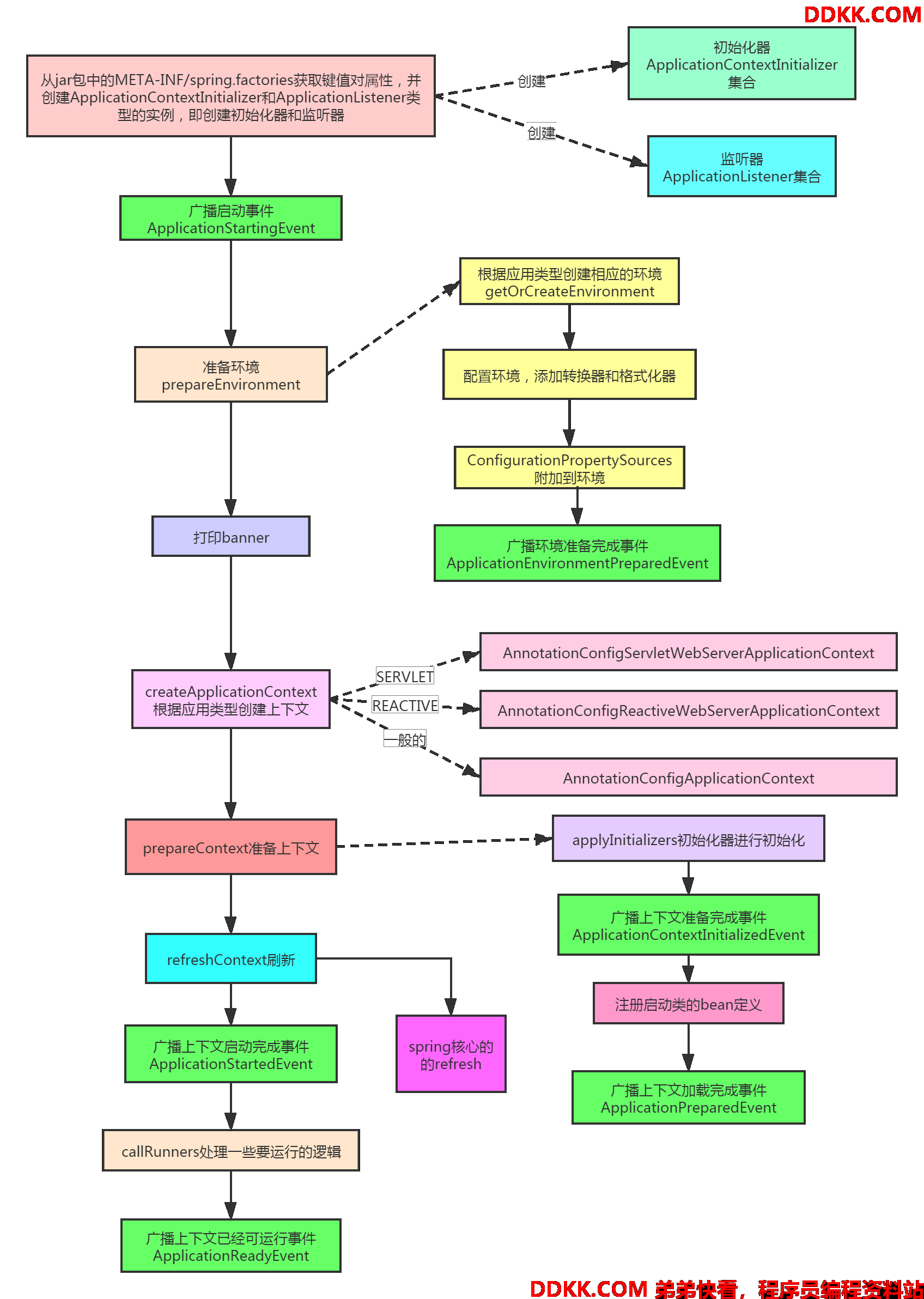
初始化基本流程
SpringApplication的setListeners设置监听器
这个跟前面的设置初始化器类似,只是要的类型是org.springframework.context.ApplicationListener。这个监听器干嘛用,其实就是有个观察者模式,spring为了让其他可以扩展,让他们知道现在初始化到哪个阶段了,他们可以参数,于是让他们注册到spring内部,再各个阶段进行通知,这样他们就可以一起初始化了。

deduceMainApplicationClass对端主启动类
这里就是推断启动类的,直接抛出异常,然后找到main方法所在的类。
private Class<?> deduceMainApplicationClass() {
try {
StackTraceElement[] stackTrace = new RuntimeException().getStackTrace();
for (StackTraceElement stackTraceElement : stackTrace) {
if ("main".equals(stackTraceElement.getMethodName())) {
return Class.forName(stackTraceElement.getClassName());
}
}
}
catch (ClassNotFoundException ex) {
// Swallow and continue
}
return null;
}
至此SpringApplication构造方法分析完了,具体做了什么事情,就是初始化类和监听器的创建。接下来分析run了。
run
其实就是给上下文做准备,会调用spring的初始化,会进行不同初始化阶段的广播,去通知监听器,监听器就可以做一些扩展的事情啦,比如初始化自己的环境什么的。
public ConfigurableApplicationContext run(String... args) {
StopWatch stopWatch = new StopWatch();//计时用
stopWatch.start();
ConfigurableApplicationContext context = null;
