概念
特点:
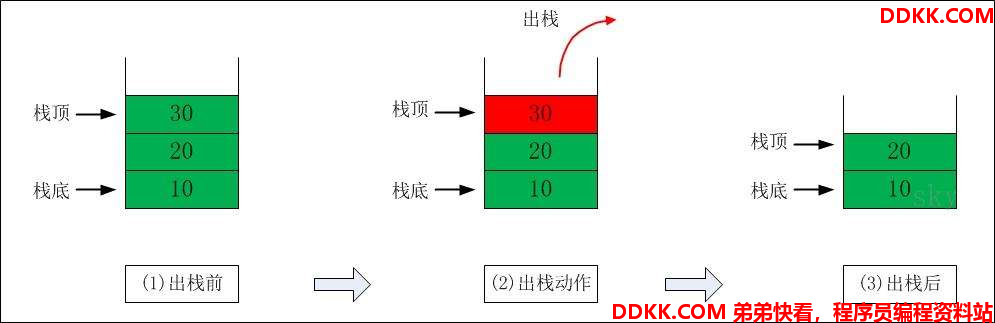
1、栈底(bottom)位置不变,栈顶(top)位置改变;
2、元素先进(push)后出(pop);
- 应用:
1、 算术计算;
2、 子程序的调用;
3、 递归调用;
4、 表达式转换(中缀、后缀表达式的转换);
5、 二叉树的遍历;
6、 图的深层优先搜索算法;
数组 - 模拟栈
代码实现
class Stack<T> {
Object[] stack;
int capacity;
int top;
public Stack(int capacity ) {
this.capacity = capacity;
stack = new Object[capacity];
top = -1;
}
// 判断是否为满
public boolean isFull() {
if(top == capacity-1) {
return true;
}
return false;
}
//判断是否为空
public boolean isEmpty() {
if(top == -1 ) {
return true;
}
return false;
}
// 将元素放入栈中
public void push(T num) {
if(isFull()) {
System.out.println("栈已经放满元素了");
return;
}
// top记录的是上次压入元素的位置,故压入元素前需要改变top的值
stack[++top] = num;
}
// 将栈顶的元素取出来,并移动top指针的位置
@SuppressWarnings("unchecked")
public T pop() {
if(isEmpty()) {
throw new RuntimeException("栈已经没有元素了");
}
// 正因为top标记的是上次压入元素的位置,故取元素先不改变top的值
return (T)stack[top--];
}
}
测试代码
public static void main(String[] args) {
Stack<String> s = new Stack<String>(5);
s.push("1发多少");
s.push("2认为");
s.push("3不VC");
s.push("4今年");
s.push("5iu一");
while(!s.isEmpty()) {
System.out.println(s.pop());
}
}
运行结果
双向链表 - 模拟栈
代码实现
class LinkedStack<T> {
// 表示栈顶、当为null时,说明无元素 -- 表示当前栈顶的元素
Node<T> top = null;
// 判断栈是否由元素
public boolean isEmpty() {
if (top == null) {
return true;
}
return false;
}
// 压栈
public void push(T date) {
// 将压入的元素封装成为节点
Node<T> newNode = new Node<T>(date);
// 当栈中无元素时压栈
if (top == null) {
top = newNode;
// 当栈中有元素时压栈
} else {
top.next = newNode;
newNode.pre = top;
top = newNode;
}
}
// 从栈顶取出一个元素
public T pop() {
if (isEmpty()) {
throw new RuntimeException("栈中已经无元素了");
} else {
T result = top.date;
top = top.pre;
return result;
}
}
// 显示当前栈顶元素是什么
public T peek() {
return top.date;
}
@SuppressWarnings("hiding")
private class Node<T> {
T date;
Node<T> next;
Node<T> pre;
Node() {
date = null;
next = null;
pre = null;
}
Node(T date) {
this.date = date;
next = null;
pre = null;
}
}
}
测试代码
public static void main(String[] args) {
LinkedStack<String> ls = new LinkedStack<String>();
ls.push("1发多少");
ls.push("2认为");
ls.push("3不VC");
ls.push("4今年");
ls.push("5iu一");
while(!ls.isEmpty()) {
System.out.println(ls.pop());
}
}
测试结果

应用:模拟算术表达式计算 - 利用上面的双向链表栈
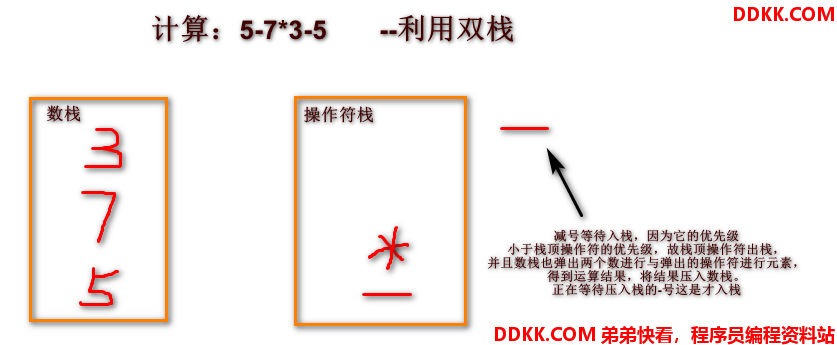
由于代码过长,我分段进行讲解,都是成员函数,如需测式,只需要复制即可以了。
图片解释
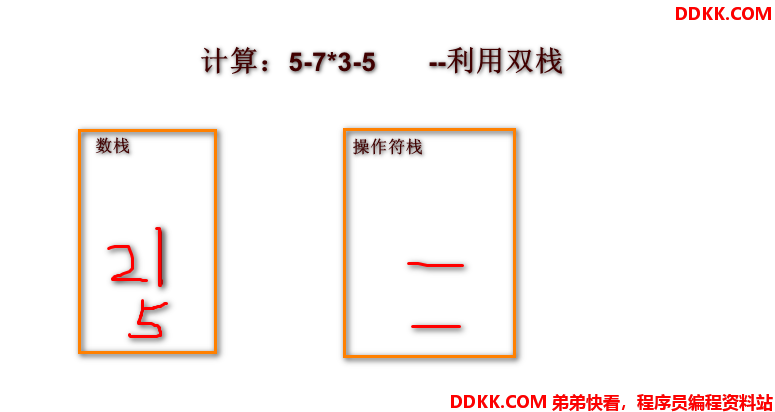



代码实现
① 定义一个OpationalExpression类#
class OperationalExpression {
// 需要计算的算术表达式
private String expression;
// 两个栈用来进行计算
LinkedStack<String> numStack = new LinkedStack<String>();
