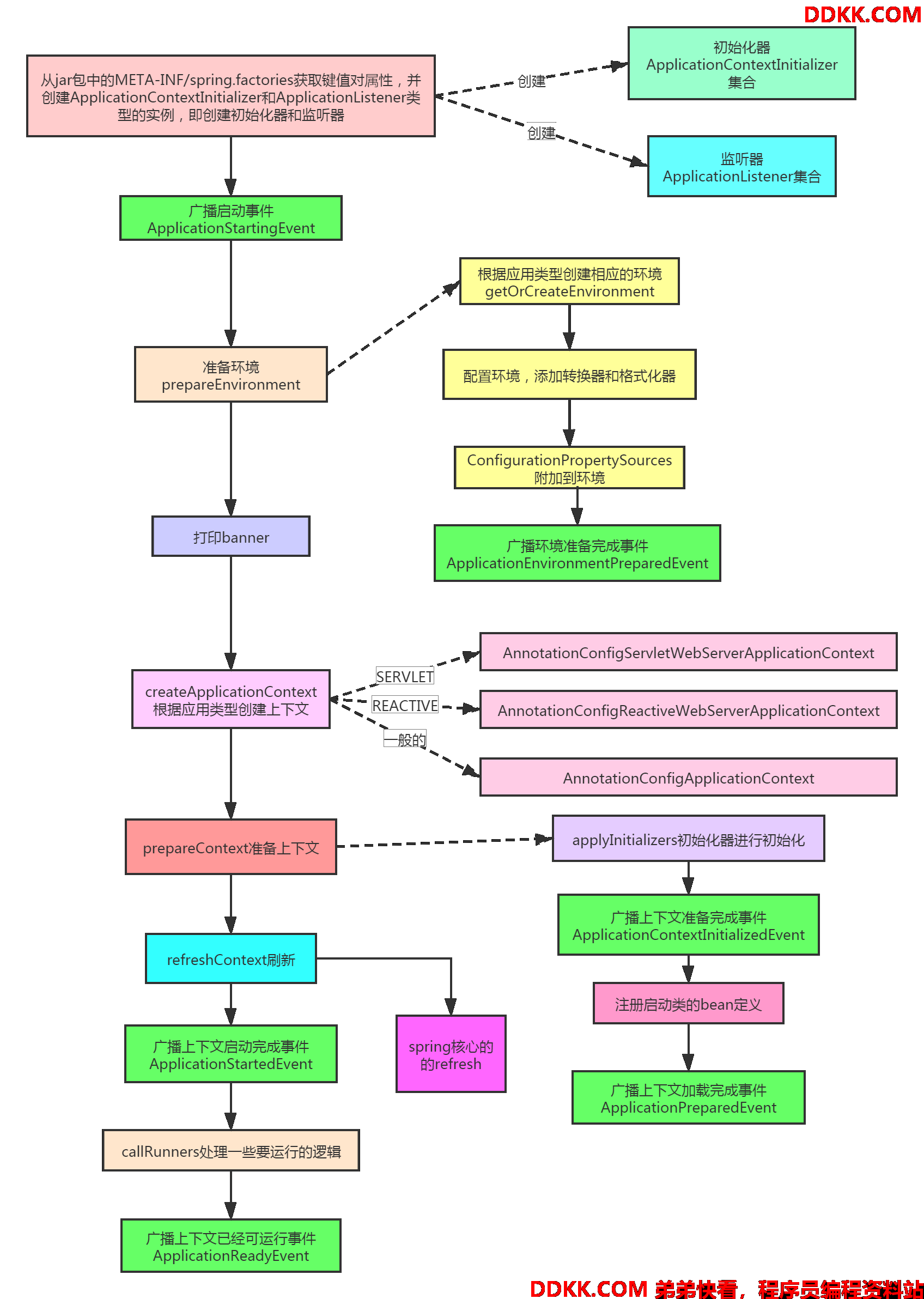
初始化基本流程
AbstractApplicationEventMulticaster的supportsEvent是否支持该事件
如果是GenericApplicationListener类型的话,就可以直接判断,不是的话要用适配器适配一下,适配器模式,接口不一致的时候,可以用这个适配,这里用的是对象适配器,持有要适配的对象。是否支持就是看事件类型和事件源类型是否支持了。
protected boolean supportsEvent(
ApplicationListener<?> listener, ResolvableType eventType, @Nullable Class<?> sourceType) {
GenericApplicationListener smartListener = (listener instanceof GenericApplicationListener ?
