文章中几乎所有图片来自百度、谷歌图片搜索引擎查找
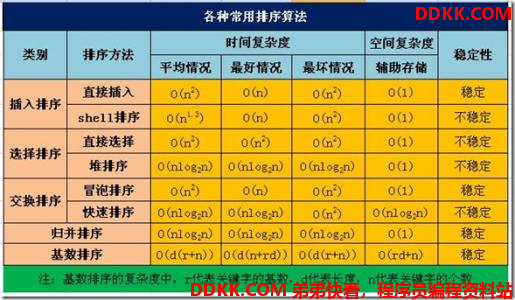
排序特点
稳定性
稳定:排序前a=b,不会因为排序后a,b的相对位置改变
不稳定:排序前a=b,可能会因为排序后a,b相对位置改变
复杂度
时间复杂度:算法执行的时间规模
空间复杂度:排序整个流程需要的内存规模
数据量
内排序::需要排序数据同时在内存中进行排序
外排序:由于需要排序数据量多,数据分块从硬盘移至内存排序
内部排序
交换排序
冒泡排序
快速排序
插入排序
直接插入排序
希尔排序
选择排序
简单选择排序
堆排序
归并排序
基数排序
1. 交换排序
1.1 冒泡排序 - 稳定
思想:相邻元素之间的交换、筛选出最大( 小 )的元素 - 像气泡一样上升
- 每循环一次 找到 最大 的元素放置 数组末尾
- 每循环一次,两两比较的对数减少,因为由上述可知,最大的元素已经排在数组后面、压根就不用比较,所以两两比较的对数会减少
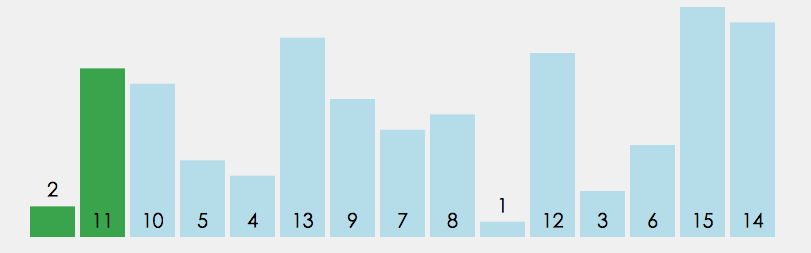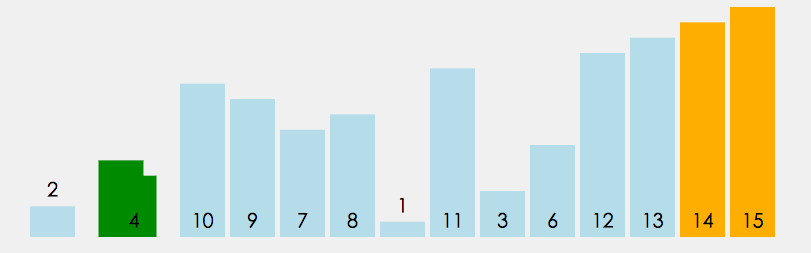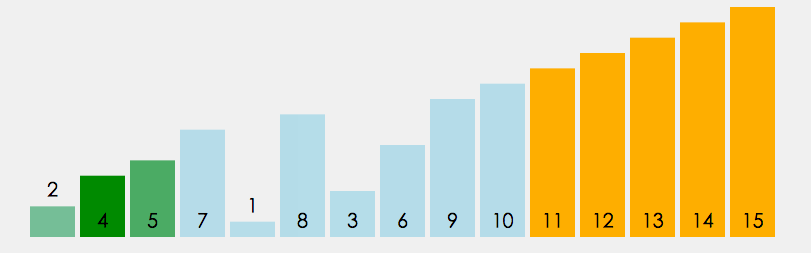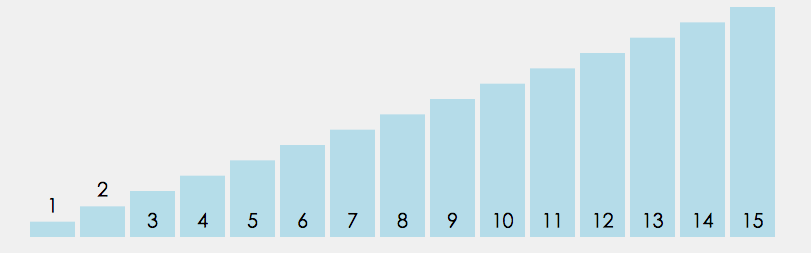
代码实现
public class BubblingSort {
public static int[] sort( int[] array ) {
int[] sortedArray = Arrays.copyOf(array, array.length);
int length = sortedArray.length;
// 一共需要循环 (length-1)次
for( int i = 0; i < length - 1; i++ ) {
// 每次循环需要遍历 length-(i+1) 次
for( int j = 0; j < length - (i+1); j++ ) {
if ( sortedArray[j] > sortedArray[j+1] ) {
int temp = sortedArray[j];
sortedArray[j] = sortedArray[j+1];
sortedArray[j+1] = temp;
}
}
}
return sortedArray;
}
public static void main(String[] args) {
int[] a = {
2,11,10,5,4,13,9,7,8,1,12,3,6,15,14 }; // 需要排序的数组
int[] sortedArray = sort(a); // 已经排序好的数组
System.out.println( "排序前:" + Arrays.toString(a) );
System.out.println( "排序后:" + Arrays.toString(sortedArray) );
}
}
1.2 快速排序 - 不稳定
思想:随意找一个基准数,从右末开始找比基准数小的元素,找到将其与基准数交换,然后从左头开始找一个比基准数大的元素,找到将其与基准数交换,直至左头与右末位置重合,此时数组分为比基准数小,比基准数大的两部分,然后将这两部分继续上述操作
-
口诀:右找小、左找大
-