LinkedStack<Character> operStack = new LinkedStack<Character>();
// 1. 存储解析expression字符串所有数字、以及操作符
String[] temp_num;
Character[] temp_oper;
// 传入的算术表达式需把所有的空格清除掉
OperationalExpression(String expression) {
this.expression = expression.replaceAll(" ", "");
}
// 显示最终去空格后的算术表达式是怎么样
public String showExpression() {
return expression;
}
// 定义操作符优先级
public int getPriority(Character operation) {
if (operation == '*' || operation == '/') {
return 1;
} else {
return 0;
}
}
}
② isArithmeticExpression() – 校验算术表达式#
// 判断传入的算术表达式是否符合计算要求 -- 并且进行操作数数组temp_num、以及操作符数组temp_oper的初始化操作
public boolean isArithmeticExpression() {
// 因为不能一开始知道表达式中有几个算术操作符,故用容器进行动态存储操作符,注意这里的函数变量名跟成员变量名不冲突
List<Character> temp_oper = new ArrayList<Character>();
// 将字符串转成字符数组进行验证是否每个字符符合要求
char[] chars = expression.toCharArray();
int index = 0; // 记录字符串指针移动的位置
int operCount = 0; // 记录操作数的个数
while (true) {
if (index == chars.length) {
break;
}
char selectedChar = chars[index];
if ((selectedChar >= '0' && selectedChar <= '9') || selectedChar == '.') {
index++;
continue;
} else if ((selectedChar >= '*' && selectedChar <= '+') || (selectedChar >= '-' && selectedChar <= '/')) {
++operCount;
index++;
temp_oper.add(selectedChar);
continue;
}
return false; // 如果存在不是 0-9、小数点、+-*/ 则直接返回 false, 说明不符合算术表达式要求
}
// 成员变量temp_oper初始化、赋值操作
this.temp_oper = temp_oper.toArray(new Character[operCount]);
// 用来查找 算术字符串中的 数字
StringTokenizer st = new StringTokenizer(expression, "+-*/", false);
// 如果 数字的个数 = 操作符+1 则返回 true,否则该算术表达式不符合要求
if (st.countTokens() == operCount + 1) {
temp_num = new String[st.countTokens()];
int tokenIndex = 0;
while (st.hasMoreTokens()) {
temp_num[tokenIndex] = st.nextToken();
++tokenIndex;
}
return true;
}
return false;
}
③ sResult() – 核心代码 - 计算数栈弹出两个元素、操作符栈弹出一个元素进行得到计算结果#
// 数栈弹出两元素、操作符栈弹出一个操作符中进行简单运算
private double sResult(String operand1, String operand2, Character operation) {
// 将操作数转成double类型,进行数字运算
Double num1 = Double.valueOf(operand1);
Double num2 = Double.valueOf(operand2);
// 核心代码 - 判断操作符栈是否为空,为空说明正在进行的是最后一次运算,不需要进行操作符转换
if (!operStack.isEmpty()) {
// 获取操作符栈顶的元素 -- 进行下列的字符转换
Character operPeek = operStack.peek();
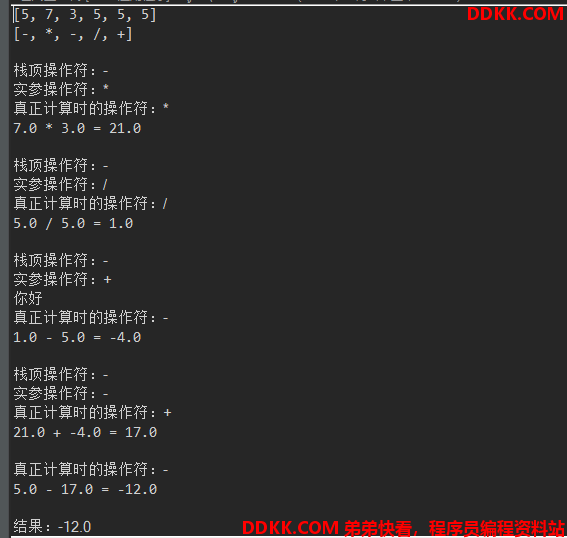
System.out.println("栈顶操作符:" + operPeek);
System.out.println("实参操作符:" + operation);
if (operPeek == '-' && operation == '+') {
System.out.println("你好");
operation = '-';
}
else if (operPeek == '-' && operation == '-') {
operation = '+';
}
else if (operPeek == '/' && operation == '/') {
operation = '*';
num2 = 1 / num2;
}
