1. 概述
算术表达式都可以转换成二叉树、然后根据要求进行遍历二叉树的元素
表达式
波兰表达式:二叉树前序遍历(中左右)
中缀表达式:二叉树中序遍历(左中右)
逆波兰表达式:二叉树后序遍历(左右中)
下面的所有已这个表达式为标准进行代码测试
计算: 2+7-8/4+8*2+7-3
表达式转为二叉树
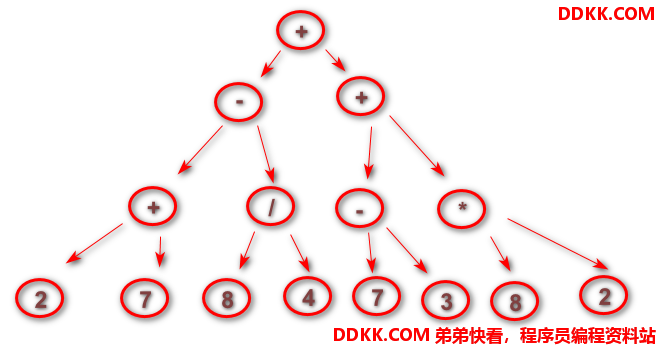
根据上面的二叉树进行遍历
- 前序遍历: + - + 2 7 / 8 4 + - 7 3 * 8 2
- 中序遍历: 2 + 7 - 8 / 4 + 7 - 3 + 8 * 2
- 后序遍历: 2 7 + 8 4 / - 7 3 - 8 2 * + +
2. 逆波兰表达式计算
逆波兰表达式:操作符在将要计算的两个操作数之后
思路:
- 1.将后缀表达式从左到右遍历,遇到数字则压入栈中
- 2.遇到操作运算符则从栈中弹出两个元素进行计算,并将结果压入栈中
- 3.然后继续遍历,重复1、2步骤,直到给出的后缀表达式遍历完成
- 4.最后的结果存放在栈中,并且只有一个元素,将栈顶元素弹出来就可以获取计算结果了
2.1 代码实现
class InversePolishExpression {
// 用来存储逆波兰表达式
String expression;
InversePolishExpression(String expression) {
this.expression = expression;
}
// 获取逆波兰表达式的结果
public int getResult() {
// 定义一个栈 -- 用来存储数字
Stack<String> stack = new Stack<String>();
// 将逆波兰表达式转为 容器进行单元素存储
List<String> elements = new ArrayList<String>(Arrays.asList(expression.split(" ")));
// 下一个元素的位置
int index = 0;
// 如果整个逆波兰表达式遍历完成,则说明计算结果在栈顶上
while(index != elements.size()) {
// 1. 获取一个元素,并将指针移动到下一个元素的位置
String element = elements.get(index);
index++;
// 2. 如果当前元素是数字,则压入栈中
if( element.matches("\\d+") ) {
stack.push(element);
continue;
// 3. 如果当前元素时操作符,则从栈中弹出两个数进行算术运算,并将结果压入栈中
}else if( element.matches("\\+|\\-|\\*|\\/") ) {
String num2 = stack.pop();
String num1 = stack.pop();
stack.push(calc(num1, num2, element) + "");
// 4. 如果前面两步都没有匹配成功,说明给的逆波兰表达式不符合要求
}else {
throw new RuntimeException("表达式出现错误,请检查你的表达式");
}
}
return Integer.valueOf(stack.pop());
}
// 用于计算从栈中弹出的两个数的结果
public int calc(String num1, String num2, String ope) {
Integer n1 = Integer.valueOf(num1);
Integer n2 = Integer.valueOf(num2);
switch(ope) {
case "+":
return n1 + n2;
case "-":
return n1 - n2;
case "*":
return n1 * n2;
case "/":
return n1 / n2;