1. 每次小循环从数组右边开始找比基准数小的元素,然后交换,在从左边开始找比基准大的数,然后交换。
-
2. 直到 left = right 的时候 已经以基准数为标准 把数组分为两部分
-
3. 左右两部分重复 1、2步骤
实际示例
// 排序前
left right
4、 10、3、1、5、7、9
// 排序中 --- 这轮以4为基准数
left right
1、 10、3、4、 5、7、9
left right
1、 4、 3、 10、 5、7、9
left right
1、 3、 4、 10、 5、7、9
left
right
1、 3、 4、 10、 5、7、9 // 从位置2开始把数组分两部分 - 重复1、2步骤
// 即 位置 0 - 1 、3 - 6 两部分 继续重复上面的步骤进行排序
代码实现1 - 找到比基准大(小)的直接跟基准元素进行位置交换
public class QuickSort {
public static quickSort( int[] array, int startIndex, int endIndex ) {
if( startIndex >= endIndex )
return;
int left = startIndex;
int right = endIndex
int temp = array[startIndex];
while( left < right ) {
while( left < right && array[right] >= temp )
right--;
array[left] = array[right];
array[right] = temp;
while( left < right && array[left] <= temp )
left++;
array[right] = array[left];
array[left] = temp;
}
quickSort( array, startIndex, left-1 );
quickSort( array, left+1, endIndex );
}
public static void main( String[] args ) {
int[] a = {
4, 10, 3, 1, 5, 7, 9};
System.out.println( "排序前:" + Arrays.toString(a) );
quickSort(a, 0, a, a.length-1);
System.out.println( "排序后:" + Arrays.toString(a) );
}
}
实际示例
//排序前:
left right
4、 10、3、1、5、7、9
//排序中:这轮以4为基准数
left right
4、 10、3、1、 5、7、9
left right
4、 10、3、1、 5、7、9
left right
4、 1、3、 10、 5、7、9
right
left
4、 1、3、 10、 5、7、9
right
left
3、 1、4、 10、 5、7、9 // left = right 时 基准元素才进行位置切换
// 以元素4的位置把分组分为两部分,重复这些操作。
代码实现2 -先找到比基准大、小 两者位置进行交换 最后实在找不到了才进行基准元素交换
public class QuickSort2 {
public static void sort(int[] array, int startIndex, int endIndex) {
