RocketMQ 刷盘支持同步刷盘和异步刷盘。为了了解其具体实现,我们以 Commitlog 的存储为例来说明 RocketMQ 是如何进行磁盘读写。
Comitlog#putMessage 首先将消息写入到 MappedFile,内存映射文件。然后根据刷盘策略刷写到磁盘,入口如下:
CommitLog#handleDiskFlush
public void handleDiskFlush(AppendMessageResult result, PutMessageResult putMessageResult, MessageExt messageExt) { // @1
// Synchronization flush
if (FlushDiskType.SYNC_FLUSH == this.defaultMessageStore.getMessageStoreConfig().getFlushDiskType()) { // @2
final GroupCommitService service = (GroupCommitService) this.flushCommitLogService;
if (messageExt.isWaitStoreMsgOK()) {
GroupCommitRequest request = new GroupCommitRequest(result.getWroteOffset() + result.getWroteBytes());
service.putRequest(request);
boolean flushOK = request.waitForFlush(this.defaultMessageStore.getMessageStoreConfig().getSyncFlushTimeout());
if (!flushOK) {
log.error("do groupcommit, wait for flush failed, topic: " + messageExt.getTopic() + " tags: " + messageExt.getTags()
+ " client address: " + messageExt.getBornHostString());
putMessageResult.setPutMessageStatus(PutMessageStatus.FLUSH_DISK_TIMEOUT);
}
} else {
service.wakeup();
}
}
// Asynchronous flush
else { // @3
if (!this.defaultMessageStore.getMessageStoreConfig().isTransientStorePoolEnable()) {
flushCommitLogService.wakeup();
} else {
commitLogService.wakeup();
}
}
}
代码@1:AppendMessageResult 参数详解。 消息写入到 MappedFile(内存映射文件中,bytebuffer)中的结果,具体属性包含:
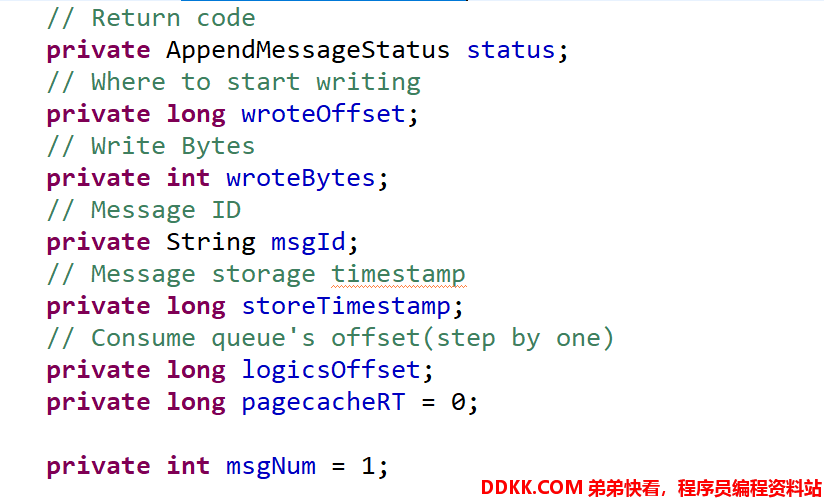
- wroteOffset
下一个写入的偏移量。 - wroteBytes
写入字节总长度。 - msgId
消息id。 - storeTimestamp
消息存储时间,也就是写入到 MappedFile 中的时间。 - logicOffset
逻辑的consumeque 偏移量。 - pagecacheRT
写入到 MappedByteBuffer (将消息内容写入到内存映射文件中的时长)。
代码@2:同步刷盘。
代码@3:异步刷盘。
1、同步刷盘线程
同步刷盘机制,核心实现类 CommitLog#GroupCommitService

同步刷盘核心类,竟然是一个线程,出乎我的意料。
1.1 核心属性
private volatile List<GroupCommitRequest> requestsWrite = new ArrayList<GroupCommitRequest>();
private volatile List<GroupCommitRequest> requestsRead = new ArrayList<GroupCommitRequest>();
- requestsWrite
写队列,主要用于向该线程添加刷盘任务。 - requestsRead
读队列,主要用于执行特定的刷盘任务,这是是 GroupCommitService 设计的一个亮点,把读写分离,每处理完requestsRead中的任务,就交换这两个队列。
1.2 putRequest 方法
添加刷盘任务。
public synchronized void putRequest(final GroupCommitRequest request) {
synchronized (this.requestsWrite) {
this.requestsWrite.add(request);
}
if (hasNotified.compareAndSet(false, true)) {
waitPoint.countDown(); // notify
}
}
该方法是很简单,就是将 GroupCommitReques t刷盘任务放入到 requestWrite 中,就返回了,但是这个类是处理同步刷盘的,那调用方什么时候才能知道该刷盘任务已经执行了呢?