default:
throw new RuntimeException("有系统不支持的运算符");
}
}
}
2.2 测试代码
public static void main(String[] args) {
InversePolishExpression ipe = new InversePolishExpression("2 7 + 8 4 / - 7 3 - 8 2 * + +");
System.out.println(ipe.getResult());
}
运行结果

3. 波兰表达式计算
波兰表达式:操作符在将要计算的两个操作数之前
3.1 代码实现
这里就不给出代码了,举一反三根据上面的逆波兰表达式计算代码,自己写吧!逆波兰表达式是从左到右遍历,而波兰表达式的计算是从右到左遍历进行计算。
4. 中缀表达式 转 后缀表达式
思路分析

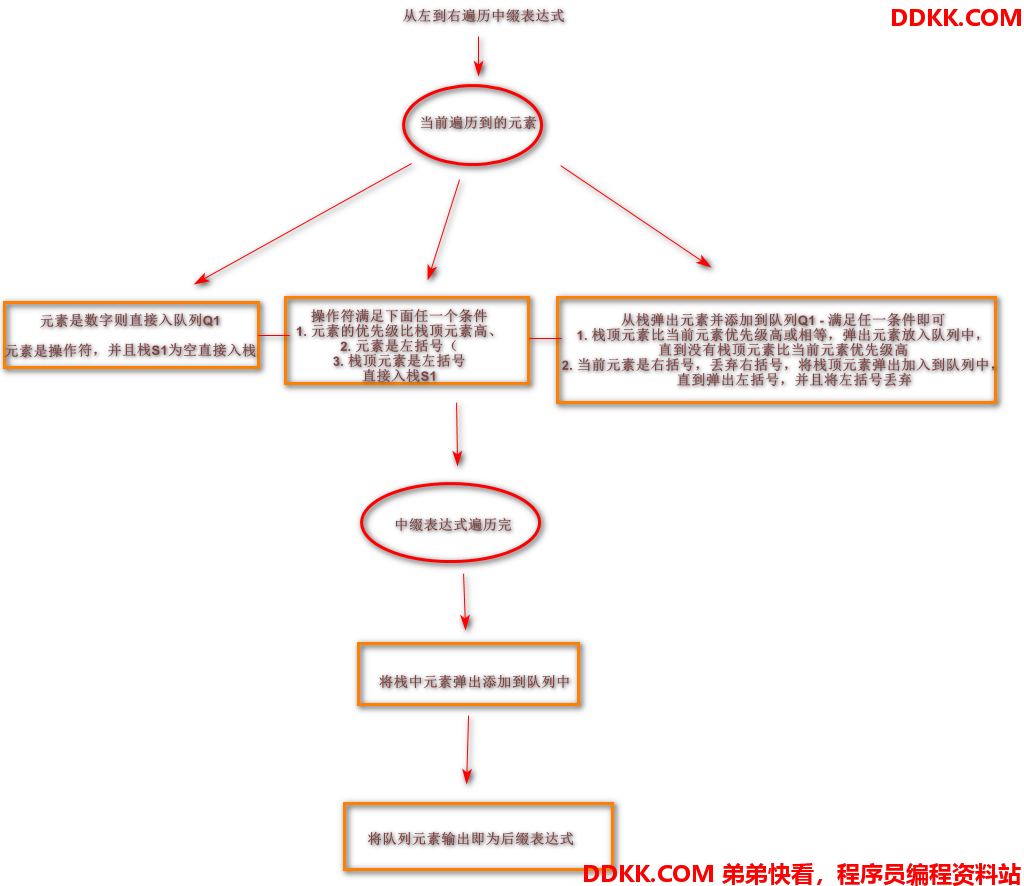
4.1 代码实现
代码过长分批进行讲解 – 注意都是成员函数
4.1.1 定义一个中缀转后缀表达式的类#
class InfixToPostfixExpression {
// 传入的中缀表达式
String infixExpression;
// 后缀表达式结果
List<String> postfixExpression;
//传入中缀表达式就转换成后缀表达式
InfixToPostfixExpression(String infixExpression) {
this.infixExpression = infixExpression;
changeExpression(infixExpression);
}
// 获取 后缀表达式
public List<String> getPostfixExpression() {
if (postfixExpression != null) {
return postfixExpression;
} else {
throw new RuntimeException("还没有");
}
}
}
4.1.2 获取操作符的优先级#
// 用来获取操作符的优先级数
public int getPriority(String ope) {
switch(ope) {
case "+":
case "-": return 0;
case "*":
case "/": return 1;
default: throw new RuntimeException("系统不支持该种操作符");
}
}
4.1.3 中缀转后缀的过程函数#
// 中缀转后缀的过程
private void changeExpression(String expression) {
// 1. 定义一个栈存放中间元素,定义一个队列存放最终结果表达式
Stack<String> tempStack = new Stack<String>();
List<String> resultList = new LinkedList<String>();
// 2.将中缀表达式转为单元素字符串数组
StringTokenizer st = new StringTokenizer(infixExpression, "()+-*/", true);
String[] strs = new String[st.countTokens()];
int index = 0;
while (st.hasMoreTokens()) {
strs[index++] = st.nextToken();
}
// 3. 开始进行表达式转换
int elementIndex = 0;
// 3.1 遍历整个字符串
while(true) {
// 3.1.1 遍历完就停止遍历
if(elementIndex == strs.length) {
break;
}
// 3.1.2 获取当前遍历到的元素,并且将指针移到下一个位置