if ( startIndex >= endIndex)
return;
int left = startIndex;
int right = endIndex;
int emp = array[startIndex];
while (left < right ) {
while ( left < right && array[right] >= emp)
right--;
while ( left < right && array[left] <= emp )
left++;
if ( left < right) {
int emp2 = array[left];
array[left] = array[right];
array[right] = emp2;
}else if ( left == right ) {
array[startIndex] = array[left];
array[left] = emp;
}
}
sort(array, startIndex, left-1);
sort(array, left+1, endIndex);
}
public static void main(String[] args) {
int[] a = {
4, 10, 3, 1, 5, 7, 9};
System.out.println( "排序前:" + Arrays.toString(a) );
sort(a, 0, a.length - 1);
System.out.println( "排序后:" + Arrays.toString(a) );
}
}
2. 插入排序
思想:在已经排序的部分中,把某个元素依次插入到这个已排序的部分中
2.1 直接插入排序 - 稳定
- 从数组中抽出一个元素,排序在已经排好序的数组上面
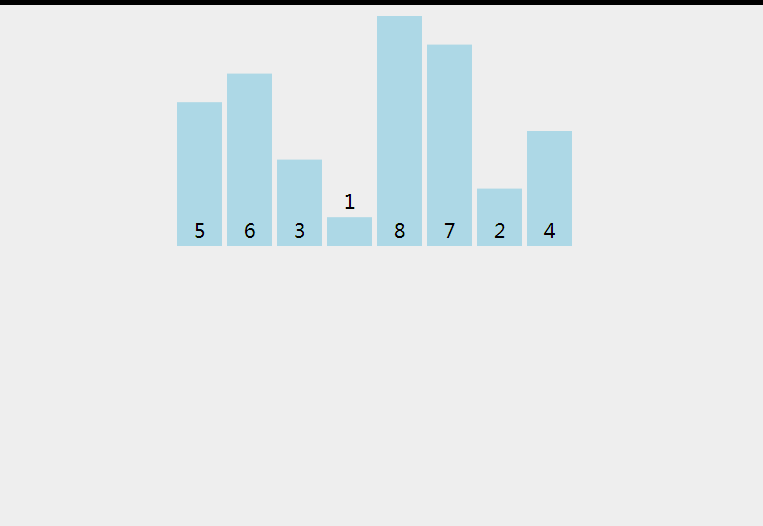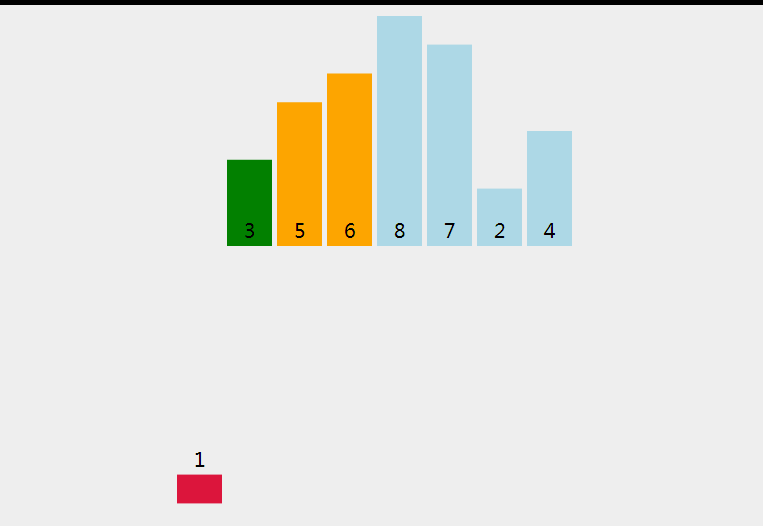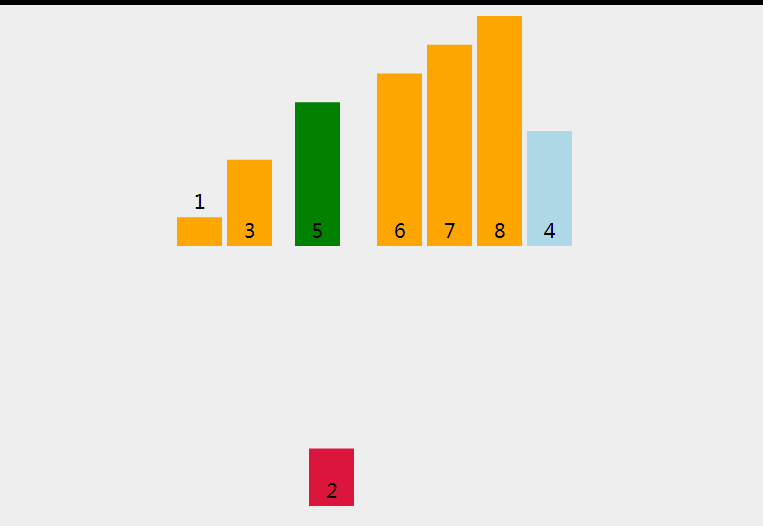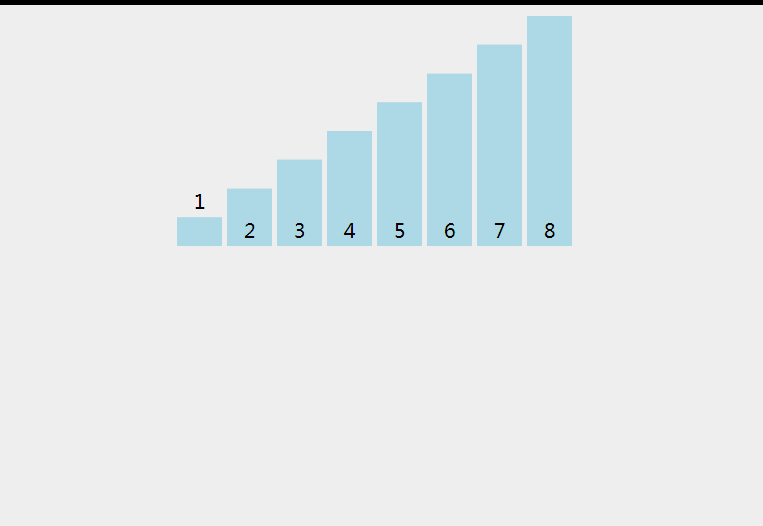
代码实现1 - 跟动图一样的实现(找到位置在插入新元素)
public class DirectInsertionSort {
public static void sort( int[] array ) {
for ( int i = 1; i < array.length; i++ ) {
temp = array[i];
int j = i - 1;
for ( ; j >= 0 && array[j] > temp; j--) {
array[j+1] = array[j];
}
array[j+1] = temp; // 最后找到插入的位置才将 需要排序的元素 插入到排序好的数组中,像动图一样。
}
}
public static void main( String[] args ) {
int[] a = {
100,11,10,5,4,13,9,7,8,1,12,3,6,15,14};
//int[] a = {4, 10, 3, 1, 5, 7, 9};
sort(a);
System.out.println(Arrays.toString(a));
}
代码实现2 - 需排序的数字一直在已经排序好的数组一直在交换位置
