{email})
</insert>
<insert id="insertBatch" parameterType="com.lhz.sharding.model.entity.User">
insert into user(id, name, phone, email)
values
<foreach collection="list" item="item" separator=",">
(#{item.id},{item.name},{item.phone},{item.email})
</foreach>
</insert>
</mapper>
7、Service类
ComplexService:
@Service
public class ComplexService {
@Resource
private ComplexMapper complexMapper;
/**
* 根据ID查询
*
* @param id
* @return
*/
public User selectById(Long id) {
// in匹配查询
List<Long> ids = new ArrayList<>();
ids.add(1L);
ids.add(3L);
ids.add(5L);
List<User> list = complexMapper.selectByIn(ids);
return complexMapper.selectById(id);
}
/**
* 范围查询
*
* @param min
* @param max
* @return
*/
public List<User> listByRange(Long min, Long max) {
return complexMapper.listByRange(min, max);
}
/**
* 根据ID删除
*
* @param id
* @return
*/
@ApiOperation(value = "根据ID删除", notes = "根据ID删除")
@ApiOperationSupport(order = 15)
@GetMapping("/deleteById")
public int deleteById(Long id) {
return complexMapper.deleteById(id);
}
/**
* 根据ID更新
*
* @param id
* @return
*/
@ApiOperation(value = "根据ID更新", notes = "根据ID更新")
@ApiOperationSupport(order = 20)
