上篇主要是讲解 RocketMQ 运行过程中消息发送者发送一条消息,进入到 commitlog 文件,然后是如何被转发到consumequeue、index索引文件中的,本节主要剖析一下,在 RocketMQ 启动过程中,是如何根据 commitlog 重构consumeque,index的,因为毕竟 commitlog 文件中的消息与 consumequeue 中的文件内容并不能确保是一致的。
入口:DefaultMessageStore#load
/**
* @throws IOException
*/
public boolean load() {
boolean result = true;
try {
boolean lastExitOK = !this.isTempFileExist(); // @1
log.info("last shutdown {}", lastExitOK ? "normally" : "abnormally");
if (null != scheduleMessageService) {
result = result && this.scheduleMessageService.load(); // @2
}
// load Commit Log
result = result && this.commitLog.load(); // @3
// load Consume Queue
result = result && this.loadConsumeQueue(); // @4
if (result) {
this.storeCheckpoint =
new StoreCheckpoint(StorePathConfigHelper.getStoreCheckpoint(this.messageStoreConfig.getStorePathRootDir())); // @5
this.indexService.load(lastExitOK); // @6
this.recover(lastExitOK); // @7
log.info("load over, and the max phy offset = {}", this.getMaxPhyOffset());
}
} catch (Exception e) {
log.error("load exception", e);
result = false;
}
if (!result) {
this.allocateMappedFileService.shutdown();
}
return result;
}
代码@1:判断 $ {ROCKET_HOME}/storepath/abort 文件是否存在,如果文件存在,则返回true,否则返回false,这个文件的作用是什么呢?原来,在DefaultMessageStore 启动时创建,在 shutdown 时删除,也就是如果该文件存在,说明不是正常的关闭。
private boolean isTempFileExist() {
String fileName = StorePathConfigHelper.getAbortFile(this.messageStoreConfig.getStorePathRootDir());
File file = new File(fileName);
return file.exists();
}
代码@2:延迟消息启动。
代码@3:commitlog文件加载。
代码@4:加载consumerqueue文件。
代码@5:文件存储检测点。
代码@6:索引文件加载。
代码@7:文件检测恢复。
接下来,本文重点分析步骤3-6都是基于物理磁盘上的文件,构建成内存映射文件(MappedFile)。
代码@7:验证commitlog、consumequeue、索引文件直接的一致性检测,也是本文重点分析内容。
1、文件恢复
DefaultMessageStore#recover
private void recover(final boolean lastExitOK) {
this.recoverConsumeQueue(); // @1
if (lastExitOK) { // @2
this.commitLog.recoverNormally(); // @21
} else {
this.commitLog.recoverAbnormally(); // @22
}
this.recoverTopicQueueTable(); // @3
}
代码@1:恢复消息队列。
代码@2:如果是正常退出,则按照正常修复;如果是异常退出,则走异常修复逻辑。
代码@3,修复主题队列。
1.1 消息队列恢复 DefaultMessageStore#recoverConsumeQueue

ConsumeQueue#recover
public void recover() {
final List<MappedFile> mappedFiles = this.mappedFileQueue.getMappedFiles(); // @1
if (!mappedFiles.isEmpty()) {
int index = mappedFiles.size() - 3;
if (index < 0) // @2
index = 0;
int mappedFileSizeLogics = this.mappedFileSize; // @3 start
