从tomcat文档,或者更具上篇我们分析的Lifecycle继承关系或者查看Server.xml配置文件可以知道,在Lifecycle继承链下tomcat有几大组件,Server、Service、Context、Engine、Host,当然Lifecycle继承链下还有其他组件。
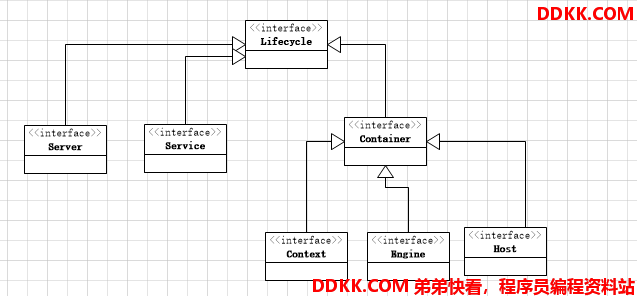
从分析Catalina那篇可以知道,Catalina的方法会调用Server的对应的start、stop等等方法,
而从上篇知道LifecycleBase会有startInternal等回调方法,通观StandServer可以发现有XXInternal方法,这篇主要关注的就是这几个方法。
startInternal和await方法:
为什么把这两个方法放一起,可以回顾下Catalina那篇,Catalina的Start方法
public void start() {
getServer().start();
……………
getServer().destroy();
………..
//BootStrap调用Catalina setAwait设置await为true
if (await) {
await(); // getServer().await();
stop();
}
}
等分析完Server的startInternal方法和await方法可以回头总结下Catalina的方法。
startInternal 方法:
protected void startInternal() throws LifecycleException {
//触发CONFIGURE_START_EVENT事件,注册这个事件的监听器会调用
fireLifecycleEvent(CONFIGURE_START_EVENT, null);
setState(LifecycleState.STARTING);
//调用globalNamingResources的start
globalNamingResources.start();
//调用services的start方法
synchronized (servicesLock) {
for (int i = 0; i < services.length; i++) {
services[i].start();
}
}
}
这里面有几个疑问,globalNamingResources和services的什么时候创建的,Digester那篇分析可以知道,在Catalian.load方法中给Digester设置rule,
然后解析来生成对象链。现在我们回头去关注跟globalNamingResources和services有关的部分
protected Digester createStartDigester() {
………….
…………
//Server部分,创建StandardServer对象,调用Catalina的setServer设值
digester.addObjectCreate("Server",
"org.apache.catalina.core.StandardServer",
"className");
digester.addSetProperties("Server");
digester.addSetNext("Server",
"setServer",
"org.apache.catalina.Server");
// Server/GlobalNamingResources部分,创建NamingResourcesImpl对象调用StandardServer的setGlobalNamingResources设值,并且给NamingResourcesImpl对象设值Server.xml上相对应的properties
digester.addObjectCreate("Server/GlobalNamingResources",
"org.apache.catalina.deploy.NamingResourcesImpl");
digester.addSetProperties("Server/GlobalNamingResources");
digester.addSetNext("Server/GlobalNamingResources",
"setGlobalNamingResources",
"org.apache.catalina.deploy.NamingResourcesImpl");
………………
…………..
// Server/Service部分, 创建StandardService,调用StandardService的addService方法设值
digester.addObjectCreate("Server/Service",
"org.apache.catalina.core.StandardService",
"className");
digester.addSetProperties("Server/Service");
digester.addSetNext("Server/Service",
"addService",
"org.apache.catalina.Service");
…………………………
}
现在简单看下上面提到的方法
public void setGlobalNamingResources
//设置globalNamingResources属性,出发PropertyChange事件
(NamingResourcesImpl globalNamingResources) {
NamingResourcesImpl oldGlobalNamingResources =
this.globalNamingResources;
this.globalNamingResources = globalNamingResources;
this.globalNamingResources.setContainer(this);
support.firePropertyChange("globalNamingResources",
oldGlobalNamingResources,
this.globalNamingResources);
}
public void addService(Service service) {
//添加新service进services数组,设置service的server属性
service.setServer(this);
synchronized (servicesLock) {
Service results[] = new Service[services.length + 1];
System.arraycopy(services, 0, results, 0, services.length);
results[services.length] = service;
services = results;
if (getState().isAvailable()) {
try {
//启动service
service.start();
} catch (LifecycleException e) {
// Ignore
}
}
support.firePropertyChange("service", null, service);
}
}
现在回头看startInternal 方法,调用GlobalNamingResources和service的start方法。这两个对象后面可以分析,重点是StandardService,这篇主要看Server。
avwait方法:
启动一个ServerSocket,监听Catalina的stopServer方法发送的SHUTDWON,当监听到SHUTDOWN ,await方法将break while,停止阻塞。
回头看Catalina的start方法,大致逻辑,调用server Start方法,然后调server Awati方法keep main thread alive。
stopInternal方法(当将tomcat作为service的时候,停止服务将调用stopInternal方法):
protected void stopInternal() throws LifecycleException {
setState(LifecycleState.STOPPING);
//触发CONFIGURE_STOP_EVENT事件
fireLifecycleEvent(CONFIGURE_STOP_EVENT, null);
//停止service
for (int i = 0; i < services.length; i++) {
services[i].stop();
}
//停止globalNamingResources
globalNamingResources.stop();
stopAwait();//设置stopAwait为true
}
initInternal 方法和destroyInternal 方法:
initInternal方法:
protected void initInternal() throws LifecycleException {
super.initInternal();
//注册StringCache为JMX
onameStringCache = register(new StringCache(), "type=StringCache");
// 注冊factory为JMX
MBeanFactory factory = new MBeanFactory();
factory.setContainer(this);
onameMBeanFactory = register(factory, "type=MBeanFactory");
//调用resource的init方法
globalNamingResources.init();
// Populate the extension validator with JARs from common and shared class loaders
if (getCatalina() != null) {
ClassLoader cl = getCatalina().getParentClassLoader();
while (cl != null && cl != ClassLoader.getSystemClassLoader()) {
if (cl instanceof URLClassLoader) {
URL[] urls = ((URLClassLoader) cl).getURLs();
for (URL url : urls) {
if (url.getProtocol().equals("file")) {
try {
File f = new File (url.toURI());
if (f.isFile() &&
f.getName().endsWith(".jar")) {
ExtensionValidator.addSystemResource(f);
}
} catch (URISyntaxException e) {
// Ignore
} catch (IOException e) {
// Ignore
}
}
}
}
cl = cl.getParent();
}
}
// Initialize our defined Services
for (int i = 0; i < services.length; i++) {
services[i].init();
}
destroyInternal 方法:
protected void destroyInternal() throws LifecycleException {
//destroy service
for (int i = 0; i < services.length; i++) {
services[i].destroy();
}
// destroy resource
globalNamingResources.destroy();
//注销onameMBeanFactory JMX
unregister(onameMBeanFactory);
//注销onameStringCache JMX
unregister(onameStringCache);
super.destroyInternal();
}
总结:
当作为CMD start 启动时,start方法再调用service的star后会因为await阻塞,当CMD stop时,Server的await启动的ServerSocket会监听Catalina的stopServer方法发送的SHUTDOWN,当监听到SHUDOWN,while break,然后调用stop,destroy。
Bootstrap.init->Catalina.Load->Server.InitInternal,
CMD–start Bootstrap.main-> Catalina.Start->Server.StartInternal,
CMD–stop Bootstrap.main-> Catalina.StopServer导致start的阻塞while break->Server.StopInternal+Server.DestroyInternal,
当作为service的时候,
Bootstrap.init->Catalina.Load->Server.InitInternal,
Bootstrap.main->Catalina.Start->Server.StartInternal,
Bootstrap.main->Catalina.Stop->Server.StopInternal+Server.DestroyInternal,