不然能说是同步刷盘呢?这又是这个类另外一个设计亮点。为了解开这个疑点,首先看一下调用方法:
GroupCommitRequest request = new GroupCommitRequest(result.getWroteOffset() + result.getWroteBytes());
service.putRequest(request);
boolean flushOK = request.waitForFlush(this.defaultMessageStore.getMessageStoreConfig().getSyncFlushTimeout());
原来奥秘在这里,放入后会调用 request.waitForFlush, 类似于 Future 模式,在这方法里进行阻塞等待。
this.countDownLatch.await(timeout, TimeUnit.MILLISECONDS),默认同步刷盘超时时间为5s,那就不需要怀疑了,刷盘后,肯定会调用 countDownLatch.countDown()。
GroupCommitRequest 具体类的工作机制就不细说了,其刷盘将调用的方法为:CommitLog.this.mappedFileQueue.flush(0);
在进入具体刷盘逻辑之前,我们再看下异步刷盘线程的实现。
2、异步刷盘线程
if (!this.defaultMessageStore.getMessageStoreConfig().isTransientStorePoolEnable()) {
flushCommitLogService.wakeup();
} else {
commitLogService.wakeup();
}
public boolean isTransientStorePoolEnable() {
return transientStorePoolEnable && FlushDiskType.ASYNC_FLUSH == getFlushDiskType()
&& BrokerRole.SLAVE != getBrokerRole();
}
什么是transientStorePoolEnable ,这个只能从 FlushRealTimeService 与 CommitRealTimeService 区别中来得出。
2.1 FlushRealTimeService 实现机制
class FlushRealTimeService extends FlushCommitLogService {
private long lastFlushTimestamp = 0;
private long printTimes = 0;
public void run() {
CommitLog.log.info(this.getServiceName() + " service started");
while (!this.isStopped()) {
boolean flushCommitLogTimed = CommitLog.this.defaultMessageStore.getMessageStoreConfig().isFlushCommitLogTimed(); // @1
int interval = CommitLog.this.defaultMessageStore.getMessageStoreConfig().getFlushIntervalCommitLog(); // @2
int flushPhysicQueueLeastPages = CommitLog.this.defaultMessageStore.getMessageStoreConfig().getFlushCommitLogLeastPages(); // @3
int flushPhysicQueueThoroughInterval =
CommitLog.this.defaultMessageStore.getMessageStoreConfig().getFlushCommitLogThoroughInterval(); // @4
boolean printFlushProgress = false;
// Print flush progress
long currentTimeMillis = System.currentTimeMillis();
if (currentTimeMillis >= (this.lastFlushTimestamp + flushPhysicQueueThoroughInterval)) {
this.lastFlushTimestamp = currentTimeMillis;
flushPhysicQueueLeastPages = 0;
printFlushProgress = (printTimes++ % 10) == 0;
}
try {
if (flushCommitLogTimed) {
Thread.sleep(interval);
} else {
this.waitForRunning(interval);
}
if (printFlushProgress) {
this.printFlushProgress();
}
long begin = System.currentTimeMillis();
CommitLog.this.mappedFileQueue.flush(flushPhysicQueueLeastPages);
long storeTimestamp = CommitLog.this.mappedFileQueue.getStoreTimestamp();
if (storeTimestamp > 0) {
CommitLog.this.defaultMessageStore.getStoreCheckpoint().setPhysicMsgTimestamp(storeTimestamp);
}
long past = System.currentTimeMillis() - begin;
if (past > 500) {
log.info("Flush data to disk costs {} ms", past);
}
} catch (Throwable e) {
CommitLog.log.warn(this.getServiceName() + " service has exception. ", e);
