路由可是说是Angular4非常重要的一个功能,这篇文章中我们将会继续使用Tour Of Heroes的例子来学习路由的使用方法。
学习目标
具体来说我们将学会:
- 使用Angular路由进行导航
- 设定路由参数
- 使用管道格式化数据
- 在多个组件之间共享服务
- 使用管道进行数据修饰
学习时间
大概需要十分钟。
事前准备
在上一篇文章全部都用来拆结构,这篇文章仍然非常俗套,从拆结构开始吧。
拆出heroes.component.ts
上篇文章中我们把HeroDetail拆了出来,这次把Hero的list也拆出来,改名为heroes.component.ts,只需要修改两处
- * class的名称 *
- * privoders的内容移到app.module.ts中 *
/workspace/HelloAngular/src/app cat heroes.component.ts
import { Component } from '@angular/core';
import { OnInit } from '@angular/core';
import { Hero } from './hero';
import { HeroService } from './hero.service';
@Component({
selector: 'my-heroes',
templateUrl: './heroes.component.html',
styleUrls: ['./heroes.component.css'],
providers: []
})
export class HeroesComponent implements OnInit {
title = 'Tour of Heroes';
selectedHero: Hero;
heroes: Hero[];
onSelect(hero: Hero): void {
this.selectedHero = hero;
}
ngOnInit(): void{
this.heroService.getHeroes().then(heroes => this.heroes = heroes);
}
constructor(private heroService: HeroService) {
}
}
/workspace/HelloAngular/src/app
另外,将如下两个文件进行重新命名
| 项番 | 改名前 | 改名后 |
|---|---|---|
| No.1 | app.component.html | heroes.component.html |
| No.2 | app.component.css | heroes.component.css |
新的app.component.ts
重新做一个没有任何实际内容的app.component.ts,这个壳基本上不再会改了。
/workspace/HelloAngular/src/app cat app.component.ts
import { Component } from '@angular/core';
@Component({
selector: 'app-root',
templateUrl: './app.component.html',
styleUrls: ['./app.component.css']
})
export class AppComponent {
title = 'Tour of Heroes';
}
/workspace/HelloAngular/src/app
app.component.css可以先touch一个文件放在那就可以,先不必设定css,而html模板文件则是使用刚刚创建的my-heroes
/workspace/HelloAngular/src/app cat app.component.ts
import { Component } from '@angular/core';
@Component({
selector: 'app-root',
templateUrl: './app.component.html',
styleUrls: ['./app.component.css']
})
export class AppComponent {
title = 'Tour of Heroes';
}
/workspace/HelloAngular/src/app
app.module.ts
把东西都放到根模块里面:
/workspace/HelloAngular/src/app cat app.module.ts
import { BrowserModule } from '@angular/platform-browser';
import { NgModule } from '@angular/core';
import { FormsModule } from '@angular/forms';
import { AppComponent } from './app.component';
import { HeroDetailComponent } from './hero-detail.component'
import { HeroService } from './hero.service';