MappedFile mappedFile = mappedFiles.get(index);
ByteBuffer byteBuffer = mappedFile.sliceByteBuffer();
long processOffset = mappedFile.getFileFromOffset(); // @3 end
long mappedFileOffset = 0;
long maxExtAddr = 1;
while (true) { //
for (int i = 0; i < mappedFileSizeLogics; i += CQ_STORE_UNIT_SIZE) { // 4 start
long offset = byteBuffer.getLong(); // @5 start
int size = byteBuffer.getInt();
long tagsCode = byteBuffer.getLong(); // @5 end
if (offset >= 0 && size > 0) {
mappedFileOffset = i + CQ_STORE_UNIT_SIZE;
this.maxPhysicOffset = offset;
if (isExtAddr(tagsCode)) {
maxExtAddr = tagsCode;
}
} else {
log.info("recover current consume queue file over, " + mappedFile.getFileName() + " "
+ offset + " " + size + " " + tagsCode);
break;
}
} // @4 end
if (mappedFileOffset == mappedFileSizeLogics) { // @6
index++;
if (index >= mappedFiles.size()) {
log.info("recover last consume queue file over, last maped file "
+ mappedFile.getFileName());
break;
} else {
mappedFile = mappedFiles.get(index);
byteBuffer = mappedFile.sliceByteBuffer();
processOffset = mappedFile.getFileFromOffset();
mappedFileOffset = 0;
log.info("recover next consume queue file, " + mappedFile.getFileName());
}
} else {
log.info("recover current consume queue queue over " + mappedFile.getFileName() + " "
+ (processOffset + mappedFileOffset));
break;
}
}
processOffset += mappedFileOffset; // @7
this.mappedFileQueue.setFlushedWhere(processOffset); // @8
this.mappedFileQueue.setCommittedWhere(processOffset); // @9
this.mappedFileQueue.truncateDirtyFiles(processOffset); // @10
if (isExtReadEnable()) {
this.consumeQueueExt.recover();
log.info("Truncate consume queue extend file by max {}", maxExtAddr);
this.consumeQueueExt.truncateByMaxAddress(maxExtAddr);
}
}
}
代码@1:获取该消息队列的所有内存映射文件。
代码@2:只从倒数第3个文件开始,这应该是一个经验值。
代码@3 :首先介绍几个局部变量。
- mappedFileSizeLogics
consumequeue 逻辑大小。 - mappedFile
该queue对应的内存映射文件。 - byteBuffer
内存映射文件对应的ByteBuffer。 - processOffset :
处理的 offset,默认从 consumequeue 中存放的第一个条目开始。
代码@4:循环验证 consumeque 包含条目的有效性(如果offset大于0并且size大于0,则表示是一个有效的条目)
代码@5:读取一个条目的内容。
- offset :commitlog中的物理偏移量
- size : 该条消息的消息总长度
- tagsCode :tag hashcode
如果offset大于0并且size大于0,则表示是一个有效的条目,设置 consumequeue 中有效的 mappedFileOffset ,继续下一个条目的验证,如果发现不正常的条目,则跳出循环。
代码@6:如果该 consumeque 文件中所有条目全部有效,则继续验证下一个文件,(index++),如果发现条目不合法,后面的文件不需要再检测。
代码@7,:processOffset 代表了当前 consuemque 有效的偏移量。
