一、实例要求
使用自定义的编码器和解码器来说明Netty的handler调用机制。客户端发送 long 类型到服务器,服务器可以按8个字节来接收;服务器发送 long 类型到客户端,客户端可以按8个字节来接收。客户端和服务器都需要一个编码器和一个解码器。
二、执行原理
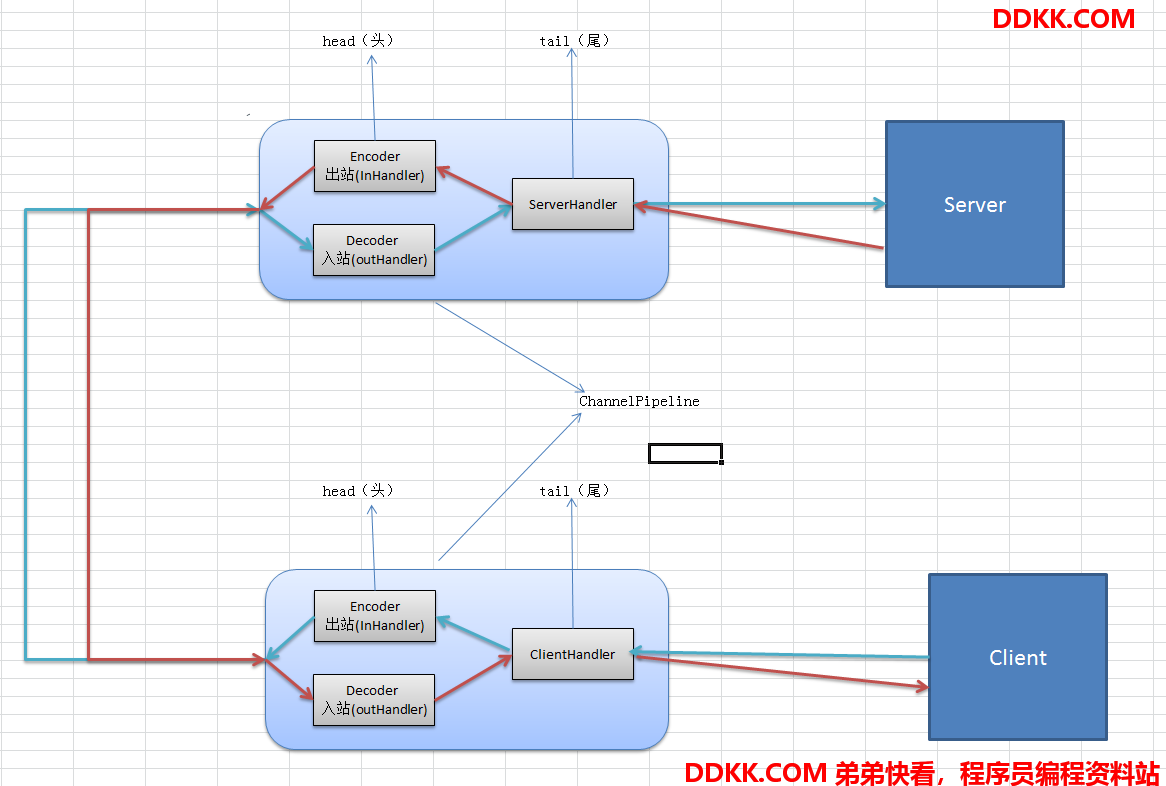
三、案例演示
3.1 编解码器
编码器:
public class MyLongToByteEncoder extends MessageToByteEncoder<Long> {
// 编码的方法
@Override
protected void encode(ChannelHandlerContext ctx, Long msg, ByteBuf out) throws Exception {
System.out.println("MyLongToByteEncoder encode 被调用");
System.out.println("msg=" + msg);
out.writeLong(msg);
}
}
解码器:
public class MyByteToLongDecoder extends ByteToMessageDecoder {
/**
* decode 会根据接收到的数据,被多次调用,直到确定没有新的元素被添加到List
* ,或者是 ByteBuf 没有更多的可读字节为止。
* 如果 List<Object> out 不为空,就会将 List 的内容传递给下一个 ChannelInboundHandler 处理,
* 该处理器的方法也会被多次调用
*
* @param ctx 上下文
* @param in 入站的ByteBuf
* @param out List 集合,将解码后的数据传给下一个handler
* @throws Exception
*/
@Override
protected void decode(ChannelHandlerContext ctx, ByteBuf in, List<Object> out) throws Exception {
System.out.println("MyByteToLongDecoder decode 被调用");
// 因为 long 8个字节,需要判断有8个字节,才能读取一个 long
if (in.readableBytes() >= 8) {
out.add(in.readLong());
}
}
}
3.2 服务器端
启动类:
public class MyServer {
public static void main(String[] args) throws InterruptedException {
EventLoopGroup bossGroup = new NioEventLoopGroup(1);
EventLoopGroup workerGroup = new NioEventLoopGroup();
try {
ServerBootstrap bootstrap = new ServerBootstrap();
bootstrap.group(bossGroup,workerGroup)
.channel(NioServerSocketChannel.class)
.childHandler(new MyServerInitializer()); // 自定义一个初始化类
ChannelFuture future = bootstrap.bind(7000).sync();
future.channel().closeFuture().sync();
}finally {
bossGroup.shutdownGracefully();
workerGroup.shutdownGracefully();
}
}
}
自定义处理器:
public class MyServerHandler extends SimpleChannelInboundHandler<Long> {
@Override
protected void channelRead0(ChannelHandlerContext ctx, Long msg) throws Exception {
System.out.println("从客户端" + ctx.channel().remoteAddress() + " 读取到long " + msg);
// 给客户端发送一个long
ctx.writeAndFlush(98765L);
}
@Override
public void exceptionCaught(ChannelHandlerContext ctx, Throwable cause) throws Exception {
cause.printStackTrace();
ctx.close();
}
}
初始化类:
public class MyServerInitializer extends ChannelInitializer<SocketChannel> {
@Override
protected void initChannel(SocketChannel ch) throws Exception {
ChannelPipeline pipeline = ch.pipeline(); // pipeline 中会标识是入站还是出站
// 入站的handler进行解码,MyByteToLongDecoder
pipeline.addLast(new MyByteToLongDecoder());