import { HeroesComponent } from './heroes.component';
@NgModule({
declarations: [
AppComponent,
HeroDetailComponent,
HeroesComponent
],
imports: [
BrowserModule,
FormsModule
],
providers: [HeroService],
bootstrap: [AppComponent]
})
export class AppModule { }
/workspace/HelloAngular/src/app
结果确认
看到如下丑陋而熟悉的页面,我们知道,准备结束了。最上面那行没有样式的Tour of Heroes是刚刚新添的app.component.ts中的内容,而旧的还没有删除,所以目前显示了两行

第一个路由例子
BASE HREF
确认index.html中已经设定了base href
/workspace/HelloAngular/src cat index.html
<!doctype html>
<html lang="en">
<head>
<meta charset="utf-8">
<title>HelloAngular</title>
<base href="/">
<meta name="viewport" content="width=device-width, initial-scale=1">
<link rel="icon" type="image/x-icon" href="favicon.ico">
</head>
<body>
<app-root></app-root>
</body>
</html>
/workspace/HelloAngular/src
路由配置
我们首先在跟模块下进行路由的配置,设定内容如下
RouterModule.forRoot([
{
path: 'heroes',
component: HeroesComponent
}
])
RouterModule是Angular/router下的一个模块,也需要import进来,路由定义包含的两项内容path和component的具体含义如下:
| 项目 | 说明 |
|---|---|
| Path | 用来匹配浏览器中的URL,将会使用heroes进行匹配 |
| Component | URL匹配的组件,比如上例中为刚刚创建的HeroesComponent的列表 |
Outlet
这样最简单的路由的定义和准备就完成了,然后我们需要定义导航的链接和位置,可以通过routerLink和router-outlet来实现,让我们简单来修改一下app.component.html的内容,将其修改成如下内容:
/workspace/HelloAngular/src/app cat app.component.html
<h1>{
{
title}}</h1>
<a routerLink="/heroes">Heroes</a>
<router-outlet></router-outlet>
/workspace/HelloAngular/src/app
routerLink将会显示一个链接,而router-outlet则指示位置
结果确认
显示如下页面信息
当点击链接或者在URL中输入/heroes进行导航,都能得到一样的页面信息

多个路由
看完第一个路由的例子之后,我们将在这个基础上稍作变化,创建一个仪表盘进行多个视图间的切换。
添加仪表盘
创建一个新的组件,并进行显示,首先生成dashboard.component.ts
/workspace/HelloAngular/src/app cat dashboard.component.ts
import { Component } from '@angular/core';
@Component({
selector: 'my-dashboard',
templateUrl: './dashboard.component.html',
styleUrls: ['./dashboard.component.css']
})
export class DashboardComponent {
title="My Dashboard";
}
/workspace/HelloAngular/src/app
仅有一个插值表达式的HTML模板页面以及touch的空css文件
/workspace/HelloAngular/src/app cat dashboard.component.html
<h3>{
{
title}}</h3>
/workspace/HelloAngular/src/app cat dashboard.component.css
/workspace/HelloAngular/src/app
设定基本的module信息
/workspace/HelloAngular/src/app cat app.module.ts
import { BrowserModule } from '@angular/platform-browser';
import { NgModule } from '@angular/core';