this.printFlushProgress();
}
}
// Normal shutdown, to ensure that all the flush before exit
boolean result = false;
for (int i = 0; i < RETRY_TIMES_OVER && !result; i++) {
result = CommitLog.this.mappedFileQueue.flush(0);
CommitLog.log.info(this.getServiceName() + " service shutdown, retry " + (i + 1) + " times " + (result ? "OK" : "Not OK"));
}
this.printFlushProgress();
CommitLog.log.info(this.getServiceName() + " service end");
}
代码@1:flushCommitLogTimed 这个主要是等待方法,如果为true,则使用Thread.sleep,如果是false使用waitForRunning。
代码@2:interval :获取刷盘的间隔时间。
代码@3:flushPhysicQueueLeastPages:每次刷盘最少需要刷新的页。
代码@4:flushPhysicQueueThoroughInterval:如果上次刷新的时间+该值 小于当前时间,则改变flushPhysicQueueLeastPages =0,并每10次输出异常刷新进度。
代码@5:CommitLog.this.mappedFileQueue.flush(flushPhysicQueueLeastPages); 调用刷盘操作。
代码@6:设置检测点的StoreCheckpoint 的physicMsgTimestamp(commitlog文件的检测点,也就是记录最新刷盘的时间戳)
暂时不深入,在本节之后详细分析刷盘机制。
2.2 CommitRealTimeService
public void run() {
CommitLog.log.info(this.getServiceName() + " service started");
while (!this.isStopped()) {
int interval = CommitLog.this.defaultMessageStore.getMessageStoreConfig().getCommitIntervalCommitLog(); // @1
int commitDataLeastPages = CommitLog.this.defaultMessageStore.getMessageStoreConfig().getCommitCommitLogLeastPages(); // @2
int commitDataThoroughInterval =
CommitLog.this.defaultMessageStore.getMessageStoreConfig().getCommitCommitLogThoroughInterval(); // @3
long begin = System.currentTimeMillis();
if (begin >= (this.lastCommitTimestamp + commitDataThoroughInterval)) {
this.lastCommitTimestamp = begin;
commitDataLeastPages = 0;
}
try {
boolean result = CommitLog.this.mappedFileQueue.commit(commitDataLeastPages);
long end = System.currentTimeMillis();
if (!result) {
this.lastCommitTimestamp = end; // result = false means some data committed.
//now wake up flush thread.
flushCommitLogService.wakeup();
}
if (end - begin > 500) {
log.info("Commit data to file costs {} ms", end - begin);
}
this.waitForRunning(interval);
} catch (Throwable e) {
CommitLog.log.error(this.getServiceName() + " service has exception. ", e);
}
}
boolean result = false;
for (int i = 0; i < RETRY_TIMES_OVER && !result; i++) {
result = CommitLog.this.mappedFileQueue.commit(0);
CommitLog.log.info(this.getServiceName() + " service shutdown, retry " + (i + 1) + " times " + (result ? "OK" : "Not OK"));
}
CommitLog.log.info(this.getServiceName() + " service end");
}
}
代码@1:interval CommitRealTimeService 执行间隔
代码@2:commitDataLeastPages :每次commit最少的页数
代码@3:与上面的对应,CommitRealTimeService 与 FlushRealTimeService 不同之处,是调用的方法不一样,
FlushRealTimeService 调用mappedFileQueue.flush,而CommitRealTimeService调用commit方法。
行文至此,我们只是了解异步刷盘,同步刷盘去线程的实现方式,接下来,是时候进入到刷盘具体逻辑,也就是 Commitlog mappedFileQueue。
3、刷盘机制实现