@GetMapping("/updateById")
public int updateById(Long id) {
return complexMapper.updateById(id);
}
/**
* 新增数据
*
* @return
*/
@ApiOperation(value = "新增数据", notes = "新增数据")
@ApiOperationSupport(order = 25)
@GetMapping("/insert")
public int insert() {
// 模拟数据
List<User> list = new ArrayList<>();
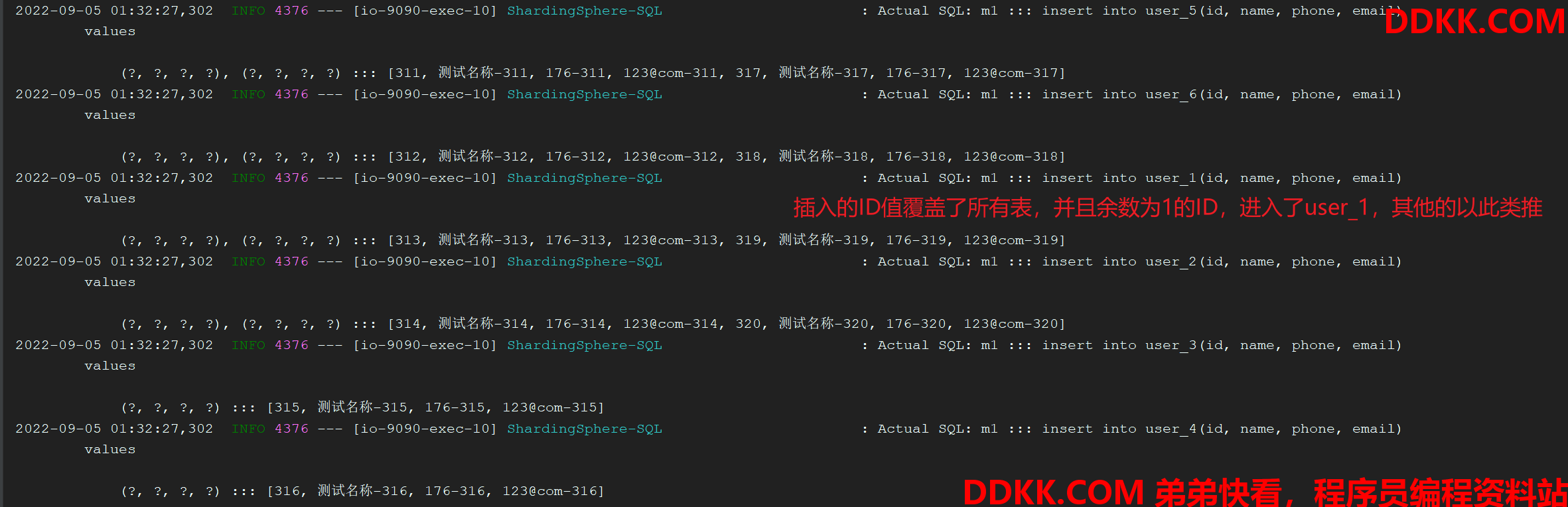
for (long a = 311; a <= 320; a++) {
User user = new User();
user.setId(a);
user.setName("测试名称-" + a);
user.setPhone("176-" + a);
user.setEmail("123@com-" + a);
list.add(user);
}
// 批量新增
complexMapper.insertBatch(list);
// 单个新增
User user = new User();
user.setId(399L);
user.setName("测试名称-" + 999);
user.setPhone("176-" + 999);
user.setEmail("123@com-" + 999);
return complexMapper.insert(user);
}
}
8、Controller类
ComplexController :
@RestController
@RequestMapping("standard")
public class ComplexController {
@Resource
private ComplexService complexService;
/**
* 根据ID查询
*
* @param id
* @return
*/
@GetMapping("/selectById")
public User selectById(Long id) {
return complexService.selectById(id);
}
/**
* 范围查询
*
* @param min
* @param max
* @return
*/
@GetMapping("/listByRange")
public List<User> listByRange(Long min, Long max) {