public class DirectInsertionSort {
public static void sort( int[] array ) {
for ( int i = 1; i < array.length; i++ ) {
temp = array[i];
int j = i - 1;
for ( ; j >= 0 && array[j] > temp; j--) {
// 每时每刻都在交换 选中的未排序的元素
array[j+1] = array[j];
array[j] = temp;
}
}
}
public static void main( String[] args ) {
int[] a = {
100,11,10,5,4,13,9,7,8,1,12,3,6,15,14};
//int[] a = {4, 10, 3, 1, 5, 7, 9};
sort(a);
System.out.println(Arrays.toString(a));
}
2.2 希尔( 递减增量 )排序 - 不稳定
不稳定的因素:组与组分别独立进行直接插入排序,间接的导致相同值的元素位置交换*
思想:
-
数组按照间隔增量进行分组、每组进行直接插入排序
-
当前间隔增量的所有分组排序完成,则间隔递减,重新分组,每个分组再次直接插入排序*
-
重复前面两步骤,最后一次是间隔增量=1的时候即整个数组直接插入排序
注意:一般开头选的间隔增量为数组的一半,然后依次对半进行增量分组排序

文字解说
// 初始序列
49 38 65 97 76 13 27 49 55 4
// 初始增量5 、即有5个分组、每组的相邻元素之间间隔为5
49 13
38 27
65 49
97 55
76 4
整体排序后
13 27 49 55 4 49 38 65 97 76
// 第二次增量5/2=2 拥有2个分组、每组的相邻元素之间间隔为2
13 49 4 38 97 排序:4 13 38 49 97
27 55 49 65 76 排序:27 49 55 65 76
整体排序后
4 27 13 49 38 55 49 65 97 76
// 第三次增量2/2=1 即1个分组、每组的相邻元素之间间隔为1即对整个数组进行直接插入排序
代码实现 - 网上有更优的代码建议读者先看懂这段长代码在读网上优化后的代码
public class ShellSort {
public static void sort( int[] array ) {
// 增量的变化
for ( int spaceIncrement = array.length/2; spaceIncrement >= 1; spaceIncrement/=2 ) {
// 每次增量需要 spaceIncremwnt组 进行排序
for ( int i = 0; i < spaceIncrement; i++ ) {
int index = i + spaceIncrement;
// 每组进行直接插入排序
for ( ; index < array.length; index+=spaceIncrement ) {
int emp = array[index];
int j = index - spaceIncrement;
for ( ; j >= 0 && array[j] > emp ; j-=spaceIncrement ) {
array[j+spaceIncrement] = array[j];