else if (operPeek == '/' && operation == '*') {
num2 = 1 / num2;
}
}
System.out.println("真正计算时的操作符:" + operation);
// 根据操作符,进行弹出的两个数字与操作符的运算
switch (operation) {
case '+': {
System.out.printf("%.1f %s %.1f = %.1f\n\n", num1, operation +"" , num2 , num1+num2);
return num1 + num2;
}
case '-': {
System.out.printf("%.1f %s %.1f = %.1f\n\n", num1, operation +"" , num2 , num1-num2);
return num1 - num2;
}
case '*': {
System.out.printf("%.1f %s %.1f = %.1f\n\n", num1, operation +"" , num2 , num1*num2);
return num1 * num2;
}
case '/': {
System.out.printf("%.1f %s %.1f = %.1f\n\n", num1, operation +"" , num2 , num1/num2);
return num1 / num2;
}
default: {
throw new RuntimeException("不支持处理" + operation + "这种操作符的表达式");
}
}
}
④ result() – 获取算术表达式的最终结果#
public double result() {
// 1. 判断表达式是否符合计算要求
if (!isArithmeticExpression()) {
throw new RuntimeException("表达式不符合要求");
}
// 2. 打印最终解析表达式后的结果
System.out.println(Arrays.toString(temp_num));
System.out.println(Arrays.toString(temp_oper) + "\n");
// 数字数组、操作符数组指针
int num_index = 0;
int oper_index = 0;
// 3. 计算双栈、压栈、弹栈计算操作
while (true) {
// 3.1 先从数字数组压入一个数字
if (num_index != temp_num.length) {
numStack.push(temp_num[num_index++]);
}
// 3.2 再从操作符数组压入一个操作符
if (oper_index != temp_oper.length) {
// 3.2.1 如果操作符栈无元素,直接压栈
if (operStack.isEmpty()) {
operStack.push(temp_oper[oper_index++]);
// 3.2.2 如果待入栈的操作符优先级小于栈顶的操作符,则需要计算一次,弹出操作符,弹出两个数,将结果压入数栈,再将待入栈的操作符入栈
} else {
Character nextOperation = temp_oper[oper_index++];
if (getPriority(nextOperation) <= getPriority(operStack.peek())) {
String num2 = numStack.pop();
String num1 = numStack.pop();
Double result = sResult(num1, num2, operStack.pop());
numStack.push(result.toString());
operStack.push(nextOperation);
} else {
operStack.push(nextOperation);
}
}
}
// 3.2.3 如果数字数组、操作符数组的元素已经全部都压入双栈,则停止循环
if (num_index == temp_num.length && oper_index == temp_oper.length) {
break;
}
}
// 4. 计算结果,弹出一个操作符,就弹出两个数,直到操作符栈没有元素可弹为止
while (!operStack.isEmpty()) {
String num2 = numStack.pop();
String num1 = numStack.pop();
Character operation = operStack.pop();
Double result = sResult(num1, num2, operation);
numStack.push(result.toString());
}
// 5. 计算结果已经压入数栈中,直接弹出即可
return Double.valueOf(numStack.pop());
}
测试代码
public static void main( String[] args ) {
{
//OperationalExpression os = new OperationalExpression("5-7*3-5");
//OperationalExpression os = new OperationalExpression("7+2*6-4");
OperationalExpression os = new OperationalExpression("5-7*3-5/5+5");
double a = os.result();
System.out.printf("结果:%.1f" , a);
}
代码运行