具体实现类:MappedFileQueue。
3.1 核心属性与构造方法
private static final int DELETE_FILES_BATCH_MAX = 10;
private final String storePath;
private final int mappedFileSize;
private final CopyOnWriteArrayList<MappedFile> mappedFiles = new CopyOnWriteArrayList<MappedFile>();
private final AllocateMappedFileService allocateMappedFileService;
private long flushedWhere = 0;
private long committedWhere = 0;
private volatile long storeTimestamp = 0;
public MappedFileQueue(final String storePath, int mappedFileSize,
AllocateMappedFileService allocateMappedFileService) {
this.storePath = storePath;
this.mappedFileSize = mappedFileSize;
this.allocateMappedFileService = allocateMappedFileService;
}
- MappedFileQueue
MappedFile 的队列,也就是 MappedFile 的容器。 - storePath
文件存储路径。 - mappedFileSize
单个MappedFile文件长度。 - mappedFiles
mappedFile集合。 - allocateMappedFileService
创建 MappedFileService。 - flushedWhere
刷盘位置。 - committedWhere
commit(已提交)位置。
我们以commitlog 为例来看一下 MappedFileQueue 在什么时候创建:
this.mappedFileQueue = new MappedFileQueue(defaultMessageStore.getMessageStoreConfig().getStorePathCommitLog(),
defaultMessageStore.getMessageStoreConfig().getMapedFileSizeCommitLog(), defaultMessageStore.getAllocateMappedFileService());
其中allocateMappedFileService 为 AllocateMappedFileService,MappedFileQueue 就是 MappedFile 的队列,也就是MappedFile的容器。
- storePath
文件存储路径。 - mappedFileSize
单个MappedFile文件长度。 - mappedFiles
mappedFile集合。 - allocateMappedFileService
创建 MappedFile 的主要实现类。 - flushedWhere
刷盘位置。 - committedWhere
commit(已提交)位置。
3.2 load
public boolean load() {
File dir = new File(this.storePath);
File[] files = dir.listFiles();
if (files != null) {
// ascending order
Arrays.sort(files);
for (File file : files) {
if (file.length() != this.mappedFileSize) {
log.warn(file + "\t" + file.length()
+ " length not matched message store config value, ignore it");
return true;
}
try {
MappedFile mappedFile = new MappedFile(file.getPath(), mappedFileSize);
mappedFile.setWrotePosition(this.mappedFileSize);
mappedFile.setFlushedPosition(this.mappedFileSize);
mappedFile.setCommittedPosition(this.mappedFileSize);
this.mappedFiles.add(mappedFile);
log.info("load " + file.getPath() + " OK");
} catch (IOException e) {
log.error("load file " + file + " error", e);
return false;
}
}
}
return true;
}
该方法主要是按顺序,创建 MappedFile,值得注意的是初始化时 wrotePosition、flushedPosition、committedPosition 全设置为最大值,这要怎么玩呢?是否还记得启动时需要恢复 commitlog、consume、index文件、(recover)方法,在删除无效文件时,会重置上述指针。
接下来,我们先梳理一下目前刷盘出现的关键属性,然后进入到刷盘机制的世界中来。
1、 MappedFileQueue与MappedFile的关系;
可以这样认为,MappedFile 代表一个个物理文件,而 MappedFileQueue 代表由一个个 MappedFile 组成的一个连续逻辑的大文件。并且每一个 MappedFile 的命名已该文件在整个文件序列中的偏移量来表示。
2、 MappedFileQueue;
1)flushedWhere: 整个刷新的偏移量,针对该MappedFileQueue。
2)committedWhere:当前提交的偏移量,针对该MappedFileQueue commit与flush的区别?