(GenericApplicationListener) listener : new GenericApplicationListenerAdapter(listener));
return (smartListener.supportsEventType(eventType) && smartListener.supportsSourceType(sourceType));
}
GenericApplicationListenerAdapter事件监听器适配器
保存监听器,然后解析出监听那种事件类型,便于后面判断。
public GenericApplicationListenerAdapter(ApplicationListener<?> delegate) {
Assert.notNull(delegate, "Delegate listener must not be null");
this.delegate = (ApplicationListener<ApplicationEvent>) delegate;
this.declaredEventType = resolveDeclaredEventType(this.delegate);//解析出对哪种ApplicationEvent事件支持的ResolvableType对象
}
supportsEventType是否支持该类型事件
如果发现被适配对象是SmartApplicationListener类型的,就直接调用他的supportsEventType方法,否则就判断事件类型是不是监听器支持的事件类型或者是事件子类类型declaredEventType 。
@Override
@SuppressWarnings("unchecked")
public boolean supportsEventType(ResolvableType eventType) {
if (this.delegate instanceof SmartApplicationListener) {
Class<? extends ApplicationEvent> eventClass = (Class<? extends ApplicationEvent>) eventType.resolve();
return (eventClass != null && ((SmartApplicationListener) this.delegate).supportsEventType(eventClass));