Collection<SpringBootExceptionReporter> exceptionReporters = new ArrayList<>();
configureHeadlessProperty();
SpringApplicationRunListeners listeners = getRunListeners(args);//获取监听器
listeners.starting();//广播启动事件
try {
ApplicationArguments applicationArguments = new DefaultApplicationArguments(args);//封装参数
ConfigurableEnvironment environment = prepareEnvironment(listeners, applicationArguments);//准备环境
configureIgnoreBeanInfo(environment);//配置要忽略的bean信息
Banner printedBanner = printBanner(environment);//打印banner
context = createApplicationContext();//创建应用上下文
exceptionReporters = getSpringFactoriesInstances(SpringBootExceptionReporter.class,
new Class[] {
ConfigurableApplicationContext.class }, context);//异常报告
prepareContext(context, environment, listeners, applicationArguments, printedBanner);//准备上下文
refreshContext(context);//刷新,就是spring的refresh
afterRefresh(context, applicationArguments);//刷新后处理
stopWatch.stop();
if (this.logStartupInfo) {
new StartupInfoLogger(this.mainApplicationClass).logStarted(getApplicationLog(), stopWatch);
}
listeners.started(context);//广播启动完成事件
callRunners(context, applicationArguments);
}
catch (Throwable ex) {
handleRunFailure(context, ex, exceptionReporters, listeners);
throw new IllegalStateException(ex);
}
try {
listeners.running(context);//广播运行中事件
}
catch (Throwable ex) {
handleRunFailure(context, ex, exceptionReporters, null);
throw new IllegalStateException(ex);
}
return context;
}
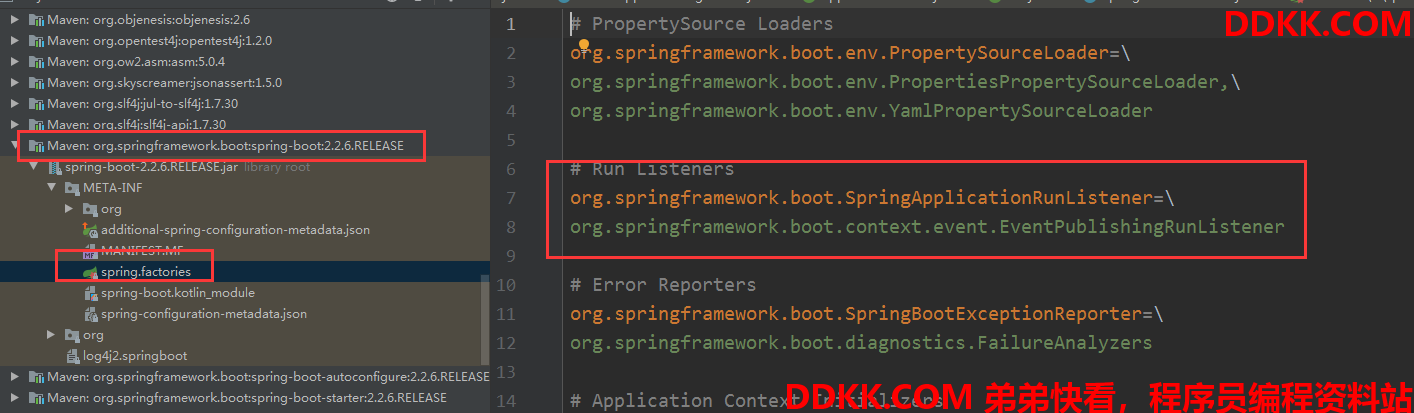
getRunListeners获取SpringApplicationRunListener监听器
这个跟前面的获取方法一样的,获取SpringApplicationRunListener类型的监听器,但是这个时候有缓存了,因为前面全加载进来啦:
private SpringApplicationRunListeners getRunListeners(String[] args) {
//给EventPublishingRunListener准备的构造方法参数类型,这样后面实例化的时候就可以传参数了
Class<?>[] types = new Class<?>[] {
SpringApplication.class, String[].class };
return new SpringApplicationRunListeners(logger,
getSpringFactoriesInstances(SpringApplicationRunListener.class, types, this, args));//这里的创建是会把SpringApplication闯进去的
}
其实你可以看到,其实是一个事件发布监听器,他的事情就是监听SpringApplication的运行事件,然后发布给其他的监听器,他里面有一个事件广播器的,可以广播给其他监听器事件。
