一、基本介绍
1、NIO 的通道类似于流,但有些区别如下:
- 通道可以同时进行读写,而流只能读或者只能写
- 通道可以实现异步读写数据
- 通道可以从缓冲读数据,也可以写数据到缓冲
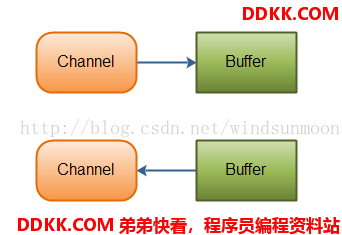 2、BIO 中的 stream 是单向的,例如 FileInputStream 对象只能进行读取数据的操作,而 NIO 中的通道(Channel)是双向的,可以读操作,也可以写操作。
2、BIO 中的 stream 是单向的,例如 FileInputStream 对象只能进行读取数据的操作,而 NIO 中的通道(Channel)是双向的,可以读操作,也可以写操作。
3、Channel 在 NIO 中是一个接口
public interface Channel extends Closeable
4、常用的 Channel 类有:FileChannel、DatagramChannel、ServerSocketChannel 和 SocketChannel
5、FileChannel 用于文件的数据读写,DatagramChannel 用于 UDP 的数据读写,ServerSocketChannel 和 SocketChannel 用于 TCP 的数据读写。
二、常用方法
2.1 FileChannel 类
FileChannel 主要用来对本地文件进行 IO 操作,常见的方法有:
| 方法 | 描述 |
|---|---|
| int read(ByteBuffer dst) | 从通道读取数据并放到缓冲区中 |
| int write(ByteBuffer src) | 把缓冲区的数据写到通道中 |
| long transferFrom(ReadableByteChannel src, long position, long count) | 从目标通道中复制数据到当前通道 |
| long transferTo(long position, long count, WritableByteChannel target) | 把数据从当前通道复制给目标通道 |
三、应用案例
3.1 本地文件写数据
案例要求
1、使用 ByteBuffer(缓冲)和 FileChannel(通道),将"Hello,World!",写入到 file01.txt 中
2、文件不存在就创建
3、代码演示
public class NIOFileChannel01 {
public static void main(String[] args) throws IOException {
String str = "Hello,World!";
// 创建一个输出流->channel
FileOutputStream fileOutputStream = new FileOutputStream("d:\\file01.txt");
// 通过 fileOutputStream 获取对应的 FileChannel
// 这个 fileChannel 真实类型是 FileChannelImpl
FileChannel fileChannel = fileOutputStream.getChannel();
// 创建一个缓冲区 ByteBuffer
ByteBuffer byteBuffer = ByteBuffer.allocate(1024);
// 将 str 放入到 byteBuffer
byteBuffer.put(str.getBytes());
// 对 byteBuffer 进行反转(flip)
byteBuffer.flip();
// 将 byteBuffer 数据写入到 fileChannel
fileChannel.write(byteBuffer);
fileOutputStream.close();
}
}
3.2 本地文件读数据
案例要求
1、使用 ByteBuffer(缓冲)和 Channel(通道),将 file01.txt 中的数据读入到程序,并显示在控制台
2、假定文件已经存在
3、代码演示
public class NIOFileChannel02 {
public static void main(String[] args) throws IOException {
// 创建文件的输入流
File file = new File("d:\\file01.txt");
FileInputStream fileInputStream = new FileInputStream(file);
// 通过 fileInputStream 获取对应的 FileChannel->FileChannelImpl
FileChannel fileChannel = fileInputStream.getChannel();
// 创建缓冲区
ByteBuffer byteBuffer = ByteBuffer.allocate((int)file.length());
// 将通道的数据读入到 byteBuffer 中
fileChannel.read(byteBuffer);
// 将 byteBuffer 中的字节数据转成字符串
System.out.println(new String(byteBuffer.array()));
fileInputStream.close();
}
}
3.3 使用一个 Buffer 完成文件读取
案例要求
1、使用 FileChannel(通道)和 方法 read、write,完成文件的拷贝
2、拷贝一个文本文件 1.txt,放在项目下即可 2.txt
3、全程只使用一个 Buffer
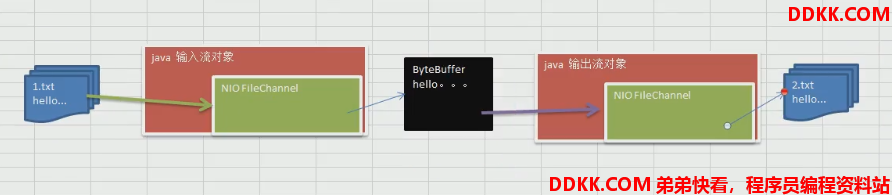
4、代码演示
public class NIOFileChannel03 {
public static void main(String[] args) throws IOException {
FileInputStream fileInputStream = new FileInputStream("1.txt");
FileChannel fileChannel01 = fileInputStream.getChannel();
FileOutputStream fileOutputStream = new FileOutputStream("2.txt");
FileChannel fileChannel02 = fileOutputStream.getChannel();
ByteBuffer byteBuffer = ByteBuffer.allocate(512);
while (true){ // 循环读取
// 这里有一个重要的操作,一定不要忘了
/*public final Buffer clear() {
position = 0;
limit = capacity;
mark = -1;
return this;
}*/
byteBuffer.clear(); // 清空 buffer
int read = fileChannel01.read(byteBuffer);
System.out.println("read =" + read);
System.out.println(new String(byteBuffer.array()));
if(read == -1){ // 表示读取完毕
break;
}
// 将 buffer 中的数据写入到 fileChannel02 --> 2.txt
byteBuffer.flip();
fileChannel02.write(byteBuffer);
}
// 关闭流
fileInputStream.close();
fileOutputStream.close();
}
}
3.4 使用transferFrom拷贝文件
案例要求
1、使用 FileChannel(通道)和 方法 transferFrom,完成文件的拷贝
2、拷贝一张图片
3、代码演示
public class NIOFileChannel04 {
public static void main(String[] args) throws IOException {
// 创建相关流
FileInputStream fileInputStream = new FileInputStream("d:\\a.jpg");
FileOutputStream fileOutputStream = new FileOutputStream("d:\\a2.jpg");
// 获取各个流对应的filechannel
FileChannel sourceCh = fileInputStream.getChannel();
FileChannel destCh = fileOutputStream.getChannel();
// 使用 transferFrom 完成拷贝
destCh.transferFrom(sourceCh,0,sourceCh.size());
// 关闭通道和流
sourceCh.close();
destCh.close();
fileInputStream.close();
fileOutputStream.close();
}
}