}
else {
return (this.declaredEventType == null || this.declaredEventType.isAssignableFrom(eventType));
}
}
//封装成ResolvableType对象
@Override
public boolean supportsEventType(Class<? extends ApplicationEvent> eventType) {
return supportsEventType(ResolvableType.forClass(eventType));
}
supportsSourceType是否支持该事件源类型
如果被适配监听器不是SmartApplicationListener类型,直接支持,否则就调用他的supportsSourceType来判断。
@Override
public boolean supportsSourceType(@Nullable Class<?> sourceType) {
return !(this.delegate instanceof SmartApplicationListener) ||
((SmartApplicationListener) this.delegate).supportsSourceType(sourceType);
}
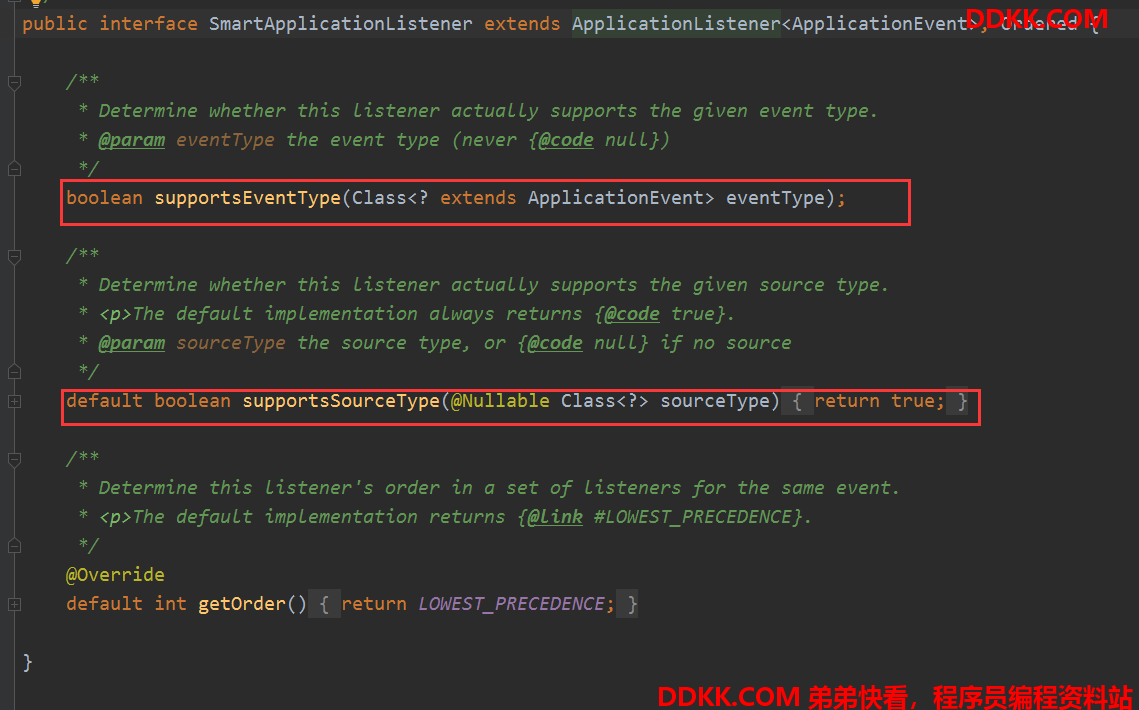
事件支持接口
SmartApplicationListener
GenericApplicationListener
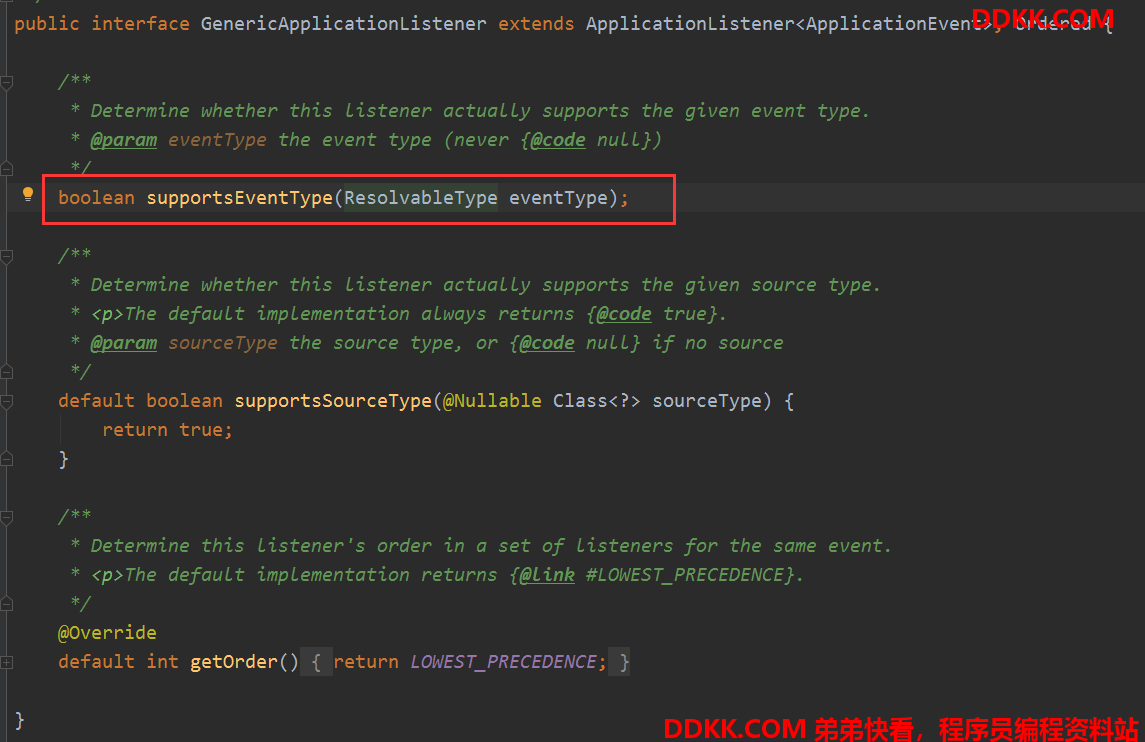
他们的区别就是supportsEventType方法的参数,一个是直接的事件类型,一个是ResolvableType,为什么要在封装一层呢,其实是为了封装一些类型相关的方法,可以方法使用,具体你可以去看ResolvableType里面的方法就知道了。
SimpleApplicationEventMulticaster的invokeListener通知监听器
将支持该事件的监听器集合获取后遍历通知。
protected void invokeListener(ApplicationListener<?> listener, ApplicationEvent event) {
ErrorHandler errorHandler = getErrorHandler();
