关键词:LeetCode,力扣,题解,算法,算法题,解析,C++, Java, Python,数组,重复数字,442
题目地址:https://leetcode-cn.com/problems/find-all-duplicates-in-an-array/open in new window
题目描述
给你一个长度为 n 的整数数组 nums ,其中 nums 的所有整数都在范围 [1, n] 内,且每个整数出现 一次 或 两次 。请你找出所有出现 两次 的整数,并以数组形式返回。
你必须设计并实现一个时间复杂度为 O(n) 且仅使用常量额外空间的算法解决此问题。
示例1:
输入:nums = [4,3,2,7,8,2,3,1]
输出:[2,3]
示例2:
输入:nums = [1,1,2]
输出:[1]
示例3:
输入:nums = [1]
输出:[]
提示:
1、n==nums.length;
2、1<=n<=10^5;
3、1<=nums[i]<=n;
4、nums中的每个元素出现一次或两次;
题目大意
题目让找出数组中出现两次的数字。要求时间复杂度是 O(N),空间复杂度是 O(1)。
条件:
- 数组长度是 n,每个数据的取值范围是 [1,n]
- 每个数字只出现一次或者两次
- 要求时间复杂度 O(N),空间复杂度是 O(1)
解题方法
原地修改数组
遇到这个题,你的第一思路是什么呢?
我想一定是使用 set 或者 hashmap保存已经出现过的数字、或者数字出现的次数。
但这就不符合题目的空间复杂度是 O(1),即不使用额外空间的限制条件。
我的第二个思路是对数组排序,排序后相同的数字会相邻。可是排序的时间复杂度是 O(N∗log(N))不符合题目的时间复杂度O(N)。
所以,只能祭出大杀器:「原地修改数组」了。
其实这个思路是沿着 hashmap的思路演化出来的,只要遇到过一次就学会了。
我们注意题目给出的条件:
- 数组长度是 n,每个数据的取值范围是 [1,n]
我们知道一个数组有 下标和 值两个概念,根据下标获取到值。
本题中,数组中数字的取值范围 [1,n],正好与下标的范围 [0,n−1]对应。