return complexService.listByRange(min, max);
}
/**
* 根据ID删除
*
* @param id
* @return
*/
@GetMapping("/deleteById")
public int deleteById(Long id) {
return complexService.deleteById(id);
}
/**
* 根据ID更新
*
* @param id
* @return
*/
@GetMapping("/updateById")
public int updateById(Long id) {
return complexService.updateById(id);
}
/**
* 新增数据
*
* @return
*/
@GetMapping("/insert")
public int insert() {
return complexService.insert();
}
}
9、测试
1、删除、更新、精确查询:
2、范围查询:
2.1、只有最大值情况:
当sql中的查询只有最大值,即<=时,比如:
select * from user where id <{max}
这种情况则hasUpperBound=true、hasLowerBound=false,并且需要处理最大值小于表数量以及最大值大于表数量的情况
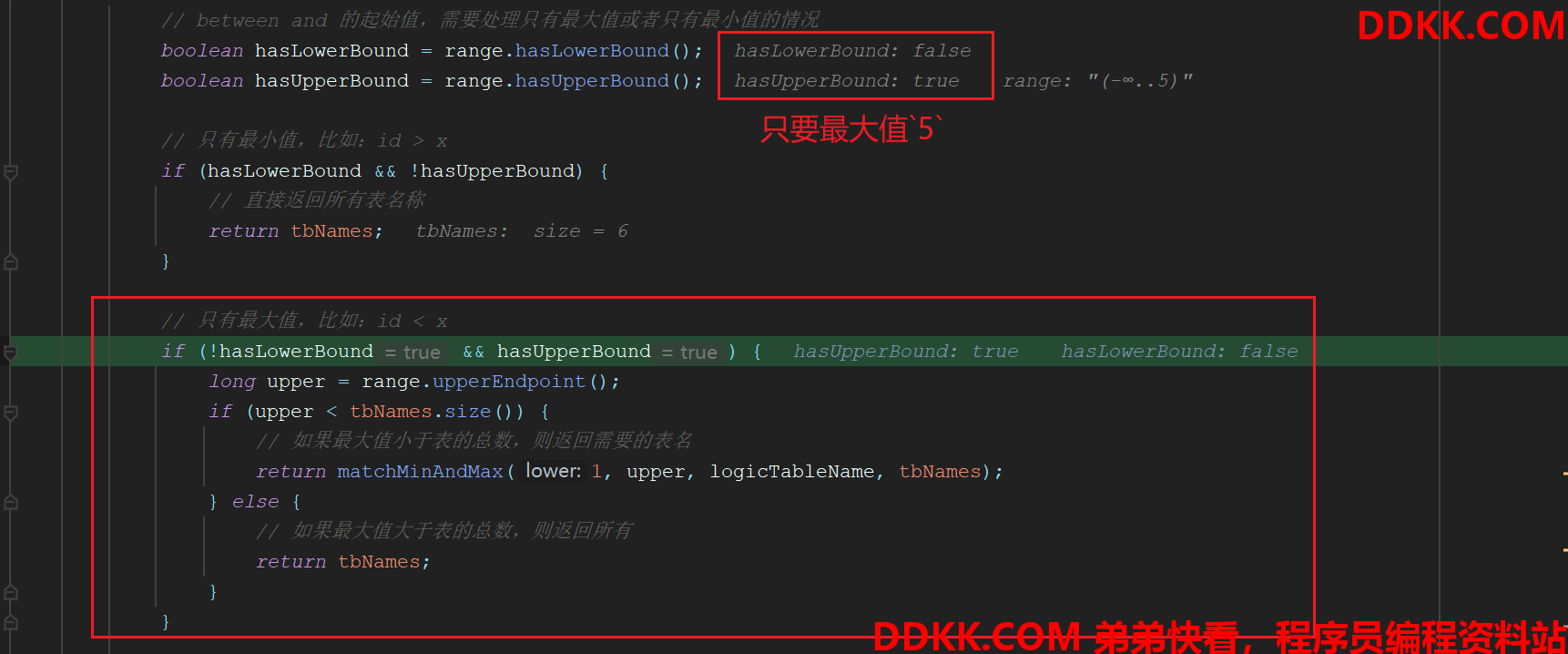
2.2、只有最小值情况:
当sql中的查询只有最大值,即<=时,比如:
select * from user where id >{min}
这种情况则hasUpperBound=false、hasLowerBound=true,那么直接返回所有表即可
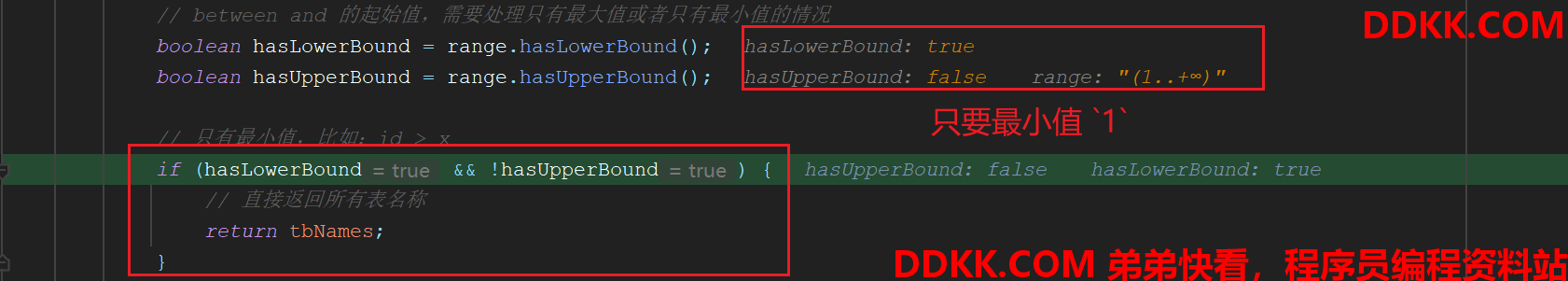
2.3、最大与最小值都存在情况:
当sql中的查询既有最大值又有最小值,比如:
select * from user where a.id >={min} and a.id <={max}
或者
select * from user where a.id between{min} and{max}
这种情况需要遍历最小值到最大值的区间,并且匹配满足要求的表名称,需要注意的是,如果遍历过程中满足要求的表已经覆盖了所有表,那么就直接返回所有表,不再继续遍历,这是为了方式查询区间过大,而分表不多,导致的过度遍历。
执行结果:
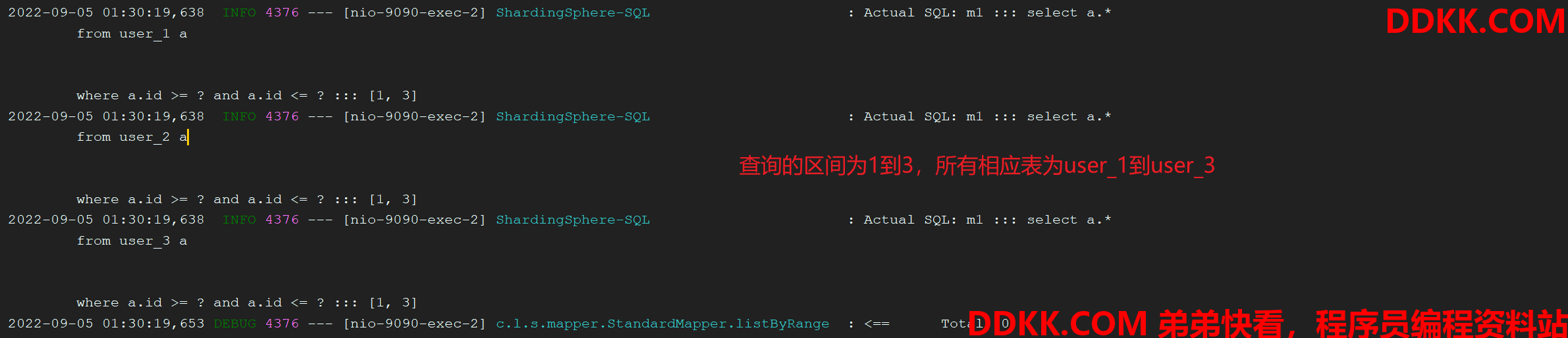
3、新增数据: