题目地址:https://leetcode.com/problems/path-sum-ii/description/
题目描述
Given a binary tree and a sum, find all root-to-leaf paths where each path's sum equals the given sum.
Note: A leaf is a node with no children.
Example:
Given the below binary tree and sum = 22,
5
/ \
4 8
/ / \
11 13 4
/ \ / \
7 2 5 1
Return:
[
[5,4,11,2],
[5,8,4,5]
]
题目大意
在一棵二叉树中,找出从根节点到叶子节点的和为target的所有路径。
解题方法
二叉树问题大多都可以用递归和迭代的方法求解。本题也是如此。
左边是BFS,按照层进行搜索;图右边是DFS,先一路走到底,然后再回头搜索。
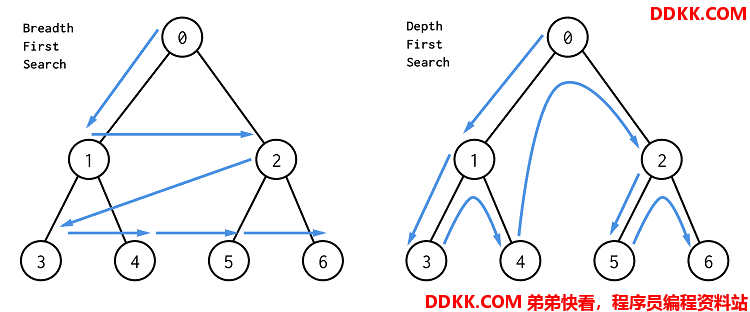
BFS
BFS使用队列,把每个还没有搜索到的点依次放入队列,然后再弹出队列的头部元素当做当前遍历点。BFS总共有两个模板:
1、 如果不需要确定当前遍历到了哪一层,BFS模板如下;
while queue 不空:
cur = queue.pop()
if cur 有效且未被访问过:
进行处理
for 节点 in cur 的所有相邻节点:
if 该节点有效:
queue.push(该节点)
1 2 3 4 5 6 7
1、 如果要确定当前遍历到了哪一层,BFS模板如下这里增加了level表示当前遍历到二叉树中的哪一层了,也可以理解为在一个图中,现在已经走了多少步了size表示在当前遍历层有多少个元素,也就是队列中的元素数,我们把这些元素一次性遍历完,即把当前层的所有元素都向外走了一步;
level = 0
while queue 不空:
size = queue.size()
while (size --) {
cur = queue.pop()
if cur 有效且未被访问过:
进行处理
for 节点 in cur的所有相邻节点:
if 该节点有效:
queue.push(该节点)
}
level ++;
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12
上面两个是通用模板,在任何题目中都可以用,是要记住的!
本题要求所有的路径,不需要按层遍历,因此使用模板一。(注:模板二的使用见102. 二叉树的层序遍历open in new window)
代码如下,使用队列,同时保存(将要处理的节点,路径,路径和),这样在访问一个节点的时候,就能知道已有的路径和「路径和」。如果当前节点是叶子节点并且,已有的「路径和」加上当前叶子的值等于sum,说明找到了一条满足题意的路径,放入结果 res 中。
# Definition for a binary tree node.
# class TreeNode:
# def __init__(self, x):
# self.val = x
# self.left = None
# self.right = None
class Solution:
def pathSum(self, root: TreeNode, sum: int) -> List[List[int]]:
res = []
que = deque()
que.append((root, [], 0)) 将要处理的节点,路径,路径和
while que:
node, path, pathSum = que.popleft()
if not node: 如果是空节点,不处理
continue
if not node.left and not node.right: 如果是叶子节点
if node.val + pathSum == sum: 加上叶子节点后,路径和等于sum
res.append(path + [node.val]) 保存路径
处理左子树
que.append((node.left, path + [node.val], pathSum + node.val))
处理右子树
que.append((node.right, path + [node.val], pathSum + node.val))
return res
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 19 20 21 22 23 24
DFS
题目要求二叉树中从根节点到叶子节点的「路径和」为 sum 的所有路径。
我们必须使用一个变量 res 保存最终的所有路径结果,用一个变量 path 保存每条路径。另外需要记录路径和,我们反其道而行之,记录到达每个节点时的sum - 「路径和」;如果遍历到叶子节点的时候,sum - 「路径和」 恰好等于叶子节点的值,那么这条从根节点到叶子节点的路径即为一条满足题目的路径。
在下面的代码中,res 变量从头到尾只有同一个,但是每次调用 dfs() 函数的时候 path 变量都是不同的。Python 中,path + [root.val] 会生成一个新的列表,因此所有的递归函数的里面的 path 操作不会互相干扰。
# Definition for a binary tree node.
# class TreeNode:
# def __init__(self, x):
# self.val = x
# self.left = None
# self.right = None
class Solution:
def pathSum(self, root: TreeNode, sum: int) -> List[List[int]]:
res = []
self.dfs(root, sum, res, [])
return res
def dfs(self, root, sum, res, path):
if not root: 空节点,不做处理
return
if not root.left and not root.right: 叶子节点
if sum == root.val: 剩余的「路径和」恰好等于叶子节点值
res.append(path + [root.val]) 把该路径放入结果中
self.dfs(root.left, sum - root.val, res, path + [root.val]) 左子树
self.dfs(root.right, sum - root.val, res, path + [root.val]) 右子树
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 19 20 21
DDKK.COM 弟弟快看-教程,程序员编程资料站,版权归原作者所有
本文经作者:负雪明烛 授权发布,任何组织或个人未经作者授权不得转发