// 出站编码器(出站handler)
pipeline.addLast(new MyLongToByteEncoder());
// 加入一个 handler 处理业务逻辑
pipeline.addLast(new MyServerHandler());
}
}
3.2 客户端
启动类:
public class MyClient {
public static void main(String[] args) throws InterruptedException {
EventLoopGroup group = new NioEventLoopGroup();
try {
Bootstrap bootstrap = new Bootstrap();
bootstrap.group(group)
.channel(NioSocketChannel.class)
.handler(new MyClientInitializer()); // 自定义一个初始化类
ChannelFuture future = bootstrap.connect("127.0.0.1", 7000).sync();
future.channel().closeFuture().sync();
}finally {
group.shutdownGracefully();
}
}
}
自定义处理器:
public class MyClientHandler extends SimpleChannelInboundHandler<Long> {
@Override
protected void channelRead0(ChannelHandlerContext ctx, Long msg) throws Exception {
System.out.println("服务器的IP=" + ctx.channel().remoteAddress());
System.out.println("收到服务器消息=" + msg);
}
// 重写channelActive,发送数据
@Override
public void channelActive(ChannelHandlerContext ctx) throws Exception {
System.out.println("MyClientHandler 发送数据");
//ctx.writeAndFlush(Unpooled.copiedBuffer(""));
ctx.writeAndFlush(123456L); // 发送的是一个 long
// 分析
// 1. "abcdabcdabcdabcd" 是 16个字节
// 2. 该处理器的上一个 handler 是 MyLongToByteEncoder
// 3. MyLongToByteEncoder 的父类是: MessageToByteEncoder
// 4. 父类 MessageToByteEncoder 的 write 方法,因此我们编写 Encoder 时要注意传入的数据类型
// 和处理的数据类型一致
/*
// 判断当前 msg,是不是应该处理的类型,如果是就处理,如果不是就跳过encode方法
if (acceptOutboundMessage(msg)) {
@SuppressWarnings("unchecked")
I cast = (I) msg;
buf = allocateBuffer(ctx, cast, preferDirect);
try {
encode(ctx, cast, buf);
} finally {
ReferenceCountUtil.release(cast);
}
if (buf.isReadable()) {
ctx.write(buf, promise);
} else {
buf.release();
ctx.write(Unpooled.EMPTY_BUFFER, promise);
}
buf = null;
} else {
ctx.write(msg, promise);
}
*/
//ctx.writeAndFlush(Unpooled.copiedBuffer("abcdabcdabcdabcd", CharsetUtil.UTF_8));
}
}
初始化类:
public class MyClientInitializer extends ChannelInitializer<SocketChannel> {
@Override
protected void initChannel(SocketChannel ch) throws Exception {
ChannelPipeline pipeline = ch.pipeline();
// 加入一个出站的handler,对数据进行编码
pipeline.addLast(new MyLongToByteEncoder());
// 入站解码器(入站handler)
pipeline.addLast(new MyByteToLongDecoder());
// 加入一个 handler 处理业务逻辑
pipeline.addLast(new MyClientHandler());
}
}
四、总结
1、不论 解码器handler 还是 编码器handler,即接收的消息类型必须与待处理的消息类型一致,否则该handler不会被执行
2、在解码器进行数据解码时,需要判断缓存区(ByteBuf)的数据是否足够,否则接收到的结果会和期望结果可能不一致