因此,就有一个思路,对于 nums[i] ,我们将下标 =nums[i]−1的位置的数字进行映射(还要能映射回去)。
映射方法通常有两种:
- 取反
- 增加偏移量
方法一:取反
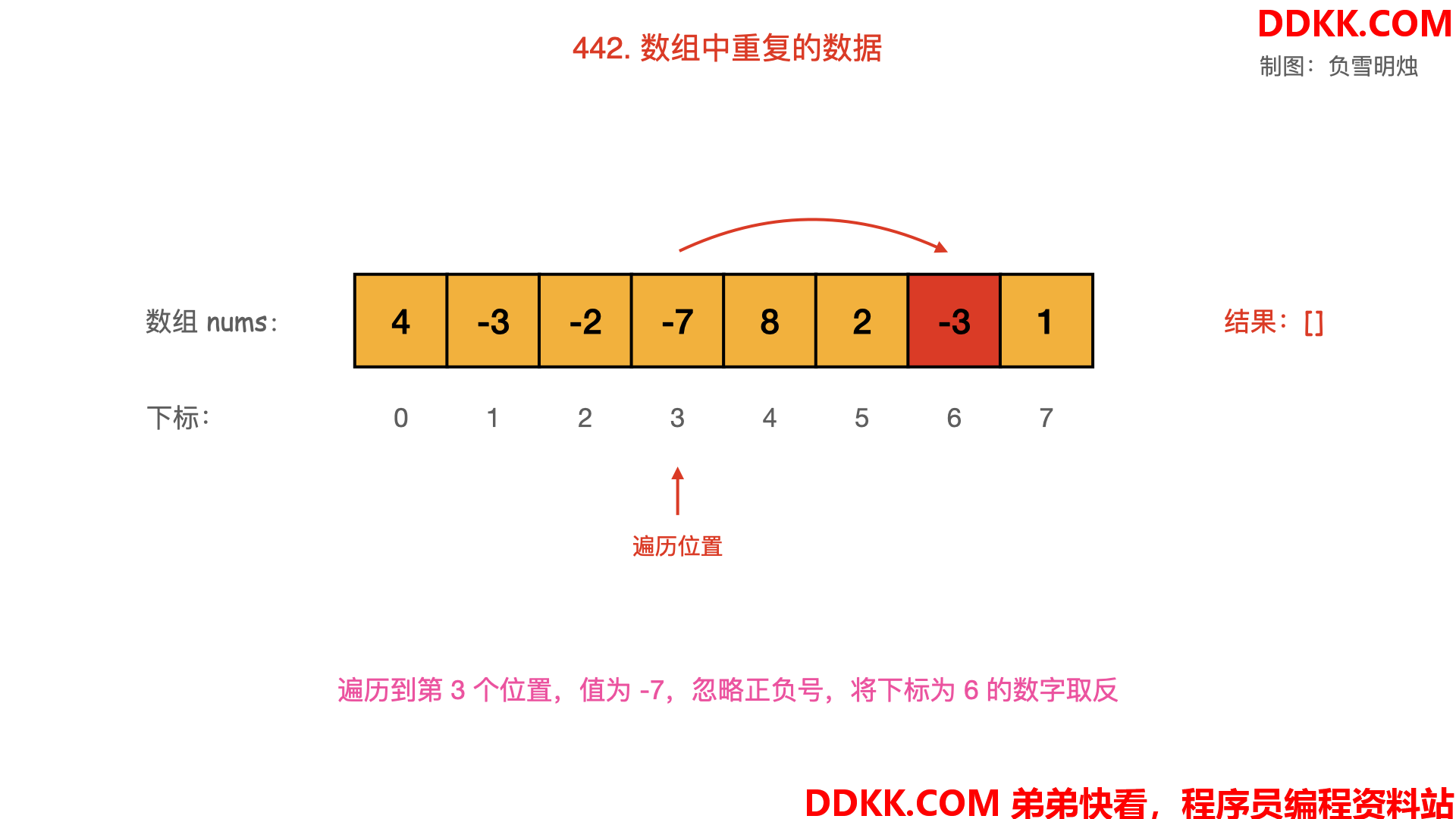
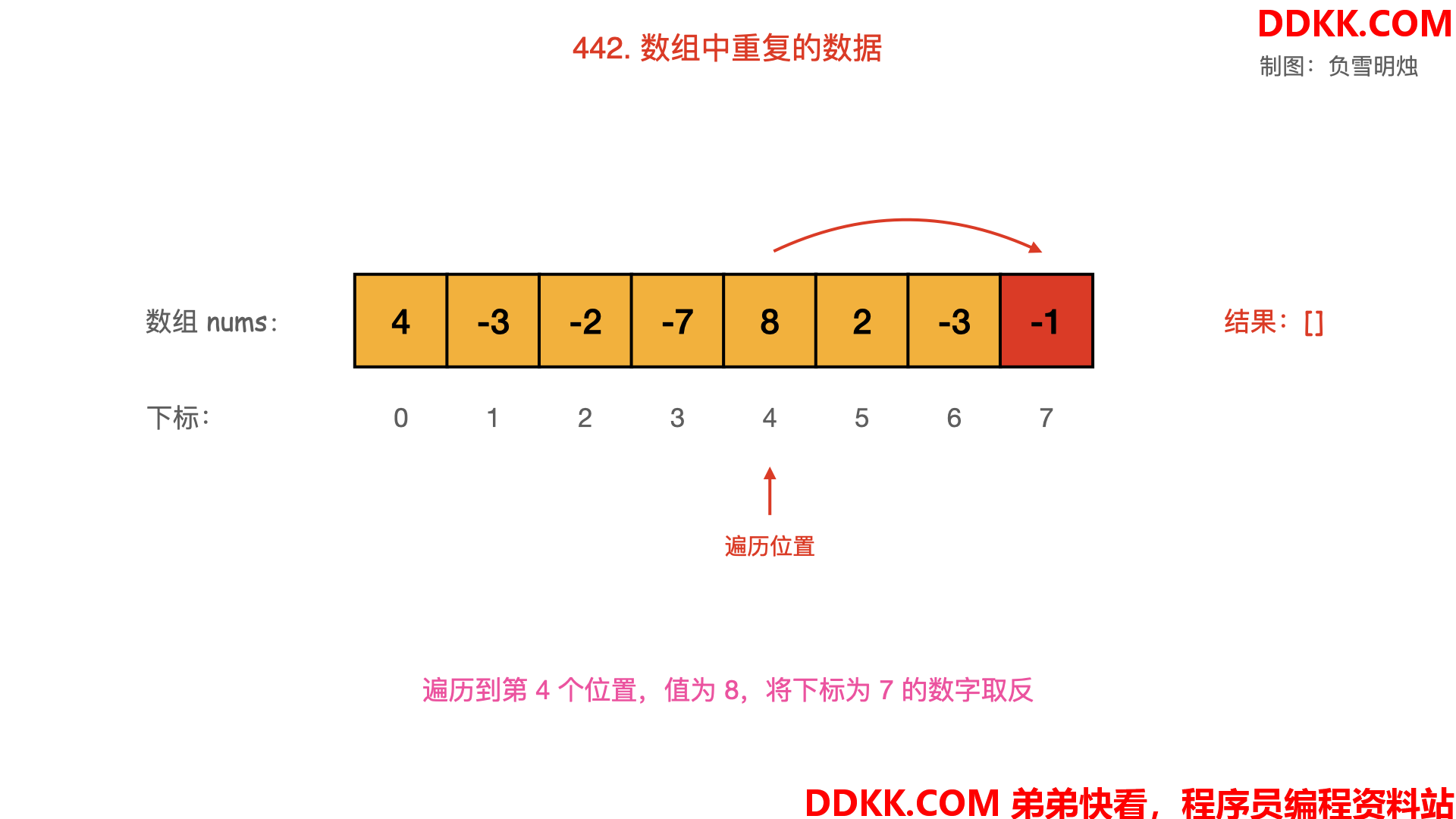
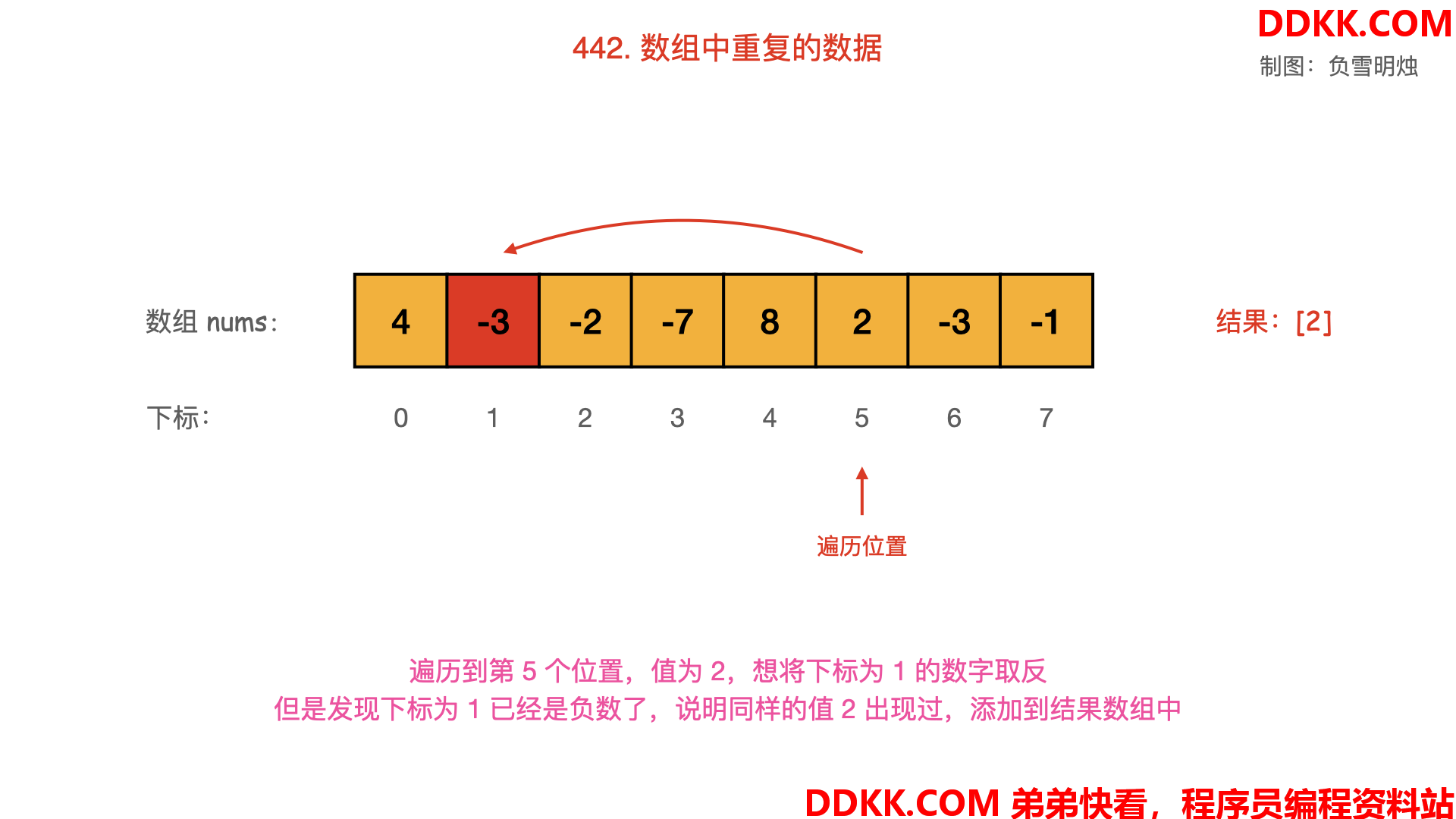
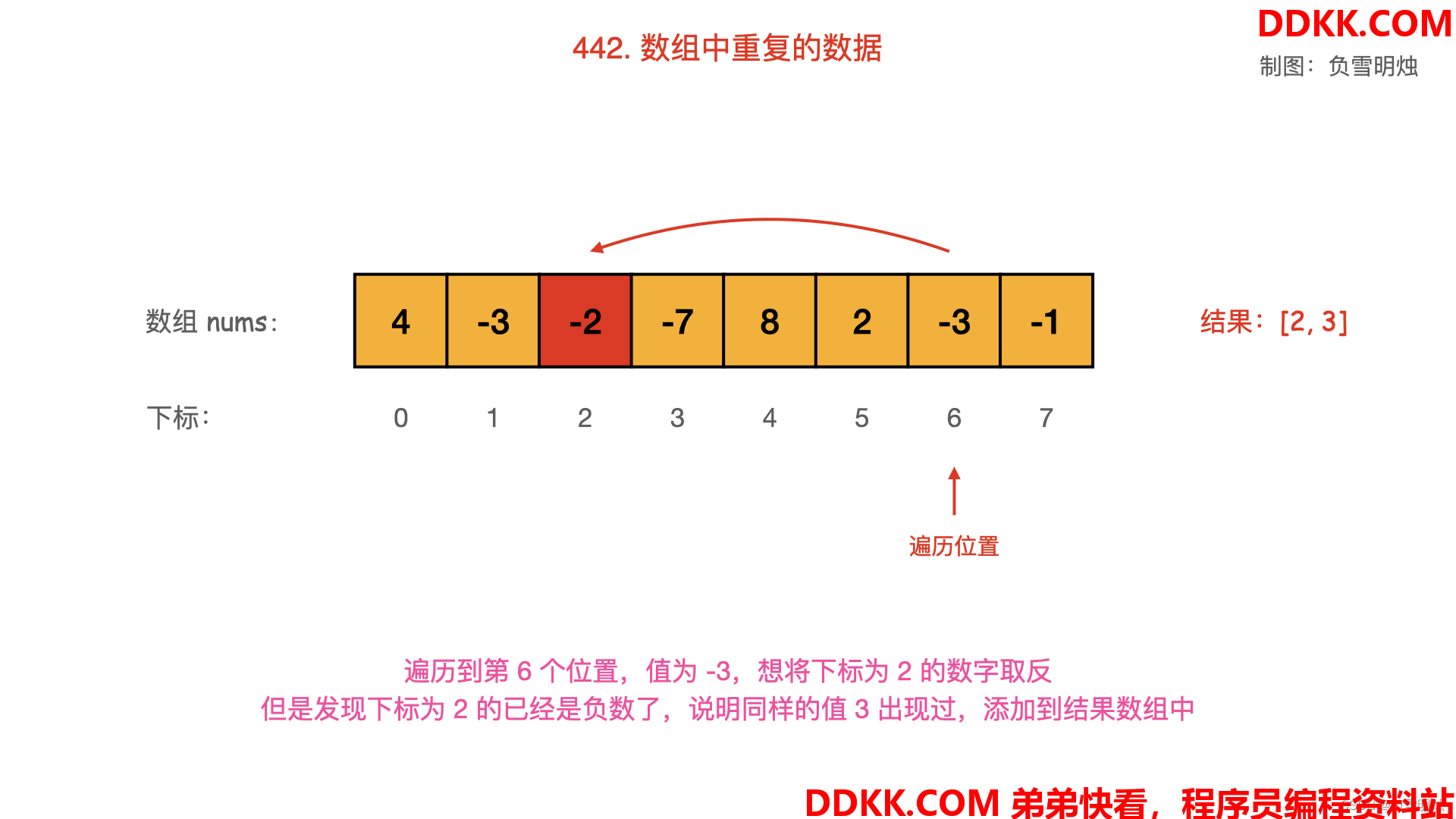
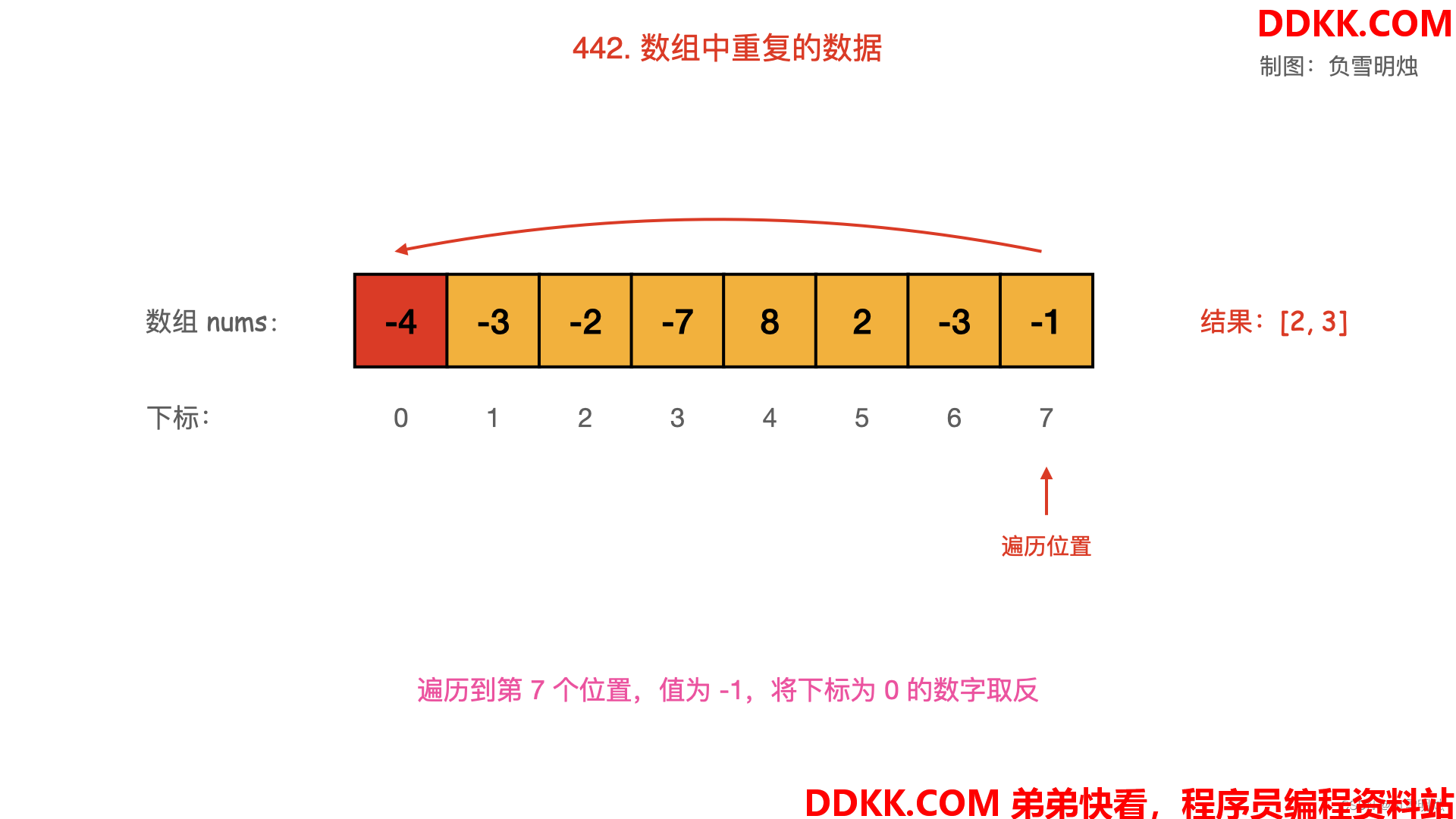
- 从起始位置进行遍历,每次将下标为 nums[i]−1的数字取反;
- 当遍历到值 nums[i] 为负数,需要忽略其负号。
- 若发现下标为 nums[i]−1的数字已经是负数,说明之前出现过同样的数字 nums[i],即找到了重复数字;
动画图解如下: 
对应的图如下,可以逐一观看:


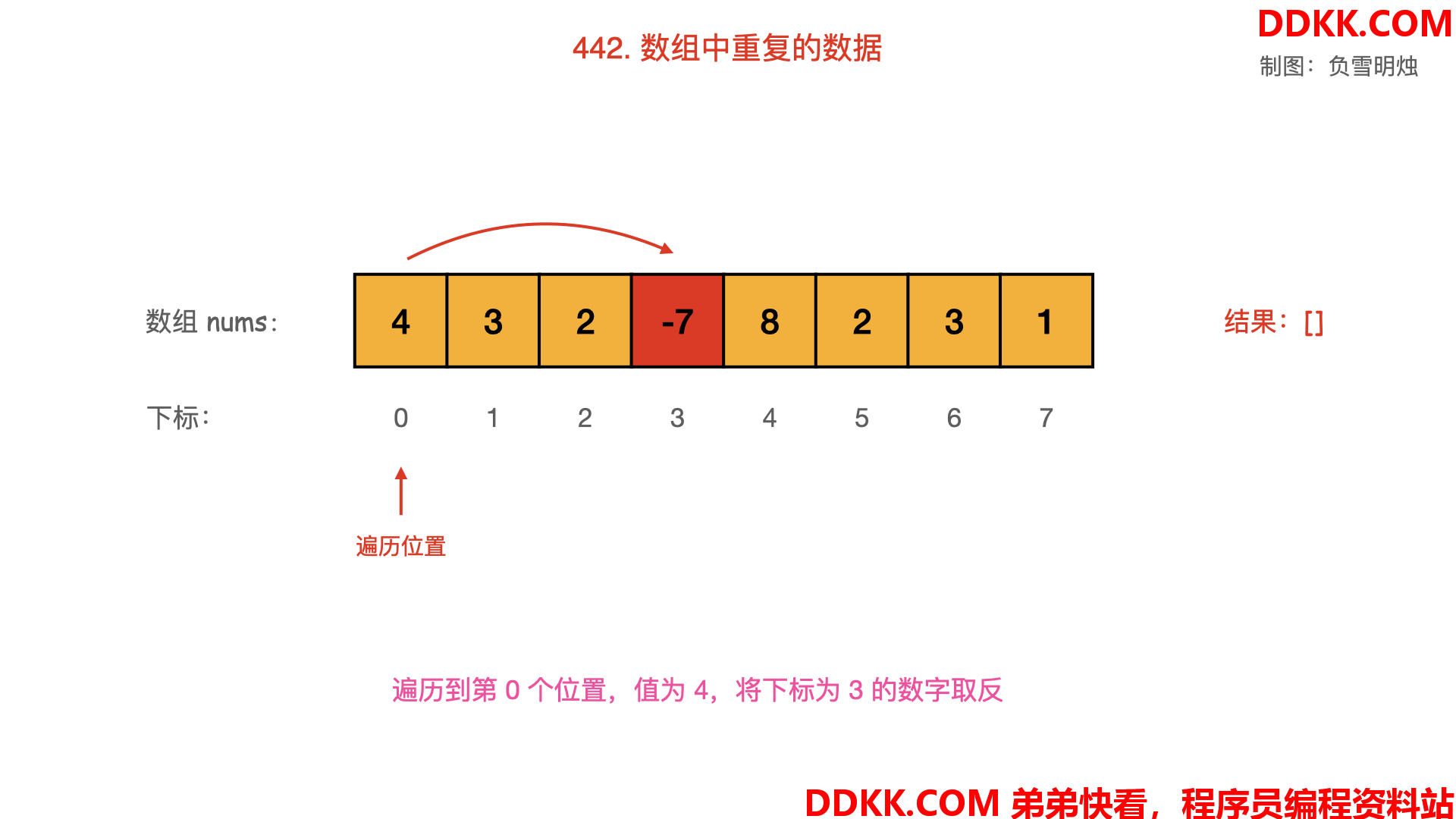
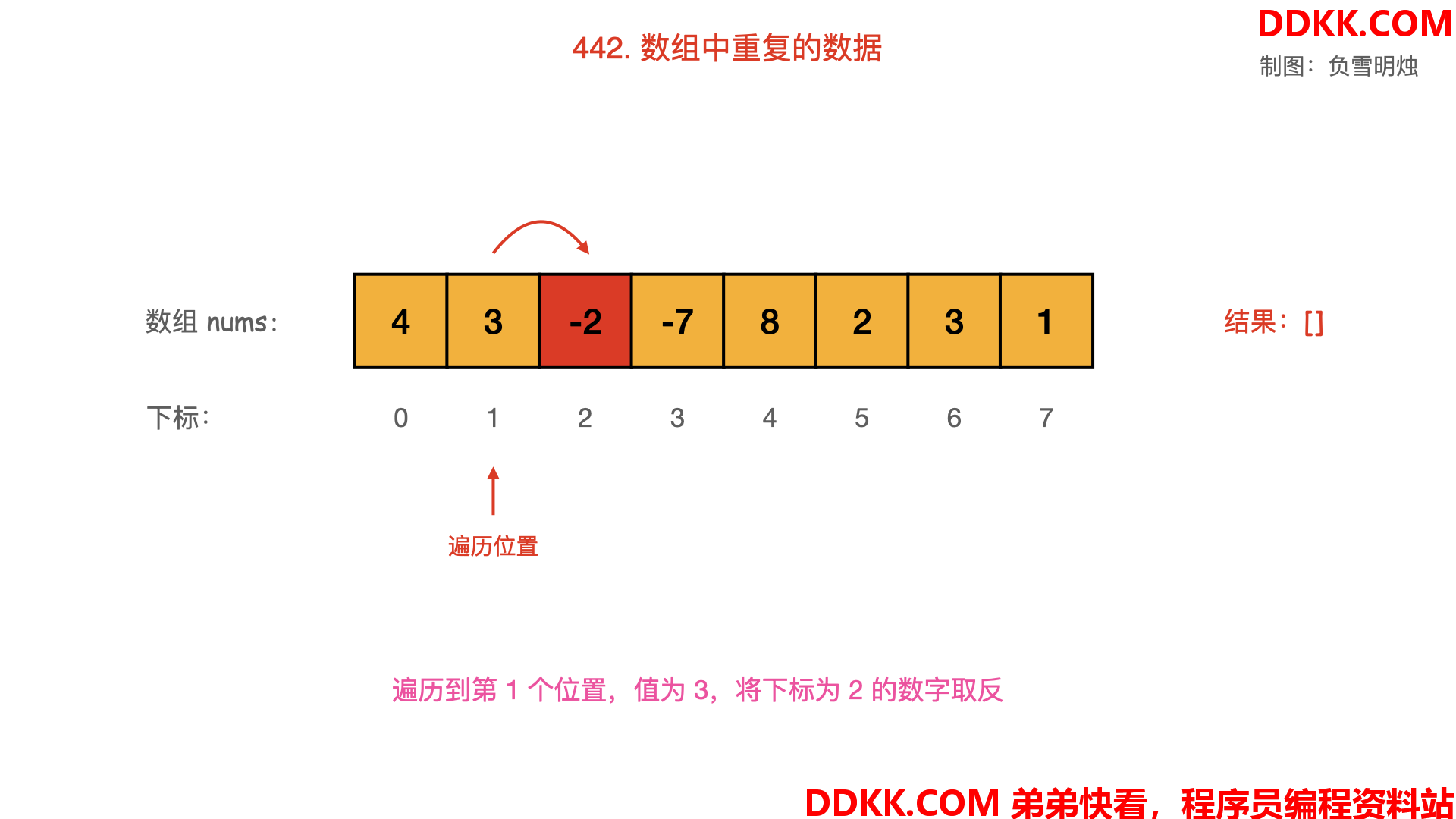
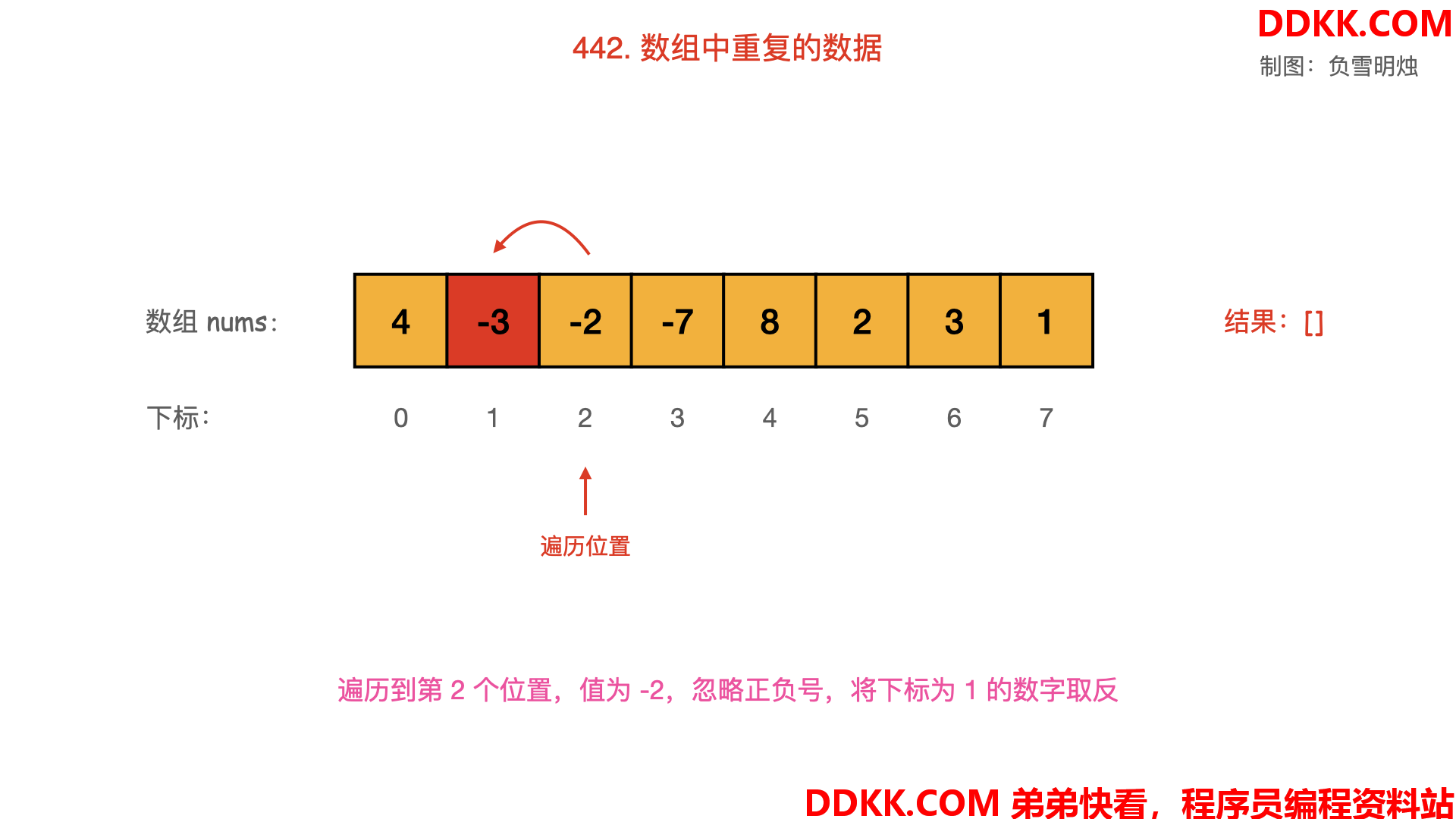

Python 语言的代码如下:
class Solution(object):
def findDuplicates(self, nums):
ans = []
for num in nums:
if nums[abs(num) - 1] < 0:
ans.append(abs(num))
nums[abs(num) - 1] *= - 1
return ans
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8
C++语言的代码如下:
class Solution {
public:
vector<int> findDuplicates(vector<int>& nums) {
const int N = nums.size();