import { FormsModule } from '@angular/forms';
import { RouterModule } from '@angular/router';
import { AppComponent } from './app.component';
import { HeroDetailComponent } from './hero-detail.component'
import { HeroService } from './hero.service';
import { HeroesComponent } from './heroes.component';
import { DashboardComponent } from './dashboard.component';
@NgModule({
declarations: [
AppComponent,
HeroDetailComponent,
HeroesComponent,
DashboardComponent
],
imports: [
BrowserModule,
FormsModule,
RouterModule.forRoot([
{
path: 'heroes',
component: HeroesComponent
},
{
path: 'dashboard',
component: DashboardComponent
}
])
],
providers: [HeroService],
bootstrap: [AppComponent]
})
export class AppModule { }
/workspace/HelloAngular/src/app
结果确认
因为页面目前没有添加占位符之类的,所以直接http://localhost:4200不会有变化,但是使用dashboard进行导航的话,会正常显示插值表达式的内容
重定向
目前只是当使用dashboard的时候才会显示dashboard的信息,如果希望缺省会重定向路由到/dashboard则可以使用redirectTo指令,具体添加如下信息:
{
path: '',
redirectTo: '/dashboard',
pathMatch: 'full'
},
添加上述信息后的app.module.ts:
而此时如果使用http://localhost:4200的URL进行访问,则会产生和刚刚一样的结果,唯一不同的是这次是被自动的重定向到的这个页面
多个导航链接
在此基础上,将Dashboard的链接也追加进去,只需要修改该app.component.ts文件:
/workspace/HelloAngular/src/app cat app.component.html
<h1>{
{
title}}</h1>
<nav>
<a routerLink="/dashboard">Dashboard</a>
<a routerLink="/heroes">Heroes</a>
</nav>
<router-outlet></router-outlet>
/workspace/HelloAngular/src/app
结果确认如下,可以看到已有两个导航链接了:
显示Top Heroes
将dashboard的内容稍作调整,显示前四位的Heroes,在dashboard.component.ts中取出前四位,放到heroes中
/workspace/HelloAngular/src/app cat dashboard.component.ts
import { Component } from '@angular/core';
import { OnInit } from '@angular/core';
import { Hero } from './hero';
import { HeroService } from './hero.service';
@Component({
selector: 'my-dashboard',
templateUrl: './dashboard.component.html',
styleUrls: ['./dashboard.component.css']
})
export class DashboardComponent implements OnInit {
title = "Top Heroes";
heroes: Hero[] = [];
constructor(private heroService: HeroService) { }
ngOnInit(): void {
this.heroService.getHeroes()
.then(heroes => this.heroes = heroes.slice(0, 4));
}
}
/workspace/HelloAngular/src/app
在HTML模板页面中,使用ngFor将数据进行显示
/workspace/HelloAngular/src/app cat dashboard.component.html
<h3>{
{
title}}</h3>
<div class="grid grid-pad">
<div *ngFor="let hero of heroes" class="col-1-4">
