题目地址:https://leetcode.com/problems/binary-search-tree-iterator/description/
题目描述
Implement an iterator over a binary search tree (BST). Your iterator will be initialized with the root node of a BST.
Calling next() will return the next smallest number in the BST.
Example:
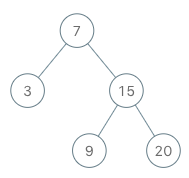
BSTIterator iterator = new BSTIterator(root);
iterator.next(); // return 3
iterator.next(); // return 7
iterator.hasNext(); // return true
iterator.next(); // return 9
iterator.hasNext(); // return true
iterator.next(); // return 15
iterator.hasNext(); // return true
iterator.next(); // return 20
iterator.hasNext(); // return false
Note: next() and hasNext() should run in average O(1) time and uses O(h) memory, where h is the height of the tree.
Credits: Special thanks to @ts for adding this problem and creating all test cases.
题目大意
实现BST的从大到小依次输出值的操作。实现两个函数,hasNext()和next(),操作的时间复杂度是O(1),空间复杂度是O(h)。
解题方法
保存全部节点
一般地,对时间要求比较严格的,我们可以使用空间进行补偿。所以使用一个栈,在初始化的过程中,就使用中序遍历,把BST的中序遍历是有序的这个特点用上。再定义hasnext()和next()就很容易了。
对中序遍历进行了小改进,导致是降序排列的。
但是我们要注意的是,下面的做法的空间复杂度是O(N)的,所以严格来说是不符合题目要求的。
python代码如下:
# Definition for a binary tree node
# class TreeNode(object):
# def __init__(self, x):
# self.val = x
# self.left = None
# self.right = None
class BSTIterator(object):
def __init__(self, root):
"""
:type root: TreeNode
"""
self.stack = []
self.inOrder(root)
def inOrder(self, root):
if not root:
return
self.inOrder(root.right)
self.stack.append(root.val)
self.inOrder(root.left)
def hasNext(self):
"""
:rtype: bool
"""
return len(self.stack) > 0
def next(self):
"""
:rtype: int
"""
return self.stack.pop()
# Your BSTIterator will be called like this:
# i, v = BSTIterator(root), []
# while i.hasNext(): v.append(i.next())
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 19 20 21 22 23 24 25 26 27 28 29 30 31 32 33 34 35 36 37
只保留左节点
下面的做法的空间复杂度是O(h),做法是每次保存要遍历的节点的所有左孩子。这样,每次最多也就是H个节点被保存,当遍历了这个节点之后,需要把该节点的右孩子的所有左孩子放到栈里,这就是个中序遍历的过程。
# Definition for a binary tree node.
# class TreeNode(object):
# def __init__(self, x):
# self.val = x
# self.left = None
# self.right = None
class BSTIterator(object):
def __init__(self, root):
"""
:type root: TreeNode
"""
self.stack = []
self.push_left(root)
def next(self):
"""
@return the next smallest number
:rtype: int
"""
node = self.stack.pop()
self.push_left(node.right)
return node.val
def hasNext(self):
"""
@return whether we have a next smallest number
:rtype: bool
"""
return self.stack
def push_left(self, root):
while root:
self.stack.append(root)
root = root.left
# Your BSTIterator object will be instantiated and called as such:
# obj = BSTIterator(root)
# param_1 = obj.next()
# param_2 = obj.hasNext()
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 19 20 21 22 23 24 25 26 27 28 29 30 31 32 33 34 35 36 37 38 39 40 41
DDKK.COM 弟弟快看-教程,程序员编程资料站,版权归原作者所有
本文经作者:负雪明烛 授权发布,任何组织或个人未经作者授权不得转发