代码8,@9:设置 flushedWhere,committedWhere 为当前有效的偏移量。
代码@10:截断无效的consumeque文件。
public void truncateDirtyFiles(long offset) {
List<MappedFile> willRemoveFiles = new ArrayList<MappedFile>();
for (MappedFile file : this.mappedFiles) {
long fileTailOffset = file.getFileFromOffset() + this.mappedFileSize;
if (fileTailOffset > offset) { // @1
if (offset >= file.getFileFromOffset()) {
file.setWrotePosition((int) (offset % this.mappedFileSize));
file.setCommittedPosition((int) (offset % this.mappedFileSize));
file.setFlushedPosition((int) (offset % this.mappedFileSize));
} else {
file.destroy(1000); // @2
willRemoveFiles.add(file);
}
}
}
this.deleteExpiredFile(willRemoveFiles); // @3
}
该方法主要就是再次遍历所有的 MappedFile,如果无效的 offset 大于 该 consumeque,则无需处理。
如果无效的 offset 小于该文件最大的偏移量,如果 consumequeue 的 offset 大于失效的 offset,则该文件整个删除,如果否,则设置 wrotePosition,commitedPosition,flushedPoisition 的值即可。
由此可见,DefaultMessageStore#recoverConsumeQueue 主要要做的就是先移除非法的offset。
下面代码摘录自:DefaultMessageStore#recover
if (lastExitOK) {
this.commitLog.recoverNormally();
} else {
this.commitLog.recoverAbnormally();
}
lastExitOk 为true,表示abort文件不存在,表示是正常退出,如果abort文件存在,则表示异常退出,
1.2 commitlog正常恢复
CommitLog#recoverNormally commitlog正常恢复与 ConsumeQueue 的恢复差不多的逻辑,就不重复跟踪。
1.3 commitlog异常恢复
CommitLog#recoverAbnormally
public void recoverAbnormally() {
// recover by the minimum time stamp
boolean checkCRCOnRecover = this.defaultMessageStore.getMessageStoreConfig().isCheckCRCOnRecover();
final List<MappedFile> mappedFiles = this.mappedFileQueue.getMappedFiles();
if (!mappedFiles.isEmpty()) {
// Looking beginning to recover from which file
int index = mappedFiles.size() - 1;
MappedFile mappedFile = null;
for (; index >= 0; index--) { // @1
mappedFile = mappedFiles.get(index);
if (this.isMappedFileMatchedRecover(mappedFile)) {
log.info("recover from this maped file " + mappedFile.getFileName());
break;
}
}
if (index < 0) {
index = 0;
mappedFile = mappedFiles.get(index);
}
ByteBuffer byteBuffer = mappedFile.sliceByteBuffer();
long processOffset = mappedFile.getFileFromOffset();
long mappedFileOffset = 0;
while (true) {
DispatchRequest dispatchRequest = this.checkMessageAndReturnSize(byteBuffer, checkCRCOnRecover); // @2
int size = dispatchRequest.getMsgSize();
// Normal data
if (size > 0) {
mappedFileOffset += size;
if (this.defaultMessageStore.getMessageStoreConfig().isDuplicationEnable()) {