}
array[j+spaceIncrement] = emp;
}
}
}
}
public static void main( String[] args ) {
int[] a = {
100,11,10,5,4,13,9,7,8,1,12,3,6,15,14};
//int[] a = {4, 10, 3, 1, 5, 7, 9};
sort(a);
System.out.println(Arrays.toString(a));
}
}
3. 选择排序 - 稳定
3.1 简单选择排序
思想:
- 在未排序的部分中选出最大(小)的元素 → 放置在已排序部分后面
跟冒泡排序很像,两者都是遍历未排序的部分筛选出最大( 最小 )的元素,区别:简单选择排序在遍历的过程不进行相邻元素的交换

代码实现
public class SimpleSelectSort {
public static void sort( int[] array ) {
int emp;
int index;
for ( int i = 0; i < array.length; i++ ) {
emp = array[i];
index = i;
for( int j = i+1; j < array.length; j++ ) {
if ( array[j] < emp ) {
emp = array[j];
index = j;
}
}
array[index] = array[i];
array[i] = emp;
}
}
public static void main ( String[] args ) {
int[] a = {
100,11,10,5,4,13,9,7,8,1,12,3,6,15,14};
//int[] a = {4, 10, 3, 1, 5, 7, 9};
sort(a);
System.out.println(Arrays.toString(a));
}
3.2 堆排序
升序采用大顶堆、降序采用小顶堆
堆排序思想:
1、 将一系列无序的数调整为大(小)顶堆;
2、 根节点与最后一个叶子节点进行位置互换;
3、 将二叉树中的最后叶子节点进行抹除;
4、 不断重复1、2、3步骤;
无序二叉树调整为 大( 小 )顶堆思路:
1、 从最后一个父节点到**第一个父节点(即根节点)**开始;
2、 琢一将各自管理的树转为大(小)顶堆→(当前的父节点、左节点、右节点这三个节点构成的二叉树必须是大(小)顶堆);
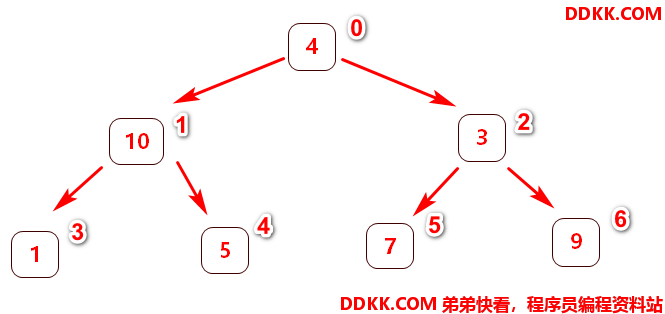
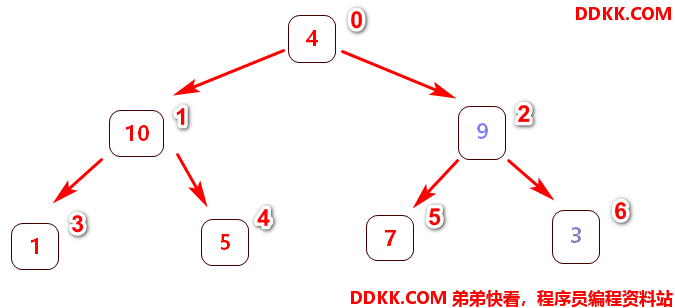
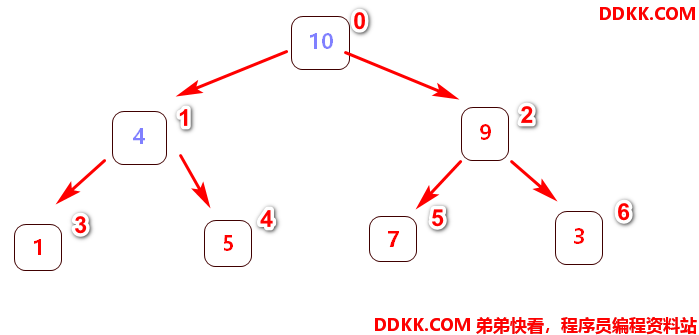
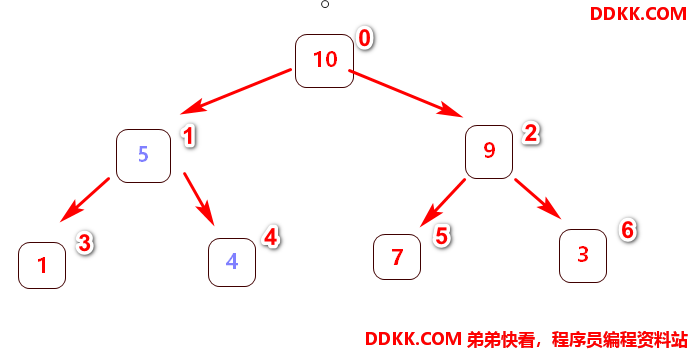
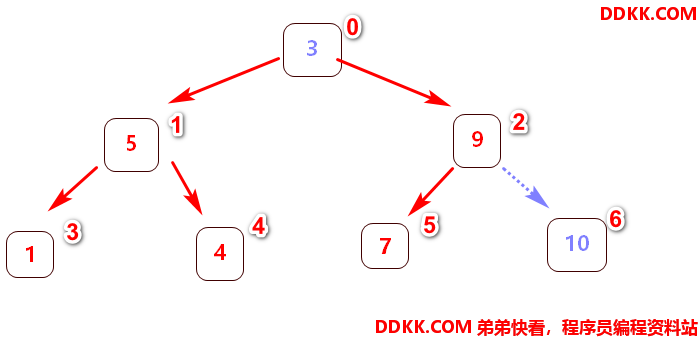
这时已经找到最大的元素是10,放置在数组末中,并且删除该最大节点,再次重新调整下图新的无序二叉树为大顶堆
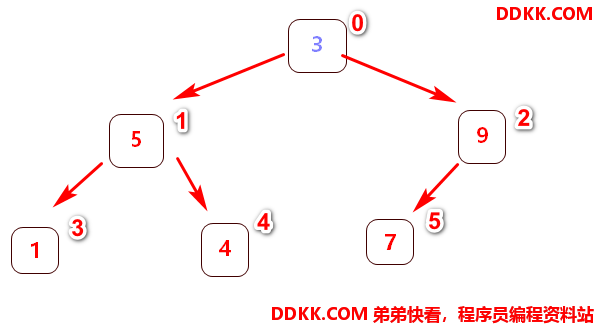
背景知识:
1、最后的父节点节点位置fIndex:length/2-1;
2、左节点位置lIndex:父节点位置*2+1;
3、右节点位置index:父节点位置*2+2或者左节点位置lIndex+1;