3、 MappedFile;
1)wrotePosition :当前待写入位置。
2)committedPosition:已提交位置。
3)flushedPosition:已刷盘位置, 应满足:commitedPosition >= flushedPosition。
接下来,主要来看 MappedFileQueue 提交与刷盘实现逻辑。
3.3 MappedFileQueue#commit
public boolean commit(final int commitLeastPages) {
boolean result = true;
MappedFile mappedFile = this.findMappedFileByOffset(this.committedWhere, false); // @1
if (mappedFile != null) {
int offset = mappedFile.commit(commitLeastPages); // @2
long where = mappedFile.getFileFromOffset() + offset; // @3
result = where == this.committedWhere; // @4
this.committedWhere = where; // @5
}
return result;
}
代码@1:根据 committedWhere 找到具体的 MappedFile 文件。
代码@2:调用 MappedFile 的 commit 函数。
代码@3:mappedFile 返回的应该是当前 commit的偏移量,加上该文件开始的偏移,表示 MappedFileQueue 当前的提交偏移量。
代码@4:如果 result = true,则可以认为 MappedFile#commit 本次并没有执行 commit 操作。
代码@5:更新当前的 ccomitedWhere 指针。
接下来继续查看MappedFile#commit的实现。
public int commit(final int commitLeastPages) { // @1
if (writeBuffer == null) { // @2
//no need to commit data to file channel, so just regard wrotePosition as committedPosition.
return this.wrotePosition.get();
}
if (this.isAbleToCommit(commitLeastPages)) { // @3
if (this.hold()) {
commit0(commitLeastPages);
this.release();
} else {
log.warn("in commit, hold failed, commit offset = " + this.committedPosition.get());
}
}
// All dirty data has been committed to FileChannel.
if (writeBuffer != null && this.transientStorePool != null && this.fileSize == this.committedPosition.get()) {
this.transientStorePool.returnBuffer(writeBuffer);
this.writeBuffer = null;
}
return this.committedPosition.get();
}
代码@1:commitLeastPages 至少提交的页数,如果当前需要提交的数据所占的页数小于 commitLeastPages ,则不执行本次提交操作。
代码@2:如果 writeBuffer 等于null,则表示 IO 操作都是直接基于 FileChannel,所以此时返回当前可写的位置,作为committedPosition 即可,这里应该就有点 commit 是个啥意思了。如果数据先写入到 writeBuffer 中,则需要提交到FileChannel(MappedByteBuffer mappedByteBuffer)。
代码@3:判断是否可以执行提交操作。
protected boolean isAbleToCommit(final int commitLeastPages) {
int flush = this.committedPosition.get();
int write = this.wrotePosition.get();
if (this.isFull()) {
return true;
}
if (commitLeastPages > 0) {
return ((write / OS_PAGE_SIZE) - (flush / OS_PAGE_SIZE)) >= commitLeastPages;
}
return write > flush;
}
@1:如果文件写满(this.fileSize == this.wrotePosition.get()) 则可以执行 commit。
@2:如果有最小提交页数要求,则(当前写入位置/ pagesize(4k) - 当前flush位置/pagesize(4k) 大于commitLeastPages时,再提交。
@3:如果没有最新提交页数要求,则只有当前写入位置大于 flush,则可提交。
@4:执行具体的提交操作。
protected void commit0(final int commitLeastPages) {
int writePos = this.wrotePosition.get();
int lastCommittedPosition = this.committedPosition.get();
if (writePos - this.committedPosition.get() > 0) {
try {
ByteBuffer byteBuffer = writeBuffer.slice(); // @1
byteBuffer.position(lastCommittedPosition);
byteBuffer.limit(writePos);
this.fileChannel.position(lastCommittedPosition);
this.fileChannel.write(byteBuffer); // @2
this.committedPosition.set(writePos); // @3
} catch (Throwable e) {
log.error("Error occurred when commit data to FileChannel.", e);
}
}
}
代码@1:这里使用 slice 方法,主要是用的同一片内存空间,但单独的指针。
代码@2:将 bytebuf 当前 上一次 commitedPosition + 当前写位置这些数据全部写入到 FileChannel中,commit 的作用原来是将writeBuffer 中的数据写入到 FileChannel 中。
