题目地址:https://leetcode.com/problems/n-ary-tree-preorder-traversal/description/
题目描述
Given an n-ary tree, return the level order traversal of its nodes' values. (ie, from left to right, level by level).
Forexample, given a 3-ary tree:
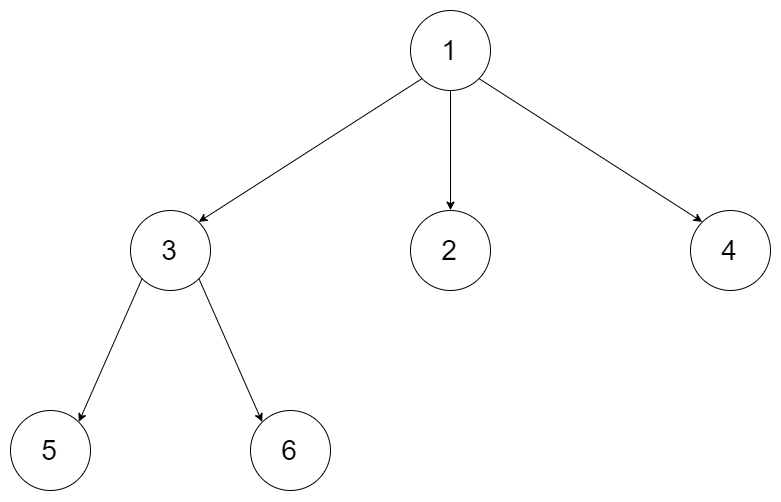
Weshould return its level order traversal:
[
[1],
[3,2,4],
[5,6]
]
Note:
1、 Thedepthofthetreeisatmost1000.;
2、 Thetotalnumberofnodesisatmost5000.;
题目大意
N叉树的层次遍历。
解题方法
方法一:BFS
首先得明白,这个N叉树是什么样的数据结构定义的。val是节点的值,children是一个列表,这个列表保存了其所有节点。
层次遍历比较好理解,就是每层的值保存在一个list中,总的再返回一个list即可。
我们知道这个属于先进先出的结构,其实就是用队列就好了。需要注意是每层都在一个list中,所以在进入队列的时候需要保存一下这个节点属于哪个层。这样当遍历它的时候,就能直接放入它那层的list的末尾即可。难点在维护这个层数。
另外犯了一个小错,当root不存在的时候应该返回的是[],而不是[[]]。
代码如下:
"""
# Definition for a Node.
class Node(object):
def __init__(self, val, children):
self.val = val
self.children = children
"""
class Solution(object):
def levelOrder(self, root):
"""
:type root: Node
:rtype: List[List[int]]
"""
if not root:
return []
queue = [(root, 0)]
res = [[]]
while queue:
node, level = queue.pop(0)
if level >= len(res):
res.append([])
res[level].append(node.val)
for child in node.children:
queue.append((child, level + 1))
return res
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 19 20 21 22 23 24 25
二刷,换了一个BFS的写法,我认为下面的这个写法更清晰,而且是个模板,可以直接交套用。
"""
# Definition for a Node.
class Node(object):
def __init__(self, val, children):
self.val = val
self.children = children
"""
class Solution(object):
def levelOrder(self, root):
"""
:type root: Node
:rtype: List[List[int]]
"""
res = []
que = collections.deque()
que.append(root)
while que:
level = []
size = len(que)
for _ in range(size):
node = que.popleft()
if not node:
continue
level.append(node.val)
for child in node.children:
que.append(child)
if level:
res.append(level)
return res
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 19 20 21 22 23 24 25 26 27 28 29
方法二:DFS
实现起来稍微难了一点,因为需要我们根据层数来添加到对应的数组里面去。不过这个比一般的递归简单的地方在于不用考虑root节点的值在什么位置进行添加,因为不在同一层,不会相互影响的。
"""
# Definition for a Node.
class Node(object):
def __init__(self, val, children):
self.val = val
self.children = children
"""
class Solution(object):
def levelOrder(self, root):
"""
:type root: Node
:rtype: List[List[int]]
"""
res = []
self.getLevel(root, res, 0)
return res
def getLevel(self, root, res, level):
if not root:
return []
if level == len(res):
res.append([])
res[level].append(root.val)
for child in root.children:
self.getLevel(child, res, level + 1)
return res
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 19 20 21 22 23 24 25 26
参考资料
637. Average of Levels in Binary Treeopen in new window
DDKK.COM 弟弟快看-教程,程序员编程资料站,版权归原作者所有
本文经作者:负雪明烛 授权发布,任何组织或个人未经作者授权不得转发