代码实现
public class HeapSort {
public static void adjustHeap( int[] arr, int pNode_index, int needSortLength) {
// 得到该父节点的左节点、如果有元素交换,则继续循环,没有则直接退出循环
for( int sNode_index = 2*pNode_index+1; sNode_index < needSortLength; sNode_index = sNode_index*2+1 ) {
// 当前父节点的元素值
int temp = arr[pNode_index];
// 判断左右节点谁大
if ( sNode_index + 1 < needSortLength && arr[sNode_index + 1] > arr[sNode_index] )
++sNode_index;
// 只要有元素交换,则会检查当前的节点与左右节点是否是 大顶堆
// 没有交换则直接退出循环
if ( arr[sNode_index] > arr[pNode_index] ) {
arr[pNode_index] = arr[sNode_index];
arr[sNode_index] = temp;
pNode_index = sNode_index;
}else {
break;
}
}
}
public static void sort( int[] array ) {
// 将当前无需二叉树转成 大顶堆
for ( int i = arr.length/2 - 1; i >= 0; i--)
adjustHeap(arr, i, arr.length);
// 已经是大顶堆则将最后的叶子节点与根节点进行交换
for( int j = arr.length -1; j >= 0; j-- ) {
int temp = arr[j];
arr[j] = arr[0];
arr[0] = temp;
adjustHeap(arr, 0, j); // 抹除最后叶子节点,重新将新的二叉树调整为大顶堆
}
}
public static void main( String[] args ) {
//int[] a = {100,11,10,5,4,13,9,7,8,1,12,3,6,15,14};
int[] a = {
4, 10, 3, 1, 5, 7, 9};
sort(a);
System.out.println(Arrays.toString(a));
}
}
4. 归并排序 - 稳定
思想:
1、 先分组,每组都是一个有序的部分;
2、 有序的分组与相邻的有序分组合并成一个更大的有序分组;
3、 循环1、2步骤→直至只有1个分组,即整个数组;
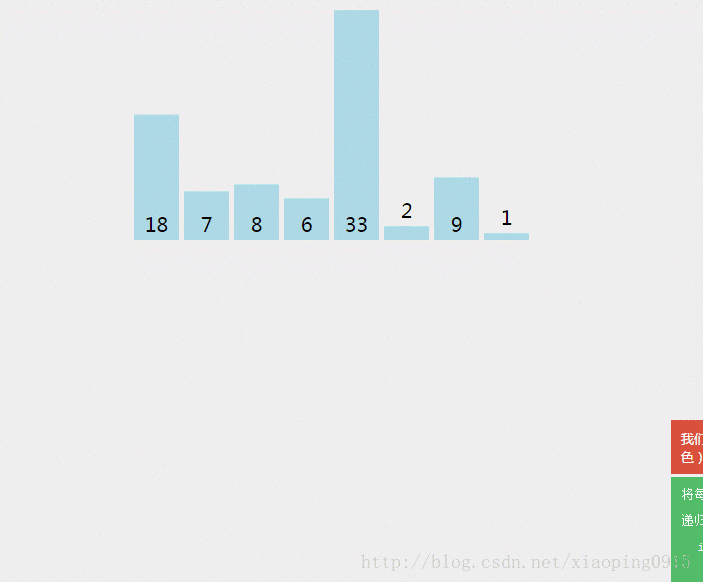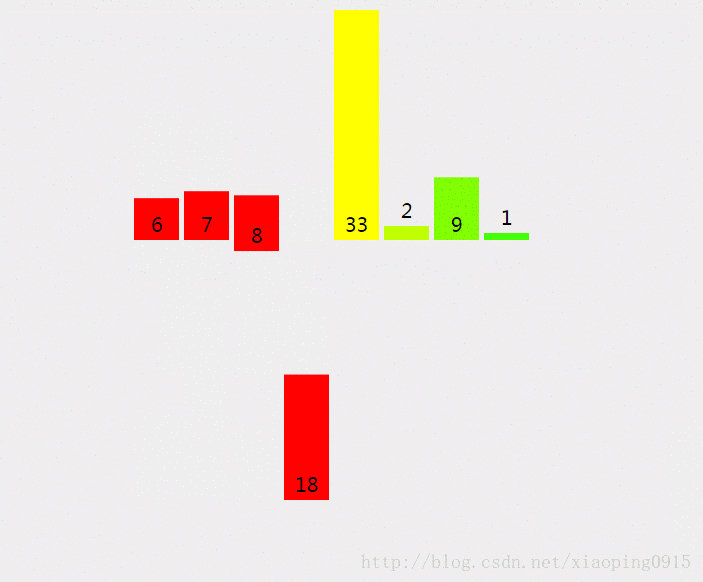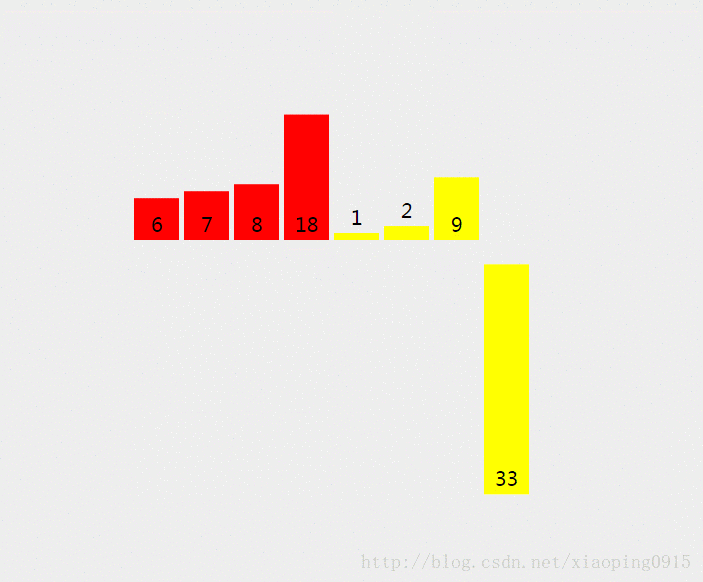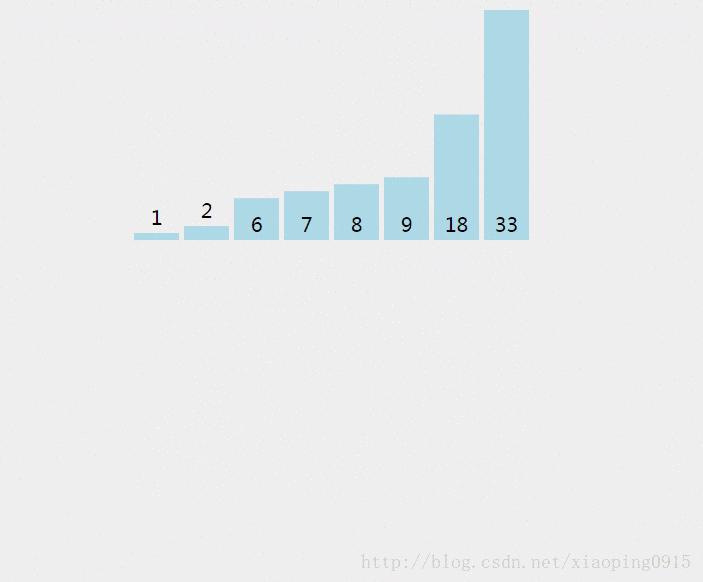
代码实现
public class MergeSort {
public static int[] sort( int[] arr ) {
// 递归的终止条件
if ( arr.length == 1 )
return arr;