代码@3:更新committedPosition的位置。
讲到这里,commit 的作用就非常明白了,为了加深理解,该是来理解MappedFile几个核心属性的时候了。
protected int fileSize;
protected FileChannel fileChannel;
protected ByteBuffer writeBuffer = null;
protected TransientStorePool transientStorePool = null;
private long fileFromOffset;
private File file;
private MappedByteBuffer mappedByteBuffer;
- int fileSize
单个文件的大小。 - FileChannel fileChannel
文件通道。 - ByteBuffer writeBuffer
写入buffer,如果开启了 transientStorePoolEnable 时不为空,writeBuffer 使用堆外内存,消息先进入到堆外内存中。 - TransientStorePool transientStorePool
writeBuffer 池,只有在开启 transientStorePoolEnable 时生效,默认为5个。 - long fileFromOffset
该文件的起始偏移量。 - File file
物理文件。 - MappedByteBuffer mappedByteBuffer
内存映射,操作系统的 PageCache。
接下来我们再看一下 flush 方法,其实基本明了了,就是调用 FileChannel 的 force() 方法。
3.4 MappedFileQueue#flush
public boolean flush(final int flushLeastPages) {
boolean result = true;
MappedFile mappedFile = this.findMappedFileByOffset(this.flushedWhere, false);
if (mappedFile != null) {
long tmpTimeStamp = mappedFile.getStoreTimestamp();
int offset = mappedFile.flush(flushLeastPages);
long where = mappedFile.getFileFromOffset() + offset;
result = where == this.flushedWhere;
this.flushedWhere = where;
if (0 == flushLeastPages) {
this.storeTimestamp = tmpTimeStamp;
}
}
return result;
}
/**
* @return The current flushed position
*/
public int flush(final int flushLeastPages) {
if (this.isAbleToFlush(flushLeastPages)) {
if (this.hold()) {
int value = getReadPosition();
try {
//We only append data to fileChannel or mappedByteBuffer, never both.
if (writeBuffer != null || this.fileChannel.position() != 0) {
this.fileChannel.force(false);
} else {
this.mappedByteBuffer.force();
}
} catch (Throwable e) {
log.error("Error occurred when force data to disk.", e);
}
this.flushedPosition.set(value);
this.release();
} else {
log.warn("in flush, hold failed, flush offset = " + this.flushedPosition.get());
this.flushedPosition.set(getReadPosition());
}
}
return this.getFlushedPosition();
}
具体代码很好理解,就不一一分析了,就时调用 FileChannel 或 MappedByteBuffer 的 force 方法。
4、总结
RocketMQ的刷盘机制就介绍到这,我们再简单做个总结。
先讲一下 RocketMQ 的存储设计亮点:(以CommitLog为例)。
单个commitlog 文件,默认大小为 1G,由多个 commitlog 文件来存储所有的消息,commitlog 文件的命名以该文件在整个commitlog中的偏移量来命名,举例如下。
例如一个 commitlog 文件,1024个字节。
第一个文件: 00000000000000000000
第二个文件: 00000000000000001024
MappedFile 封装一个一个的 CommitLog 文件,而 MappedFileQueue 就是封装的就是一个逻辑的 commitlog 文件。mappedFile队列,从小到大排列。
使用内存映射机制,MappedByteBuffer, 具体封装类为MappedFile。
1、同步刷盘每次发送消息,消息都直接存储在 MapFile 的 mappdByteBuffer,然后直接调用 force() 方法刷写到磁盘,等到 force 刷盘成功后,再返回给调用方(GroupCommitRequest#waitForFlush)就是其同步调用的实现。
2、 异步刷盘;
分为两种情况,是否开启堆外内存缓存池,具体配置参数:MessageStoreConfig#transientStorePoolEnable。
1)transientStorePoolEnable = true
消息在追加时,先放入到 writeBuffer 中,然后定时 commit 到 FileChannel,然后定时flush。
2)transientStorePoolEnable=false(默认)
消息追加时,直接存入 MappedByteBuffer(pageCache) 中,然后定时 flush。
MappedFile 重要的指针:
- wrotePosition
当前写入的指针。 - committedPosition
上一次提交的指针 (transientStorePoolEnable=true时有效)。 - flushedPosition
上一次flush的指针。 - OS_PAGE_SIZE = 1024 * 4
一页大小,4K。
flushedPosition <= committedPosition <= wrotePosition <= fileSIze