vector<int> res;
for (int i = 0; i < N; i++) {
if (nums[abs(nums[i]) - 1] < 0)
res.push_back(abs(nums[i]));
nums[abs(nums[i]) - 1] *= -1;
}
return res;
}
};
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13
Java 语言的代码如下:
class Solution {
public List<Integer> findDuplicates(int[] nums) {
List<Integer> res = new ArrayList<>();
for (int num : nums) {
if (nums[Math.abs(num) - 1] < 0) {
res.add(Math.abs(num));
} else {
nums[Math.abs(num) - 1] *= -1;
}
}
return res;
}
}
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13
方法二:增加偏移量
除了取反之外,我们还可以增加一个偏移量,只要映射后与原数组的范围区分开就行。
思路和取反一样,只是为了映射后与映射前的数组不混淆。
比如,本题中数字的范围是 [1,105],我们可以增加一个偏移量 105,即映射到了一个新的数组空间。
做法:
- 从起始位置进行遍历,每次将下标为 nums[i]−1的数字 +100000;
- 遍历到值 nums[i]超过 100000,需要将其 −100000 恢复原值;
- 若发现下标为 nums[i]−1 的数字已经超过 100000,说明之前出现过同样的数字 nums[i],即找到了重复数字;
Python 语言的代码如下:
class Solution(object):
def findDuplicates(self, nums):
res = []
for num in nums:
if nums[(num % 100000) - 1] > 100000:
res.append(num % 100000)
else:
nums[(num % 100000) - 1] += 100000
return res
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9
C++语言的代码如下:
class Solution {
public:
vector<int> findDuplicates(vector<int>& nums) {
vector<int> res;
for (int num : nums) {
if (nums[(num % 100000) - 1] > 100000) {
res.push_back(num % 100000);
}
nums[(num % 100000) - 1] += 100000;
}
return res;
}
};
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13
Java 语言的代码如下:
class Solution {
public List<Integer> findDuplicates(int[] nums) {
List<Integer> res = new ArrayList<>();
for (int num : nums) {
if (nums[(num % 100000) - 1] > 100000) {
res.add(num % 100000);
} else {
nums[(num % 100000) - 1] += 100000;
}
}
return res;
}
}
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13
复杂度
- 时间复杂度:O(N)
- 空间复杂度:O(1)
总结
1、 这个题是技巧题目,看懂了我的题解以后,以后遇到同样的题目,应该就会了;
DDKK.COM 弟弟快看-教程,程序员编程资料站,版权归原作者所有
本文经作者:负雪明烛 授权发布,任何组织或个人未经作者授权不得转发