if (errorHandler != null) {
//有错误处理的,可以捕获异常
try {
doInvokeListener(listener, event);
}
catch (Throwable err) {
errorHandler.handleError(err);
}
}
else {
doInvokeListener(listener, event);//一般的
}
}
SimpleApplicationEventMulticaster的doInvokeListener真正执行的
其实就是调用监听器的的onApplicationEvent啦,传入事件event。
private void doInvokeListener(ApplicationListener listener, ApplicationEvent event) {
try {
listener.onApplicationEvent(event);
}
catch (ClassCastException ex) {
String msg = ex.getMessage();
if (msg == null || matchesClassCastMessage(msg, event.getClass())) {
// Possibly a lambda-defined listener which we could not resolve the generic event type for
// -> let's suppress the exception and just log a debug message.
Log logger = LogFactory.getLog(getClass());
if (logger.isTraceEnabled()) {
logger.trace("Non-matching event type for listener: " + listener, ex);
}
}
else {
throw ex;
}
}
}
比如我们的LoggingApplicationListener,会根据不同类型做出不同响应:
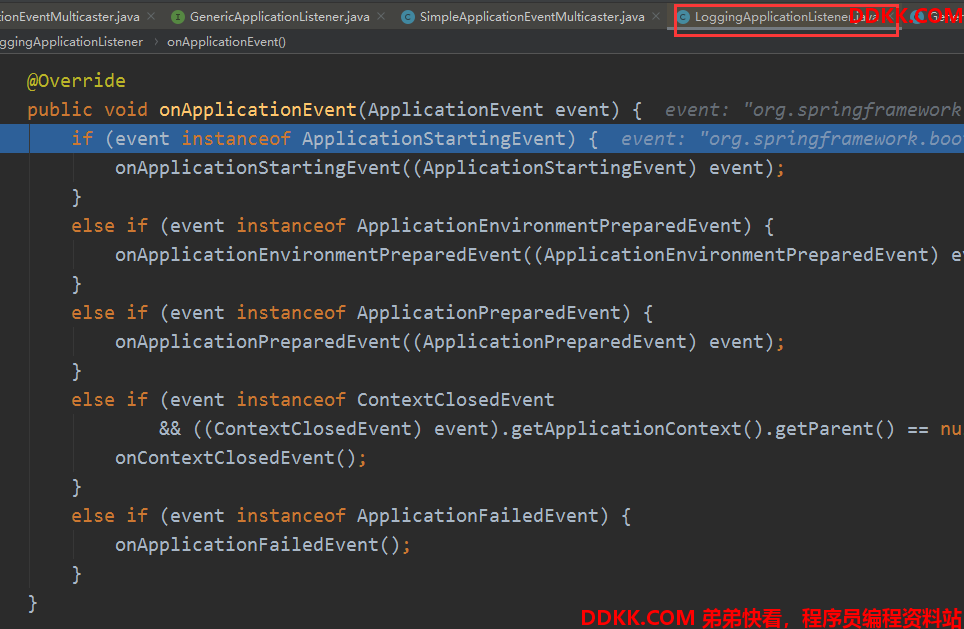
至此,启动广播完成了,监听器们收到了ApplicationStartingEvent事件,然后进行处理,目前这些监听器会支持该事件:
好了,今天就到这里了,希望对学习理解有帮助,大神看见勿喷,仅为自己的学习理解,能力有限,请多包涵。