初始化基本流程
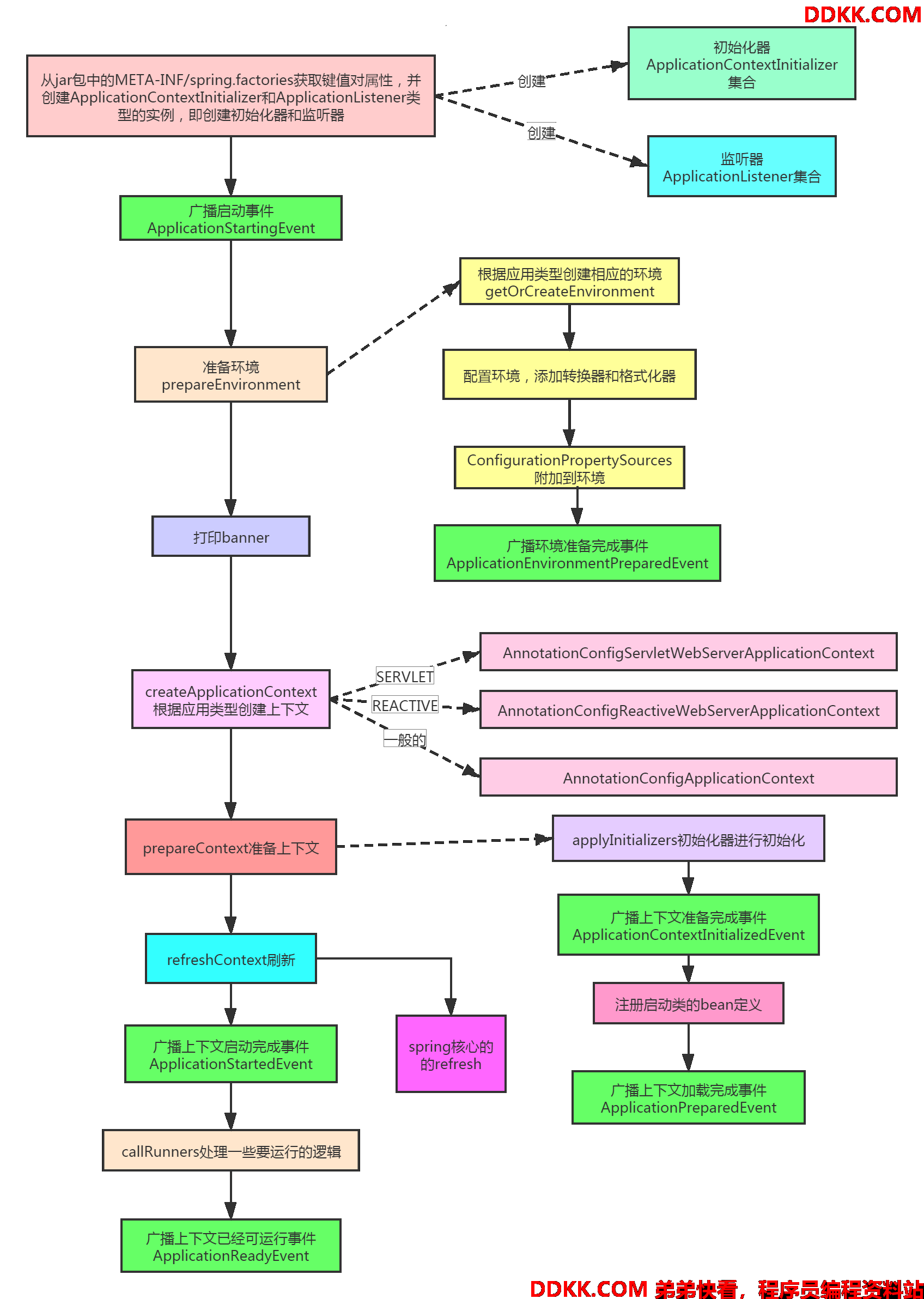
SpringApplication的prepareContext准备上下文
这里面有干了很多事,他会将最前面获得的初始化器都初始化,然后广播上下文准备好事件,然后这里居然还设置了不能覆盖同名bean定义,这样就避免了用户去捣乱了。最后会把启动类的注册到bean定义里,然后广播上下文加载完成事件。
private void prepareContext(ConfigurableApplicationContext context, ConfigurableEnvironment environment,
SpringApplicationRunListeners listeners, ApplicationArguments applicationArguments, Banner printedBanner) {
context.setEnvironment(environment);//配置环境
postProcessApplicationContext(context);//一些设置处理
applyInitializers(context);//初始化监听器进行初始化
listeners.contextPrepared(context);//广播上下文准备好的事件ApplicationContextInitializedEvent
if (this.logStartupInfo) {
//控制台打启动信息
logStartupInfo(context.getParent() == null);
logStartupProfileInfo(context);
}
// Add boot specific singleton beans
ConfigurableListableBeanFactory beanFactory = context.getBeanFactory();
beanFactory.registerSingleton("springApplicationArguments", applicationArguments);
if (printedBanner != null) {
beanFactory.registerSingleton("springBootBanner", printedBanner);
}
if (beanFactory instanceof DefaultListableBeanFactory) {
((DefaultListableBeanFactory) beanFactory)//不允许同名的bean定义的覆盖
.setAllowBeanDefinitionOverriding(this.allowBeanDefinitionOverriding);
}
if (this.lazyInitialization) {
context.addBeanFactoryPostProcessor(new LazyInitializationBeanFactoryPostProcessor());
}
// Load the sources
Set<Object> sources = getAllSources();//获取启动源集合,就是传给SpringApplication的参数类
Assert.notEmpty(sources, "Sources must not be empty");
load(context, sources.toArray(new Object[0]));//注册启动类的bean定义
listeners.contextLoaded(context);//广播上下文加载完成事件ApplicationPreparedEvent
}
postProcessApplicationContext处理