<div class="module hero">
<h4>{
{
hero.name}}</h4>
</div>
</div>
</div>
/workspace/HelloAngular/src/app
这样我们就得到了这样的一个页面信息

修改css,使其变得好看一些
/workspace/HelloAngular/src/app cat dashboard.component.css
[class*='col-'] {
float: left;
padding-right: 20px;
padding-bottom: 20px;
}
[class*='col-']:last-of-type {
padding-right: 0;
}
a {
text-decoration: none;
}
*, *:after, *:before {
-webkit-box-sizing: border-box;
-moz-box-sizing: border-box;
box-sizing: border-box;
}
h3 {
text-align: center; margin-bottom: 0;
}
h4 {
position: relative;
}
.grid {
margin: 0;
}
.col-1-4 {
width: 25%;
}
.module {
padding: 20px;
text-align: center;
color:eee;
max-height: 120px;
min-width: 120px;
background-color:607D8B;
border-radius: 2px;
}
.module:hover {
background-color:EEE;
cursor: pointer;
color:607d8b;
}
.grid-pad {
padding: 10px 0;
}
.grid-pad > [class*='col-']:last-of-type {
padding-right: 20px;
}
@media (max-width: 600px) {
.module {
font-size: 10px;
max-height: 75px; }
}
@media (max-width: 1024px) {
.grid {
margin: 0;
}
.module {
min-width: 60px;
}
}
/workspace/HelloAngular/src/app
经过css修饰的页面,现在变成了这样,所以你可以看出每个组件的装饰器为什么都要设定这三个东西了。

顺便修改一下app.component.css的页面布局
h1 {
font-size: 1.2em;
color:999;
margin-bottom: 0;
}
h2 {
font-size: 2em;
margin-top: 0;
padding-top: 0;
}
nav a {
padding: 5px 10px;
text-decoration: none;
margin-top: 10px;
display: inline-block;
background-color:eee;
border-radius: 4px;
}
nav a:visited, a:link {
color:607D8B;
}
nav a:hover {
color:039be5;
background-color:CFD8DC;
}
nav a.active {
color:039be5;
}
这样现在页面变成这样了:

配置路由参数
现在所显示的4个Top Heroes,我们希望点击每个Hero的时候会直接使用HeroDetailComponent进行显示。还记得在英雄列表里面的单机实现的方式么?我们实际使用的绑定的方式,通过绑定组件中的hero属性,从而进行数据的传递。
/workspace/HelloAngular/src/app cat heroes.component.html
<h1>{
{
title}}</h1>
<h2>My Heroes</h2>
<ul class="heroes">
<li *ngFor="let hero of heroes" [class.selected]="hero === selectedHero" (click)="onSelect(hero)">
<span class="badge">{
{
hero.id}}</span> {
{
hero.name}}
</li>
</ul>
<hero-detail [hero]="selectedHero"></hero-detail>
/workspace/HelloAngular/src/app
但是在路由这里却碰到了一点问题,一般来说我们不会希望在URL里面嵌入一个对象的,一般来说在这里可以传递一个Hero的id倒是经常的做法,于是这引出了一个问题,路由的时候如何进行参数的传递,具体格式如下
{
path: 'detail/:id',
component: HeroDetailComponent
},
detail/:id中的冒号 (:) 表示:id是一个占位符,当导航到组件HeroDetailComponent时,它将被填入一个特定的id。
事前准备