// 将数组对半分成两部分,可能奇数长度数组,left数组长度比right数组长度多一个
int group_length = arr.length/2;
int[] left = Arrays.copyOfRange( arr, 0, group_length );
int[] right = Arrays.copyOfRange( arr, group_length, arr.length );
return mergeArray( sort(left), sort(right) );
}
public static int[] mergeArray( int[] left, int[] right ) {
int leftIndex = 0, rightIndex = 0, Index = 0;
int[] merge = new int[ left.length + right.length ];
//left、right数组两部分都是有序数组
// 这条循环运行完 - left、right其中一个数组所有元素都在 merge数组中
while( leftIndex < left.length && rightIndex < right.length ) (
if ( leftIndex[ leftIndex ] <= rightIndex[ rightIndex ] ) {
merge[ index ] = leftIndex[ leftIndex ];
++index;
++leftIndex;
}else {
merge[ index ] = rightIndex[ rightIndex ];
++index;
++rightIndex;
}
}
// 如果 left中还有元素 没在 merge数组中,则直接将剩下的复制到merge尾部
while ( leftIndex < left.length ) {
merge[ index ] = leftIndex[ leftIndex ];
++index;
++leftIndex;
}
// 如果right中还有元素 没在 merge数组中,则直接将剩下的复制到merge尾部
while ( rightIndex < right.length ) {
merge[ index ] = rightIndex[ rightIndex ];
++index;
++rightIndex;
}
return merge;
}
public static void main(String[] args) {
//int[] a = {100,11,10,5,4,13,9,7,8,1,12,3,6,15,14};
int[] a = {
4, 10, 3, 1, 5, 7, 9};
int sortedA = sort(a);
System.out.println(Arrays.toString( sortedA ));
}
}
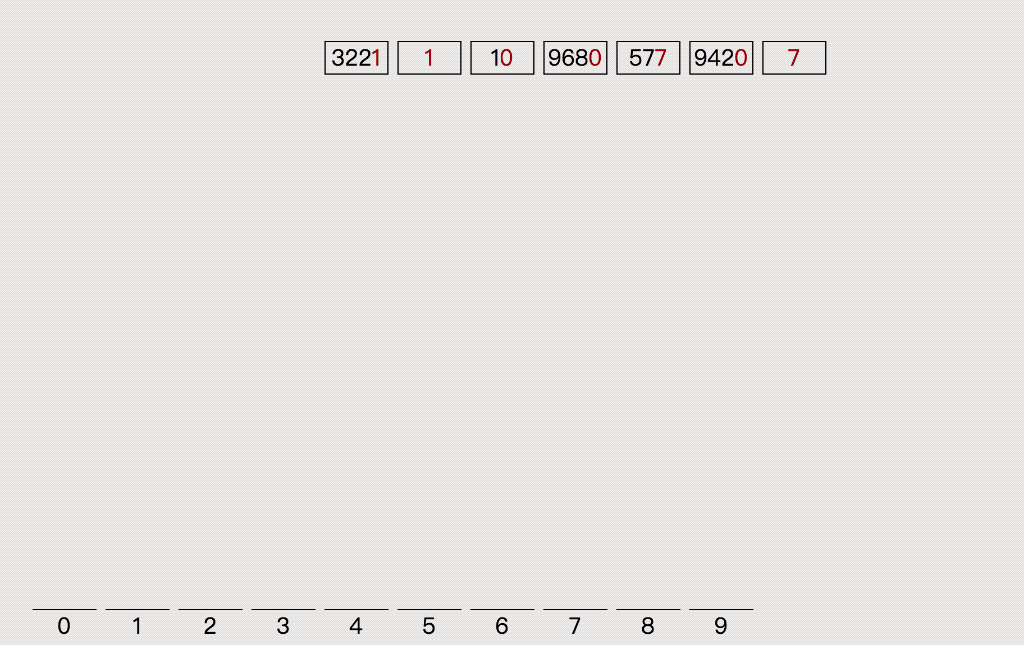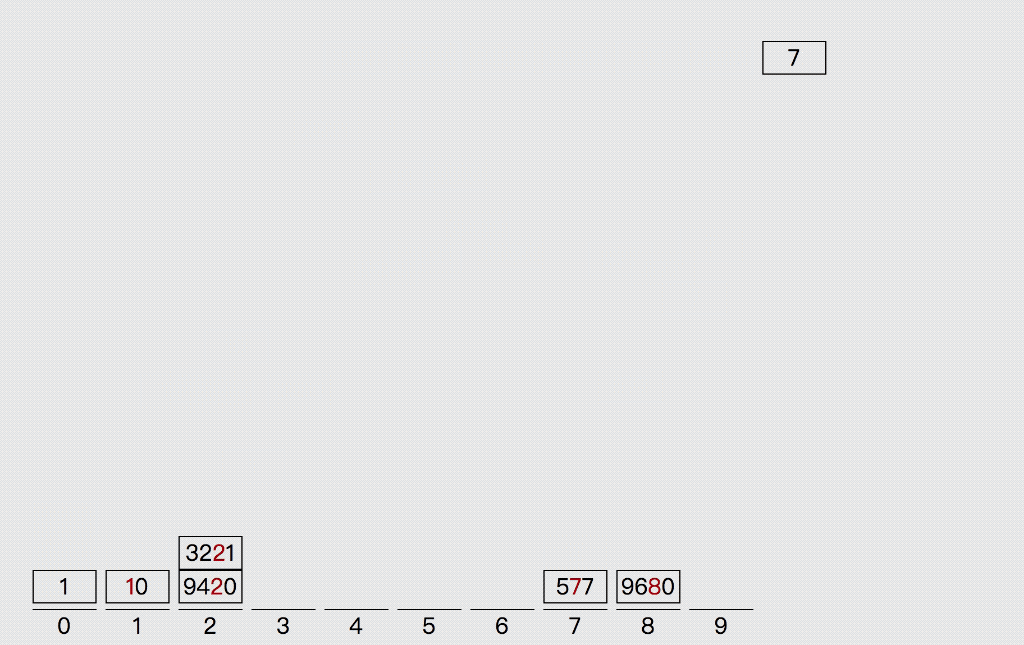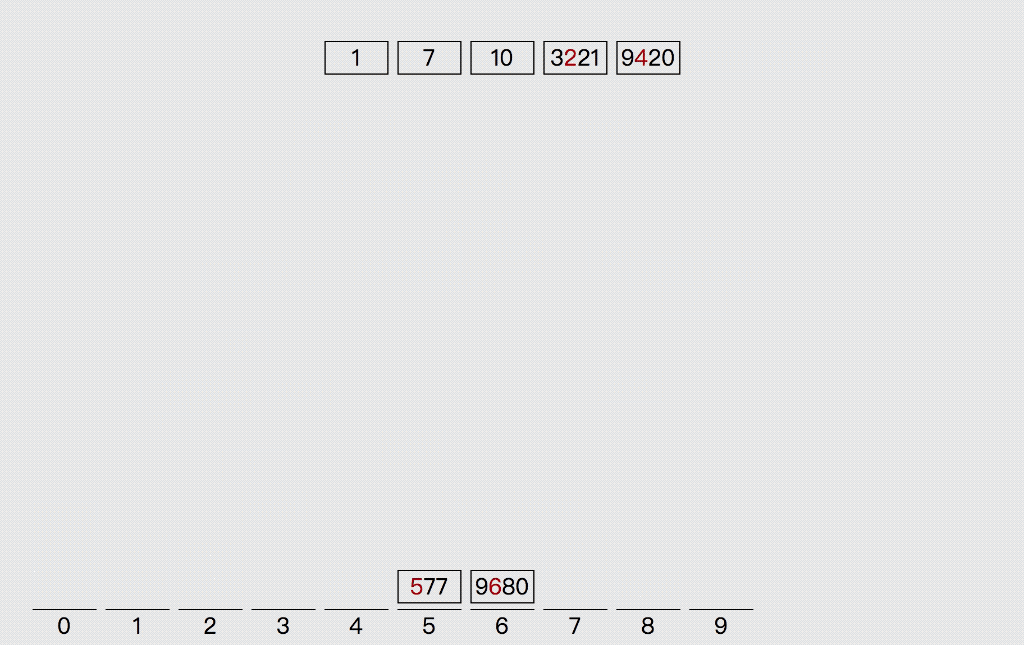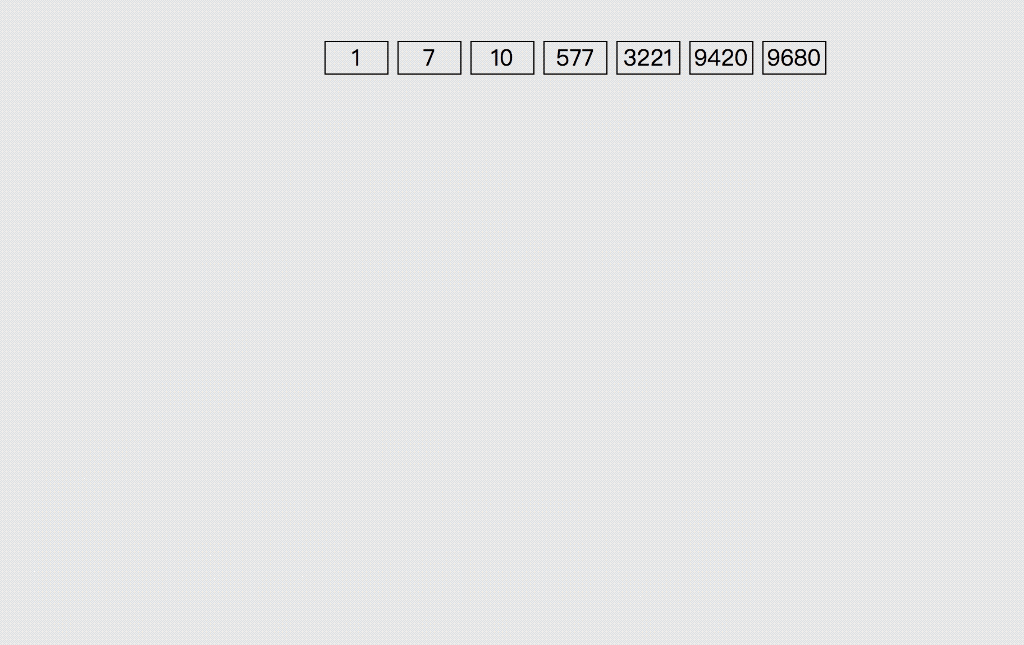
5. 基数( 桶 )排序 - 稳定
基数排序
MSD:从最高位开始排序
LSD:从最低位开始排序
思路:
-
将数组中所有元素统一固定的位数,位数不够的元素在元素前补0
-
每次排序有10个分组 - 元素所属的分组按照当前元素指定位的数字决定
代码示例:正数的基数排序
public class RadixSort {
public static void sort( int[] arr ) {
int max_digit = num_digit(maxNum(arr)); // 算出数组最大元素的位数
int[][] buckets = new int[10][arr.length]; // 桶
int base = 10; // 计算对应位的数字基数
int[] bucketCapacity = new int[10]; // 所有桶当前含有的元素个数
int currentCapacity; // 当前所在桶含有的元素个数
int jishu; // 数组元素 对应位 的 数字
// 桶排序的次数 与 数组最大位数相对应
for(int i = 0; i < max_digit; i++) {
// 进行桶排序前需要初始化所有桶的容量
for( int m = 0; m < bucketCapacity.length; m++)
bucketCapacity[m] = 0;
// 将数组中的元素放入对应桶中
for(int number : arr) {
jishu = ( number % base ) / ( base/10 );
currentCapacity = bucketCapacity[jishu];
buckets[jishu][currentCapacity] = number;
bucketCapacity[jishu] += 1;
}
int index = 0;
// 将所有桶含有的元素 放入 数组中
for(int j = 0; j <buckets.length; j++) {
for (int m = 0; m < bucketCapacity[j]; m++) {
arr[index] = buckets[j][m];
++index;
}
}
base *= 10;
}
}
public static int num_digit( int num ) {
int count;
// while(<u>num</u> != 0) {
// <u>num</u> /= 10;
// count++;
// }
String integer = Integer.toUnsignedString(num);
count = integer.length();
return count;
}
public static int maxNum( int[] arr ) {
int max = arr[0];
for( int i = 1; i < arr.length; i++) {
if ( arr[i] > max )
max = arr[i];
}
return max;
}
public static void main( String[] args ) {
//int[] a = {100,11,10,5,4,13,9,7,8,1,12,3,6,15,14};
int[] a = {
4, 10, 3, 1, 5, 7, 9};
int sortedA = sort(a);
System.out.println(Arrays.toString( sortedA ));
}
}