普通构造函数的定义:
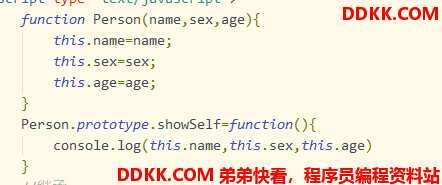
class定义:
所有的属性写在constructor构造器中,原型方法(省略function)直接写在构造函数体中

普通构造函数继承:
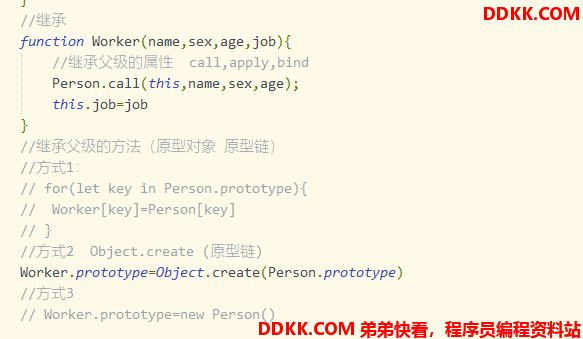
class继承:
class 子级构造函数名名 extend 父级函数名 {}
属性继承:super(父级属性1,父级属性2,…)
原型继承继承结果与普通函数Object.create()作用一样。直接将子一级的原型指向父一级的原型,值拷贝。
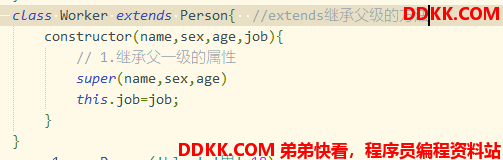
整体比较:
官方构造函数方法
function Person(name,sex,age){
this.name=name;
this.sex=sex;
this.age=age;
}
Person.prototype.showSelf=function(){
console.log(this.name,this.sex,this.age)
}
//继承
function Worker(name,sex,age,job){
//继承父级的属性 call,apply,bind
Person.call(this,name,sex,age);
this.job=job
}
//继承父级的方法(原型对象 原型链)
//方式1:
// for(let key in Person.prototype){
// Worker[key]=Person[key]
// }
//方式2 Object.create (原型链)
Worker.prototype=Object.create(Person.prototype)
//方式3
// Worker.prototype=new Person()
//多态
Worker.prototype.showSelf=function(){
console.log(this.name,this.sex,this.age,this.job)
}
var p1=new Person('blue','man',18,'boss');
var w1=new Worker('woker1','man',30,'boss');
p1.showSelf()
w1.showSelf()
Worker.prototype.run=function(){
}
console.log(p1.__proto__)
console.log(w1.__proto__)