在做这个之前,我们先做两件事情来热一下身,首先在给Hero组件添加一个按Id取对象的函数:
/workspace/HelloAngular/src/app cat hero.service.ts
import { Injectable } from '@angular/core';
import { Hero } from './hero';
import { HEROES } from './mock-heroes';
@Injectable()
export class HeroService {
getHeroes(): Promise<Hero[]> {
return Promise.resolve(HEROES);
}
getHero(id: number): Promise<Hero> {
return this.getHeroes()
.then(heroes => heroes.find(hero => hero.id === id));
}
}
/workspace/HelloAngular/src/app
然后稍微休整一下hero-detail.component.ts文件
/workspace/HelloAngular/src/app cat hero-detail.component.ts
import { Component, Input } from '@angular/core';
import { OnInit } from '@angular/core';
import { ActivatedRoute, ParamMap } from '@angular/router';
import 'rxjs/add/operator/switchMap';
import { Hero } from './hero';
import { HeroService } from './hero.service';
@Component({
selector: 'hero-detail',
template:
<div *ngIf="hero">
<h2>{
{hero.name}} details!</h2>
<div><label>id: </label>{
{hero.id}}</div>
<div>
<label>name: </label>
<input [(ngModel)]="hero.name" placeholder="name"/>
</div>
</div>
})
export class HeroDetailComponent implements OnInit {
@Input() hero: Hero;
constructor(
private heroService: HeroService,
private route: ActivatedRoute
) {
}
ngOnInit(): void {
this.route.paramMap
.switchMap((params: ParamMap) => this.heroService.getHero(+params.get('id')))
.subscribe(hero => this.hero = hero);
}
}
/workspace/HelloAngular/src/app
其实做了这样几件事情:
- 添加了构造函数
- 添加了LifeHook的OnInit
- 通过ActivatedRoute使用id来取得相关的数据
整体修改完毕之后,页面没有发生变化

设定路由参数
修改dashboard.component.html,从
<div *ngFor="let hero of heroes" class="col-1-4">
修改为
<div *ngFor="let hero of heroes" [routerLink]="['/detail', hero.id]" class="col-1-4">
这样则就将参数传递过去了,再点击每个Hero的时候,就会直接链接到详细信息
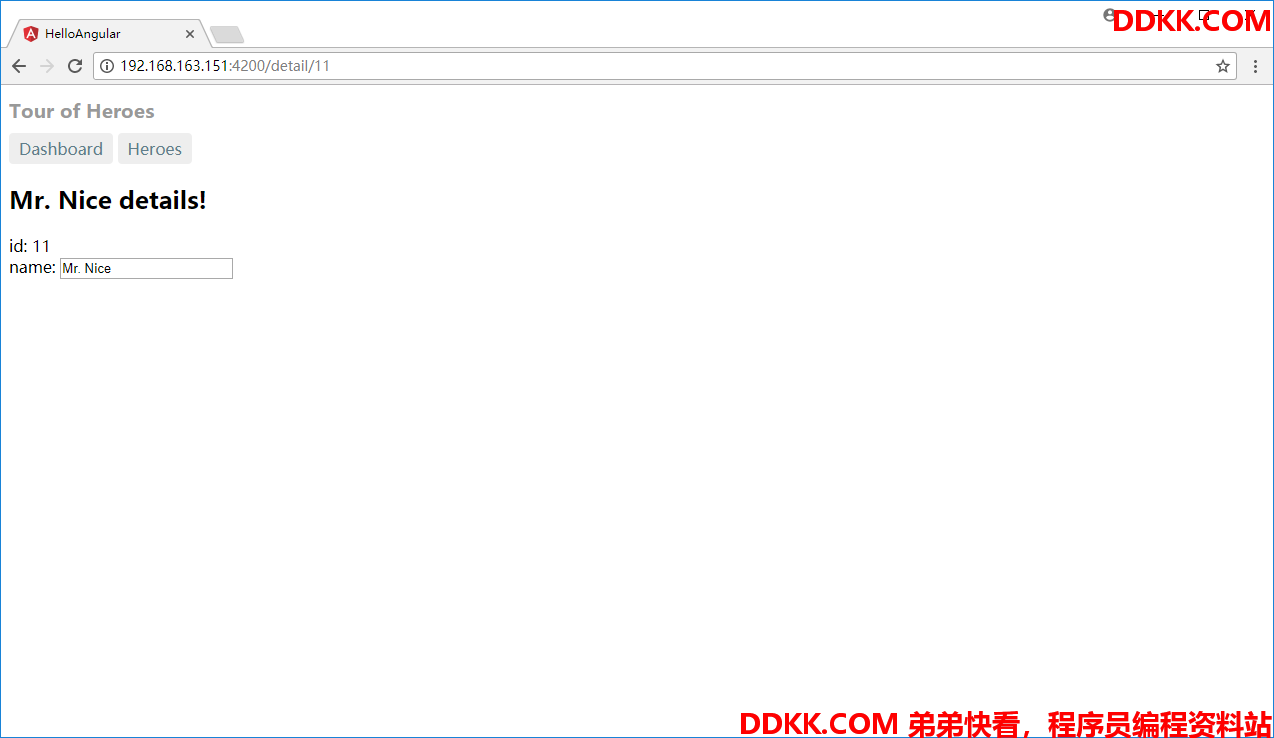
Location
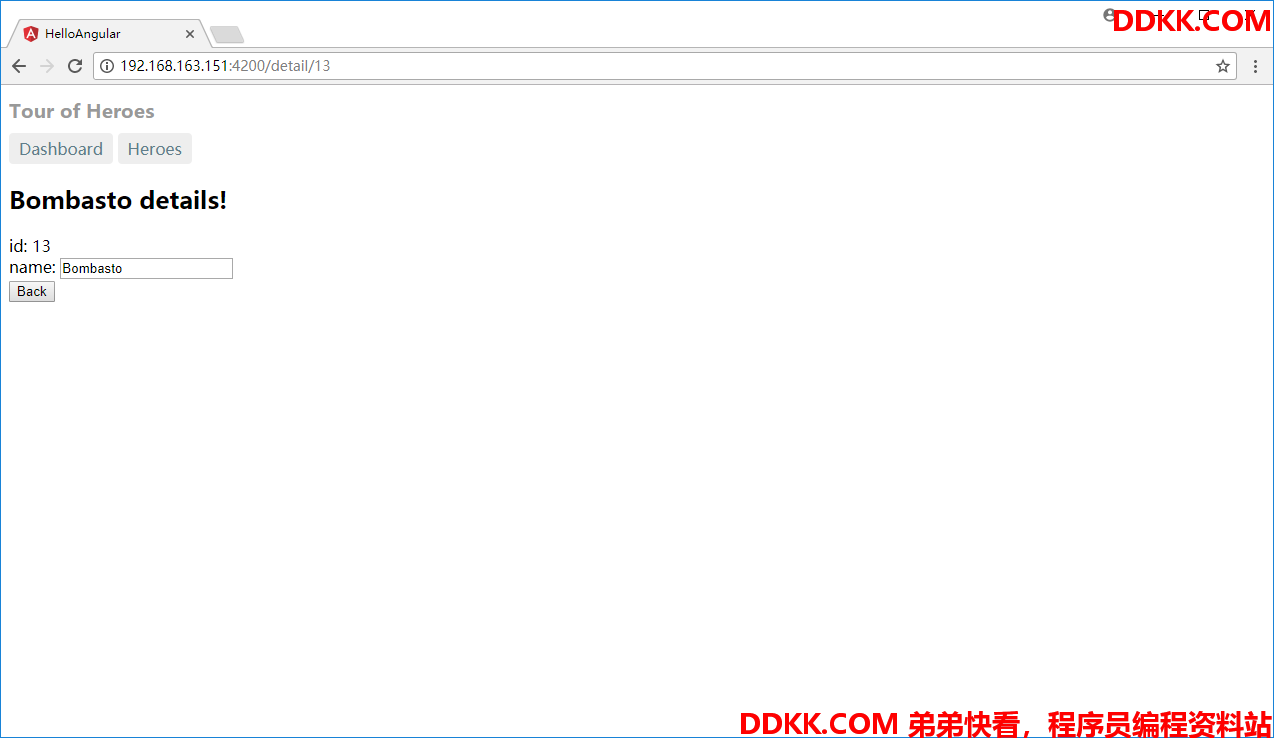
点击每个Hero会到详细信息页面,我们可以利用@angular/common的Location进行回退,当然在实际的项目中往往要结合CanDeactivate进行使用,这里我们就简单看一下其back函数的动作。
我们在hero-detail.component.ts中添加一个goBack函数,利用注入的location服务进行回退,然后再加一个回退的按钮与之关联,具体代码如下:
/workspace/HelloAngular/src/app cat hero-detail.component.ts
import { Component, Input } from '@angular/core';
import { OnInit } from '@angular/core';
import { ActivatedRoute, ParamMap } from '@angular/router';
import { Location } from '@angular/common';
import 'rxjs/add/operator/switchMap';