就是提前去注册bean名字生成器,资源加载器,还有前面创建的转换器也要放进来。
protected void postProcessApplicationContext(ConfigurableApplicationContext context) {
if (this.beanNameGenerator != null) {
context.getBeanFactory().registerSingleton(AnnotationConfigUtils.CONFIGURATION_BEAN_NAME_GENERATOR,
this.beanNameGenerator);
}
if (this.resourceLoader != null) {
if (context instanceof GenericApplicationContext) {
((GenericApplicationContext) context).setResourceLoader(this.resourceLoader);
}
if (context instanceof DefaultResourceLoader) {
((DefaultResourceLoader) context).setClassLoader(this.resourceLoader.getClassLoader());
}
}
if (this.addConversionService) {
//添加转换器
context.getBeanFactory().setConversionService(ApplicationConversionService.getSharedInstance());
}
}
applyInitializers初始化器初始化
获取最开始创建的初始化器,遍历每一个初始化器,进行初始化。
protected void applyInitializers(ConfigurableApplicationContext context) {
for (ApplicationContextInitializer initializer : getInitializers()) {
Class<?> requiredType = GenericTypeResolver.resolveTypeArgument(initializer.getClass(),
ApplicationContextInitializer.class);//获取ApplicationContextInitializer接口的泛型类型
Assert.isInstanceOf(requiredType, context, "Unable to call initializer.");//context不是requiredType类型是不行的
initializer.initialize(context);//初始化
}
}
load
创建bean定义加载器,进行bean定义的加载,就是把sources注册到bean定义里。
protected void load(ApplicationContext context, Object[] sources) {
if (logger.isDebugEnabled()) {
logger.debug("Loading source " + StringUtils.arrayToCommaDelimitedString(sources));
}
BeanDefinitionLoader loader = createBeanDefinitionLoader(getBeanDefinitionRegistry(context), sources);
if (this.beanNameGenerator != null) {
