题目地址:https://leetcode.com/problems/n-ary-tree-postorder-traversal/description/
题目描述
Given an n-ary tree, return the postorder traversal of its nodes' values.
Forexample, given a 3-ary tree:
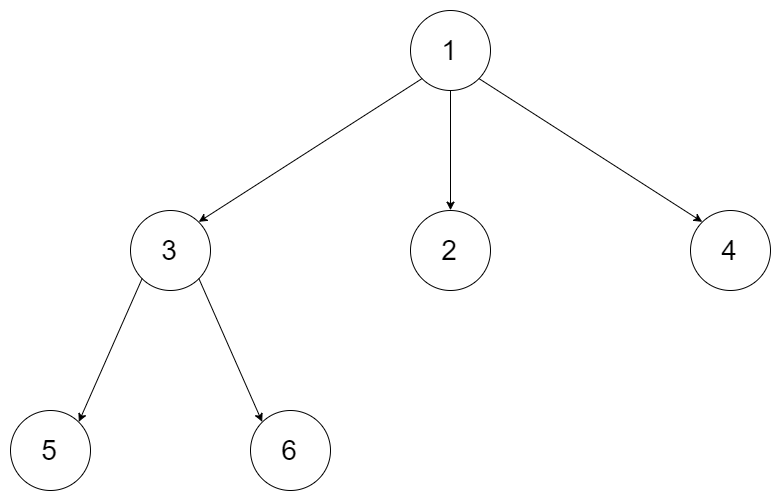
Return its postorder traversal as: [5,6,3,2,4,1].
Note: Recursive solution is trivial, could you do it iteratively?
题目大意
N叉树的后序遍历。
解题方法
递归
首先得明白,这个N叉树是什么样的数据结构定义的。val是节点的值,children是一个列表,这个列表保存了其所有节点。
后序遍历,如果通过递归还是非常简单的。对其子节点遍历,在对其本身节点遍历即可。由于所有的子节点是个列表,这样甚至比二叉树还要简单,只需对列表进行循环就行了。
Python代码如下:
"""
# Definition for a Node.
class Node(object):
def __init__(self, val, children):
self.val = val
self.children = children
"""
class Solution(object):
def postorder(self, root):
"""
:type root: Node
:rtype: List[int]
"""
res = []
if not root:
return res
for child in root.children:
res.extend(self.postorder(child))
res.append(root.val)
return res
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 19 20
C++代码如下:
/*
// Definition for a Node.
class Node {
public:
int val;
vector<Node*> children;
Node() {}
Node(int _val, vector<Node*> _children) {
val = _val;
children = _children;
}
};
*/
class Solution {
public:
vector<int> postorder(Node* root) {
vector<int> res;
if (!root) return res;
for (Node* child : root->children) {
vector<int> child_vector = postorder(child);
res.insert(res.end(), child_vector.begin(), child_vector.end());
}
res.push_back(root->val);
return res;
}
};
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 19 20 21 22 23 24 25 26 27 28
迭代
这个题希望我们使用迭代方法去做,即使用迭代的方法得到后序遍历。由于后序遍历把根节点放到了最后,而我们在遍历的过程中,一定先获得到根节点,那么我们可以先倒序,然后再反转。
后序遍历:左->右->根。 我们的做法:根->右->左,然后再反转。
即,先把根节点放入栈中,然后把它的孩子从左到右依次放入,这样我们下次对栈内的元素遍历得到的顺序就是从右向左的,对于栈中弹出的每个节点都是如此。
得到的顺序是根->右子树(节点全部入栈)->左子树的遍历方式,最后需要加一个翻转即可得到想要的后序遍历。
Python代码如下:
"""
# Definition for a Node.
class Node(object):
def __init__(self, val, children):
self.val = val
self.children = children
"""
class Solution(object):
def postorder(self, root):
"""
:type root: Node
:rtype: List[int]
"""
res = []
if not root:
return res
stack = [root,]
while stack:
node = stack.pop()
stack.extend(node.children)
res.append(node.val)
return res[::-1]
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 19 20 21 22
C++代码如下:
/*
// Definition for a Node.
class Node {
public:
int val;
vector<Node*> children;
Node() {}
Node(int _val, vector<Node*> _children) {
val = _val;
children = _children;
}
};
*/
class Solution {
public:
vector<int> postorder(Node* root) {
vector<int> res;
if (!root) return res;
stack<Node*> st;
st.push(root);
while (!st.empty()) {
Node* node = st.top(); st.pop();
if (!node) continue;
for (Node* child : node->children) {
st.push(child);
}
res.push_back(node->val);
}
reverse(res.begin(), res.end());
return res;
}
};
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 19 20 21 22 23 24 25 26 27 28 29 30 31 32 33 34
相似题目
https://blog.csdn.net/fuxuemingzhu/article/details/81021950
参考资料
https://leetcode.com/articles/n-ary-tree-postorder-transversal/
DDKK.COM 弟弟快看-教程,程序员编程资料站,版权归原作者所有
本文经作者:负雪明烛 授权发布,任何组织或个人未经作者授权不得转发