import { Hero } from './hero';
import { HeroService } from './hero.service';
@Component({
selector: 'hero-detail',
template:
<div *ngIf="hero">
<h2>{
{hero.name}} details!</h2>
<div><label>id: </label>{
{hero.id}}</div>
<div>
<label>name: </label>
<input [(ngModel)]="hero.name" placeholder="name"/>
</div>
<button (click)="goBack()">Back</button>
</div>
})
export class HeroDetailComponent implements OnInit {
@Input() hero: Hero;
constructor(
private heroService: HeroService,
private route: ActivatedRoute,
private location: Location
) {
}
ngOnInit(): void {
this.route.paramMap
.switchMap((params: ParamMap) => this.heroService.getHero(+params.get('id')))
.subscribe(hero => this.hero = hero);
}
goBack(): void {
this.location.back();
}
}
/workspace/HelloAngular/src/app
可以看出增加了一个back的按钮,点击则会回退到刚才的页面。
路由模块
我们通过在app.module.ts中设定路由信息来达到整体路由设定的目的,可以想象,稍微复杂一点之后app.module.ts将会充满了路由设定信息,在实际的项目开发中更多的是将路由模块进行独立,我们将其抽出形成一个独立的路由模块,依据惯例其应该包含routing一词,并对其相应的组件。我们创建一个app-routing.module.ts文件:
/workspace/HelloAngular/src/app cat app-routing.module.ts
import { NgModule } from '@angular/core';
import { RouterModule, Routes } from '@angular/router';
import { DashboardComponent } from './dashboard.component';
import { HeroesComponent } from './heroes.component';
import { HeroDetailComponent } from './hero-detail.component';
const routes: Routes = [
{ path: '', redirectTo: '/dashboard', pathMatch: 'full' },
{ path: 'dashboard', component: DashboardComponent },
{ path: 'detail/:id', component: HeroDetailComponent },
{ path: 'heroes', component: HeroesComponent }
];
@NgModule({
imports: [ RouterModule.forRoot(routes) ],
exports: [ RouterModule ]
})
export class AppRoutingModule {}
/workspace/HelloAngular/src/app
这样,app.module.ts就会得到很大的简化:
/workspace/HelloAngular/src/app cat app.module.ts
import { BrowserModule } from '@angular/platform-browser';
import { NgModule } from '@angular/core';
import { FormsModule } from '@angular/forms';
import { AppComponent } from './app.component';
import { HeroDetailComponent } from './hero-detail.component'
import { HeroService } from './hero.service';
import { HeroesComponent } from './heroes.component';
import { DashboardComponent } from './dashboard.component';
import { AppRoutingModule } from './app-routing.module';