loader.setBeanNameGenerator(this.beanNameGenerator);
}
if (this.resourceLoader != null) {
loader.setResourceLoader(this.resourceLoader);
}
if (this.environment != null) {
loader.setEnvironment(this.environment);
}
loader.load();
}
//遍历每一个加载
int load() {
int count = 0;
for (Object source : this.sources) {
count += load(source);
}
return count;
}
根据不同类型加载,最后都是registerBean:
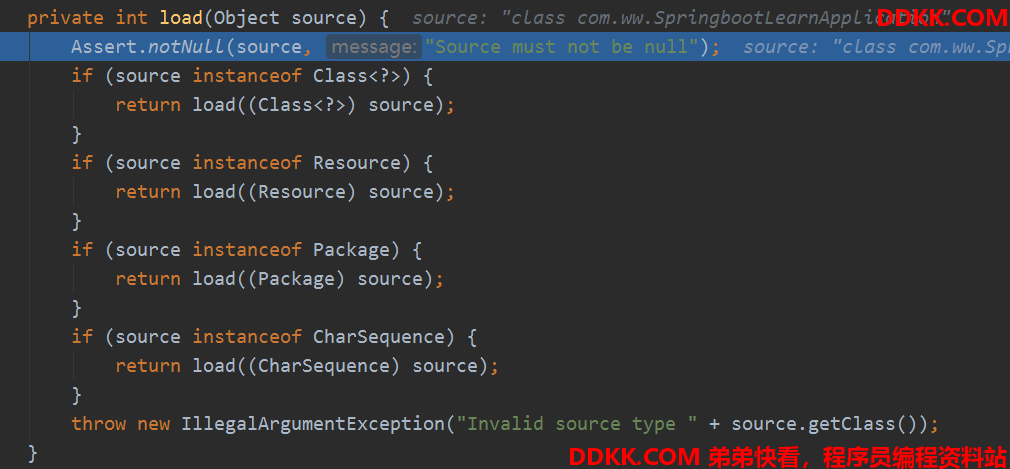
SpringApplication的refreshContext刷新上下文
除了刷新外,还注册了一个钩子,
private void refreshContext(ConfigurableApplicationContext context) {
refresh(context);
if (this.registerShutdownHook) {
try {
context.registerShutdownHook();
}
catch (AccessControlException ex) {
// Not allowed in some environments.
}
}
}
refresh
调用当前上下文AbstractApplicationContext类型的refresh,当前上下文是ServletWebServerApplicationContext类型的,所以会调用到他的refresh。
protected void refresh(ApplicationContext applicationContext) {
Assert.isInstanceOf(AbstractApplicationContext.class, applicationContext);
((AbstractApplicationContext) applicationContext).refresh();
}
ServletWebServerApplicationContext的refresh
然后他又调用父类的refresh。
@Override
public final void refresh() throws BeansException, IllegalStateException {
try {
super.refresh();
}
catch (RuntimeException ex) {
stopAndReleaseWebServer();
throw ex;
}
}
里面就是spring的refresh方法,进行初始化,就不讲了,可以看我写的spring源码文章,其实内部干了不少事情,后面会讲,毕竟前面那么多初始化器初始化了,肯定会对后面spring初始化有所作用。
看看钩子方法,其实就是注册一个关闭线程:
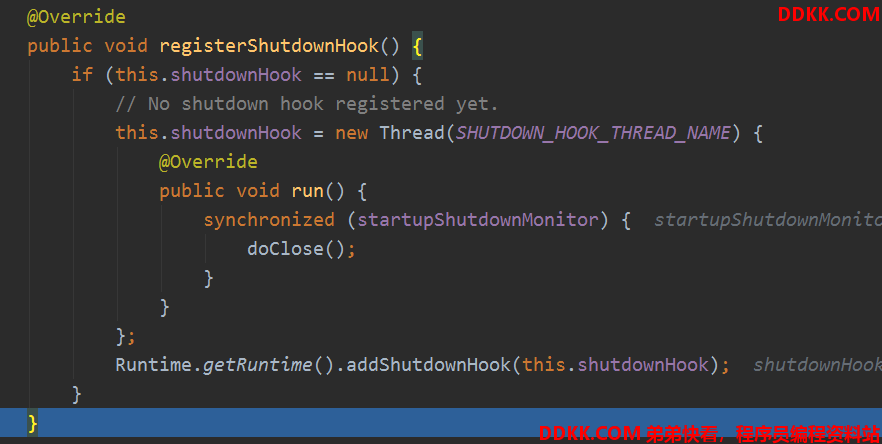
刷新完成后基本没啥事了,就进行启动完成事件通知,还有一些的ApplicationRunner和CommandLineRunner类型的bean要处理,一般是没有的:
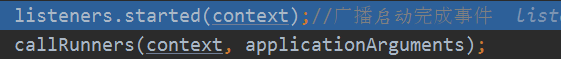
最后再通知一个运行事件初始化就完成了:
初始化基本讲完了,但是还有好多细节没讲,比如我们的tomcat怎么启动的呀,哪些自动配置怎么回事,我们下次讲啦。
好了,今天就到这里了,希望对学习理解有帮助,大神看见勿喷,仅为自己的学习理解,能力有限,请多包涵。