实例化的时候根据参数调用构造方法:
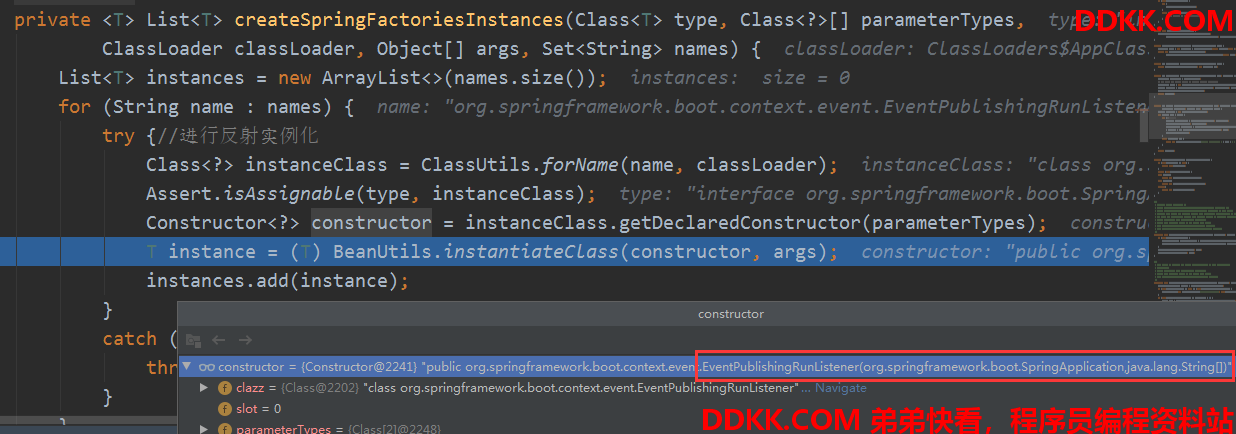
EventPublishingRunListener的构造方法
这里是有参数传进去的,这样他就能获取所有的监听器,然后创建一个事件广播SimpleApplicationEventMulticaster,把监听器都注册进去。
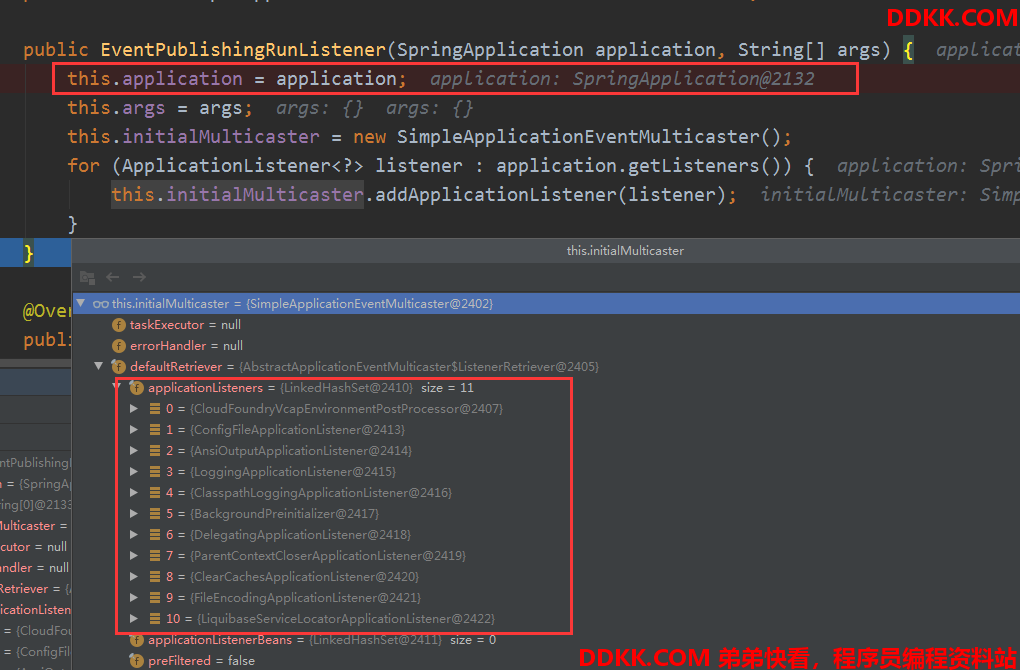
SimpleApplicationEventMulticaster的注册监听器细节
注册的时候有个细节,他会把代理类型的监听器剔除,防止重复通知,还会清除事件和监听器映射的缓存,因为:
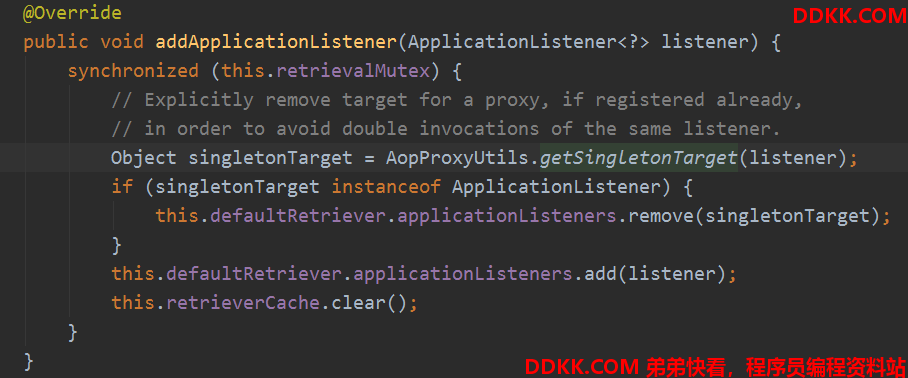
最后封装到SpringApplicationRunListeners中。
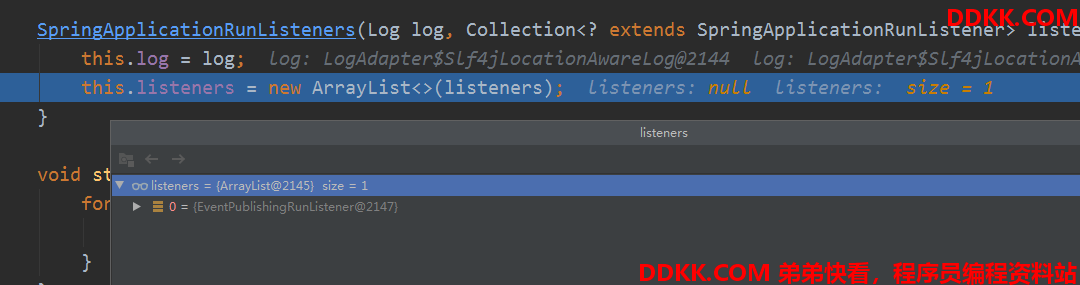
SpringApplicationRunListeners的starting广播启动事件
调用每一个SpringApplicationRunListener的starting,其实就是调用EventPublishingRunListener的,因为现在只有一个。
void starting() {
for (SpringApplicationRunListener listener : this.listeners) {
listener.starting();
}
}
EventPublishingRunListener的starting广播启动事件
果然是广播事件,事件就是ApplicationStartingEvent,里面会封装事件源this.application。
@Override
public void starting() {
this.initialMulticaster.multicastEvent(new ApplicationStartingEvent(this.application, this.args));//封装事件源
}
这个事件继承JDK里的EventObject的:
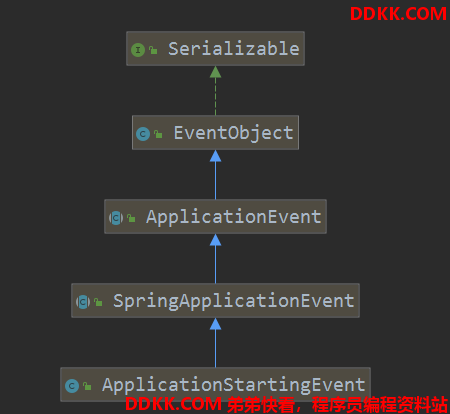
具体的怎么广播的下次讲吧。
好了,今天就到这里了,希望对学习理解有帮助,大神看见勿喷,仅为自己的学习理解,能力有限,请多包涵。