这篇开始分析tomcat内核处理请求部分(分析了tomcat处理socket概况,后面部分具体分析处理socket的处理),在十七篇中分析了tomcat将socket处理和tomcat内核连接起来的地方,下面是代码片段:
Public class CoyoteAdapter{
Public void server(…….){
………………..
connector.getService().getContainer().getPipeline().getFirst().invoke(request, response);
……………….
}
}
上面的代码片段最后会调用到StandardEngineValve的invoke方法,前面篇章的分析知道Container继承链下的组件构造方法都有类似的处理,下面是Engine的代码片段:
public StandardEngine() {
super();
// StandardEngineValve就是上面的First
pipeline.setBasic(new StandardEngineValve());
/* Set the jmvRoute using the system property jvmRoute */
try {
setJvmRoute(System.getProperty("jvmRoute"));
} catch(Exception ex) {
log.warn(sm.getString("standardEngine.jvmRouteFail"));
}
// By default, the engine will hold the reloading thread
backgroundProcessorDelay = 10;
}
每个Container都有Pipeline属性,Pipeline是Valve的集合,每个Container都可以在Server.xml配置跟自己相关的Valve,每个Container会有默认的Valve也就是StandardXXXValve(First)。
现在看下Valve的继承链
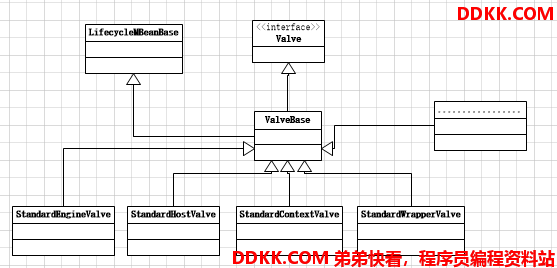
关注Valve重点看invoke方法,这篇看StandardEngineValve
final class StandardEngineValve extends ValveBase {
………………………………..
@Override
public final void invoke(Request request, Response response)
throws IOException, ServletException {
//得到跟当前request相关的host
Host host = request.getHost();
if (host == null) {
//如果为空,则返回400的错误
response.sendError
(HttpServletResponse.SC_BAD_REQUEST,
sm.getString("standardEngine.noHost",
request.getServerName()));
return;
}
if (request.isAsyncSupported()) {
//如果request是支持async,最后决定是否async取决于host的pipeline是否支持async
request.setAsyncSupported(host.getPipeline().isAsyncSupported());
}
//继续调用该Engine下的跟当前request相关Host的valve的invoke方法
host.getPipeline().getFirst().invoke(request, response);
}
}