String curElement = strs[elementIndex++];
// 3.1.3 如果是数字,则直接加入到结果队列
if(curElement.matches("\\d+")) {
resultList.add(curElement);
continue;
// 3.1.4 如果不是数字,而是操作符,并且栈为空,则直接压入栈
}else if(tempStack.size() == 0) {
tempStack.add(curElement);
continue;
// 3.1.5 如果是左括号(或者栈顶是左括号(,则直接压栈, 如果是右括号准备弹出多个元素从栈中加入到队列
}else if( curElement.matches("\\(|\\)") || "(".equals(tempStack.peek())) {
if(curElement.equals("(") || "(".equals(tempStack.peek()) ) {
tempStack.add(curElement);
}else {
// 当前元素是右括号的处理
while(!"(".equals(tempStack.peek())) {
resultList.add(tempStack.pop());
}
tempStack.pop(); //丢弃左括号(
}
continue;
// 3.1.6 如果当前元素的优先级高于栈顶元素,则直接压栈
}else if( getPriority(curElement) > getPriority(tempStack.peek())) {
tempStack.add(curElement);
continue;
// 3.1.7 如果当前元素的优先级等于或者低于栈顶元素,则直接弹出元素,并且将弹出元素压入到队列中
}else {
while(!tempStack.isEmpty()) {
String top = tempStack.peek();
if(getPriority(curElement) > getPriority(top) ) {
break;
}
resultList.add(tempStack.pop());
}
tempStack.add(curElement);
}
}
// 将栈中剩余的元素全部弹出加入到 队列中
while(!tempStack.isEmpty()) {
resultList.add(tempStack.pop());
}
// 将结果赋给成员变量
postfixExpression = resultList;
}
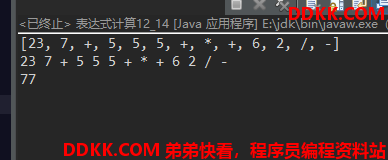
4.1 测试代码
使用到前面写的逆波兰表达式类进行计算
public static void main(String[] args) {
// 中缀转后缀表达式
InfixToPostfixExpression ipe = new InfixToPostfixExpression("23+7+5*(5+5)-6/2");
List<String> lists = ipe.getPostfixExpression();
System.out.println(lists);
// 将后缀表达式List,转为字符串,字符字符之间有空格隔开
StringBuilder sb = new StringBuilder();
for(String str : lists) {
sb.append(str);
sb.append(" ");
}
sb.deleteCharAt(sb.length()-1);
System.out.println(sb);
// 输出后缀表达式的计算结果
System.out.println(new InversePolishExpression(sb.toString()).getResult());
}
运算结果