if (dispatchRequest.getCommitLogOffset() < this.defaultMessageStore.getConfirmOffset()) {
this.defaultMessageStore.doDispatch(dispatchRequest);
}
} else {
this.defaultMessageStore.doDispatch(dispatchRequest);
}
}
// Intermediate file read error
else if (size == -1) {
log.info("recover physics file end, " + mappedFile.getFileName());
break;
}
// Come the end of the file, switch to the next file
// Since the return 0 representatives met last hole, this can
// not be included in truncate offset
else if (size == 0) {
index++;
if (index >= mappedFiles.size()) {
// The current branch under normal circumstances should
// not happen
log.info("recover physics file over, last maped file " + mappedFile.getFileName());
break;
} else {
mappedFile = mappedFiles.get(index);
byteBuffer = mappedFile.sliceByteBuffer();
processOffset = mappedFile.getFileFromOffset();
mappedFileOffset = 0;
log.info("recover next physics file, " + mappedFile.getFileName());
}
}
}
processOffset += mappedFileOffset;
this.mappedFileQueue.setFlushedWhere(processOffset);
this.mappedFileQueue.setCommittedWhere(processOffset);
this.mappedFileQueue.truncateDirtyFiles(processOffset);
// Clear ConsumeQueue redundant data
this.defaultMessageStore.truncateDirtyLogicFiles(processOffset);
}
// Commitlog case files are deleted
else {
this.mappedFileQueue.setFlushedWhere(0);
this.mappedFileQueue.setCommittedWhere(0);
this.defaultMessageStore.destroyLogics();
}
}
代码@1:从最后一个文件开始检测,先找到第一个正常的 commitlog 文件,然后从该文件开始去恢复。查找文件的逻辑:
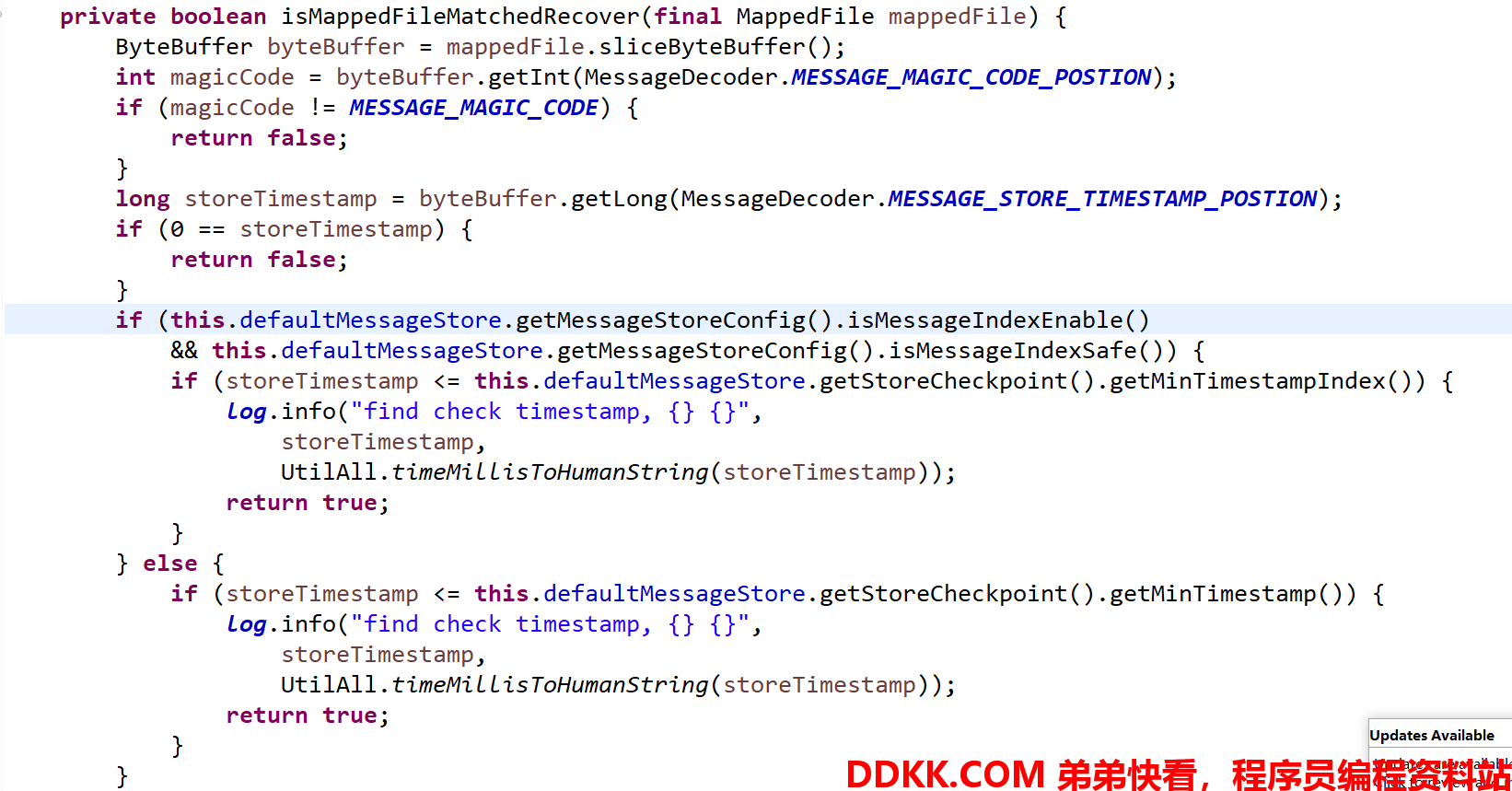
判断一个文件是否正常,主要是如下几个条件:
1、 魔数正确;
2、 消息存储时间不为0;
3、 存储时间小于等于检测点(checkpoint);
代码@2:创建转发对象,该方法在消费队列,Index索引文件存储上篇已分析过。
代码@3:转发给对象,会同步更新consumequeue,index文件
代码@4:检测到非法的 commitlog 时,停止恢复,然后设置 commitlog 的检测点,然后删除多于的不符合格式的文件。
1.4 recoverTopicQueueTable
HashMap<String/\* topic-queueid \*/, Long/\* offset \*/> topicQueueTable 恢复Commitlog 中队列的最大偏移量。
2、总结
rocketmq关于commitlog文件、消息消费ConsumeQueue队列、索引文件Index的恢复机制就介绍到这,下面我再来总结一下RocketMQ recover机制。
1、 首先先加载相关文件到内存(内存映射文件);
包含Commitlog文件、ConsumeQueue文件、存储检测点(CheckPoint)文件、索引文件。
2、 执行文件恢复;
引入临时文件 abort 来区分是否是异常启动。在存储管理启动时(DefaultMessageStore)创建 abort 文件,结束时(shutdown)会删除 abort 文件,也就是如果在启动的时候,如果发现存储在该临时文件,则认为是异常。
恢复顺序:
1、 先恢复consumeque文件,把不符合的consueme文件删除,一个consume条目正确的标准(commitlog偏移量>0size>0)[从倒数第三个文件开始恢复];
2、 如果abort文件存在,此时找到第一个正常的commitlog文件,然后对该文件重新进行转发,依次更新consumeque,index文件;