基本流程图,方法查看
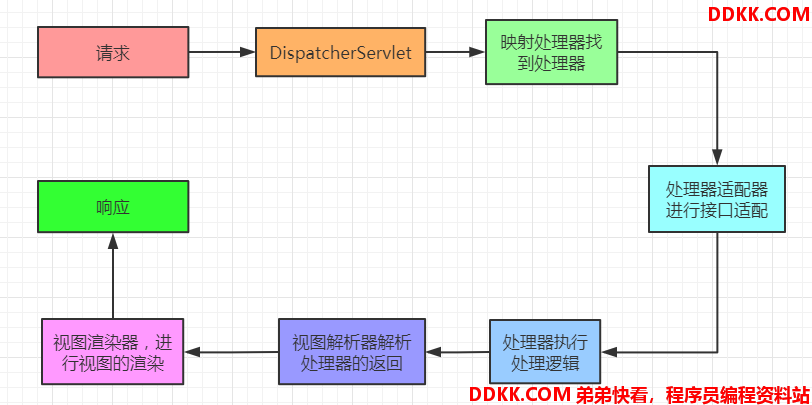
DispatcherServlet的doDispatch的核心方法分析
getHandler获取处理器
看起来好像就没多少,其实内部东西还是挺多的,这里就是我们前面初始化的处理器映射器的作用,找到处理器,然后加入拦截器,封装成执行链HandlerExecutionChain 。遍历所有的处理器映射器,找到合适的就返回了。接下去我们看看他们是怎么找的,主要分析RequestMappingHandlerMapping和BeanNameUrlHandlerMapping,其他的有兴趣自己可以看,常用的是RequestMappingHandlerMapping。
@Nullable
protected HandlerExecutionChain getHandler(HttpServletRequest request) throws Exception {
if (this.handlerMappings != null) {
for (HandlerMapping mapping : this.handlerMappings) {
HandlerExecutionChain handler = mapping.getHandler(request);
if (handler != null) {
return handler;
}
}
}
return null;
}
RequestMappingHandlerMapping的getHandler
我们研究一般的流程,不考虑CORS,其实就是尝试获取处理器,这里的处理器其实是封装的方法HandlerMethod,然后进行拦截器的封装。
@Override
@Nullable
public final HandlerExecutionChain getHandler(HttpServletRequest request) throws Exception {
Object handler = getHandlerInternal(request);
if (handler == null) {
handler = getDefaultHandler();
}
if (handler == null) {
return null;
}
// Bean name or resolved handler?
if (handler instanceof String) {
//如果没有实例化就实例化
String handlerName = (String) handler;
handler = obtainApplicationContext().getBean(handlerName);
}
//获取执行链
HandlerExecutionChain executionChain = getHandlerExecutionChain(handler, request);
...
return executionChain;
}
AbstractHandlerMethodMapping的getHandlerInternal
核心方法是lookupHandlerMethod。
@Override
protected HandlerMethod getHandlerInternal(HttpServletRequest request) throws Exception {
String lookupPath = getUrlPathHelper().getLookupPathForRequest(request);//获取查找路径
request.setAttribute(LOOKUP_PATH, lookupPath);
this.mappingRegistry.acquireReadLock();
try {
HandlerMethod handlerMethod = lookupHandlerMethod(lookupPath, request);//查找方法
return (handlerMethod != null ? handlerMethod.createWithResolvedBean() : null);
}
finally {
this.mappingRegistry.releaseReadLock();
}
}
AbstractHandlerMethodMapping的lookupHandlerMethod
首先去uri映射注册器里找是否有这个方法的集合,有的话直接处理,没有的话就遍历所有的uri处理,找出最匹配的HandlerMethod 返回。
@Nullable
protected HandlerMethod lookupHandlerMethod(String lookupPath, HttpServletRequest request) throws Exception {
List<Match> matches = new ArrayList<>();
List<T> directPathMatches = this.mappingRegistry.getMappingsByUrl(lookupPath);
if (directPathMatches != null) {
//有path匹配的直接处理
addMatchingMappings(directPathMatches, matches, request);
}
if (matches.isEmpty()) {
//没有就遍历所有的处理
// No choice but to go through all mappings...
addMatchingMappings(this.mappingRegistry.getMappings().keySet(), matches, request);
}
if (!matches.isEmpty()) {
//有匹配的
Match bestMatch = matches.get(0);
if (matches.size() > 1) {
//多个匹配的情况
Comparator<Match> comparator = new MatchComparator(getMappingComparator(request));
matches.sort(comparator);
bestMatch = matches.get(0);
if (logger.isTraceEnabled()) {
logger.trace(matches.size() + " matching mappings: " + matches);
}
if (CorsUtils.isPreFlightRequest(request)) {
return PREFLIGHT_AMBIGUOUS_MATCH;
}
Match secondBestMatch = matches.get(1);
if (comparator.compare(bestMatch, secondBestMatch) == 0) {
Method m1 = bestMatch.handlerMethod.getMethod();
Method m2 = secondBestMatch.handlerMethod.getMethod();
String uri = request.getRequestURI();
throw new IllegalStateException(
"Ambiguous handler methods mapped for '" + uri + "': {" + m1 + ", " + m2 + "}");
}
}//handlerMethod设置到属性里
request.setAttribute(BEST_MATCHING_HANDLER_ATTRIBUTE, bestMatch.handlerMethod);
handleMatch(bestMatch.mapping, lookupPath, request);
return bestMatch.handlerMethod;
}
else {
return handleNoMatch(this.mappingRegistry.getMappings().keySet(), lookupPath, request);
}
}
MappingRegistry的getMappingsByUrl
这个会先进行uri匹配,如果获取到了就直接返回,那这些uri是怎么来的,我们还是要先弄明白。
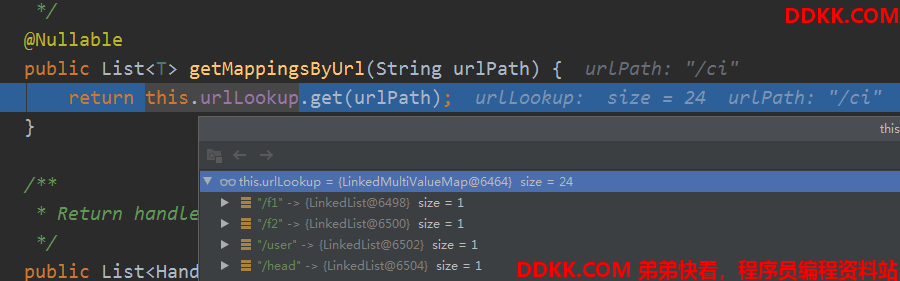
下篇介绍下这个uri怎么来的。
好了,今天就到这里了,希望对学习理解有帮助,大神看见勿喷,仅为自己的学习理解,能力有限,请多包涵。