@NgModule({
declarations: [
AppComponent,
HeroDetailComponent,
HeroesComponent,
DashboardComponent
],
imports: [
BrowserModule,
FormsModule,
AppRoutingModule
],
providers: [HeroService],
bootstrap: [AppComponent]
})
export class AppModule { }
/workspace/HelloAngular/src/app
确认之后,发现页面仍然跟修改之前一样正常动作。
管道
我们在shell中使用find . -name ‘*.ts’ |xargs grep -i routing就可以使用管道很方便的操作,在Angular中也可以直接使用管道做很多事情,修改前的heroes.component.html是这样的:
/workspace/HelloAngular/src/app cat heroes.component.html
<h1>{
{
title}}</h1>
<h2>My Heroes</h2>
<ul class="heroes">
<li *ngFor="let hero of heroes" [class.selected]="hero === selectedHero" (click)="onSelect(hero)">
<span class="badge">{
{
hero.id}}</span> {
{
hero.name}}
</li>
</ul>
<hero-detail [hero]="selectedHero"></hero-detail>
/workspace/HelloAngular/src/app
我们把它修改成如下内容:
/workspace/HelloAngular/src/app cat heroes.component.html
<h1>{
{
title}}</h1>
<h2>My Heroes</h2>
<ul class="heroes">
<li *ngFor="let hero of heroes" [class.selected]="hero === selectedHero" (click)="onSelect(hero)">
<span class="badge">{
{
hero.id}}</span> {
{
hero.name}}
</li>
</ul>
<div *ngIf="selectedHero">
<h2>
{
{
selectedHero.name | uppercase}} is my hero
</h2>
<button (click)="gotoDetail()">View Details</button>
</div>
/workspace/HelloAngular/src/app
这样的话需要点击一下View Detail按钮才能看到信息,同时Hero的名字也会被大写,为了实现这些,当然还需要再heroes组件中田间对应的gotoDetail方法。
/workspace/HelloAngular/src/app cat heroes.component.ts
import { Component } from '@angular/core';
import { OnInit } from '@angular/core';
import { Router } from '@angular/router';
import { Hero } from './hero';
import { HeroService } from './hero.service';
@Component({
selector: 'my-heroes',
templateUrl: './heroes.component.html',
styleUrls: ['./heroes.component.css'],
providers: []
})
export class HeroesComponent implements OnInit {
title = 'Tour of Heroes';
selectedHero: Hero;
heroes: Hero[];
onSelect(hero: Hero): void {
this.selectedHero = hero;
}
ngOnInit(): void{
this.heroService.getHeroes().then(heroes => this.heroes = heroes);
}
constructor(
private router: Router,
private heroService: HeroService) {
}
gotoDetail(): void {
this.router.navigate(['/detail', this.selectedHero.id]);
}
}
/workspace/HelloAngular/src/app

可以看到管道和View Details按钮都能按照预期进行动作了。
总结
通过这篇文章,我们大体了解了Angular中的路由是如何使用的,接下来将会进一步学习如何对服务器端的WebAPI发起调用。