console.log(p1.__proto__==w1.__proto__)
console.log(Worker.prototype,Person.prototype)
console.log(Worker.prototype==Person.prototype)
class构造函数方法
class Person{
constructor(name,sex,age){
this.name=name;
this.sex=sex;
this.age=age;
}
showSelf(){
console.log(this.name,this.sex,this.age)
}
}
class Worker extends Person{
//extends继承父级的方法
constructor(name,sex,age,job){
// 1.继承父一级的属性
super(name,sex,age)
this.job=job;
}
}
var p1=new Person('blue','男',18);
p1.showSelf()
var w1=new Worker('grenn','女',20,'play')
w1.showSelf()
Worker.prototype.showSelf=function(){
//多态
console.log(this.name,this.sex,this.age,this.job)
}
w1.showSelf()
p1.showSelf()
console.log(Worker.prototype,Person.prototype,Worker.prototype==Person.prototype)
注意:在使用构造函数时(无论是普通构造函数,还是class构造函数),如果函数内部出现了事件绑定或者定时器,那么一定要注意事件处理函数和定时器函数的this指向问题。
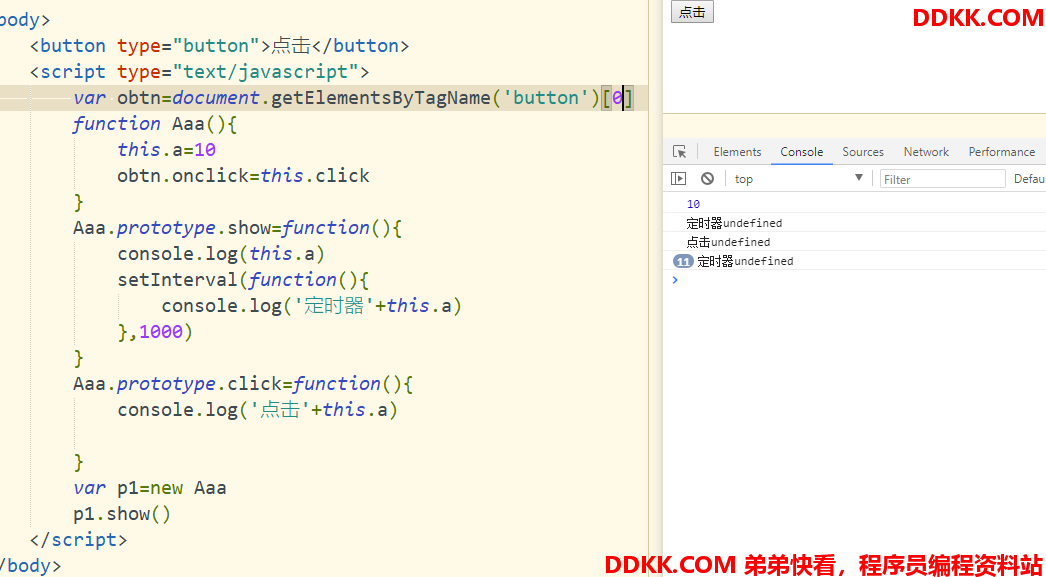
解决方式:
1、 bind、call、apply;
2、 箭头函数;
3、 使用变量保存this;
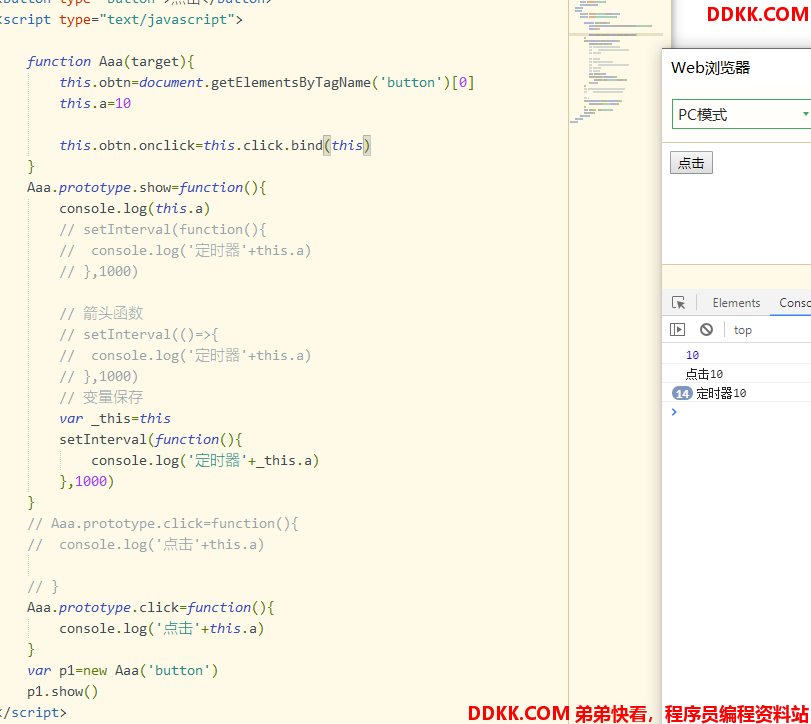
案例:拖拽
普通的拖拽
var oG=document.getElementById('green');
oG.onmousedown=function(ev){
var e=ev||window.event;
// var left=e.clientX-oG.offsetLeft;
// var top=e.clientY-oG.offsetTop;
// console.log(e.offsetX,e.offsetY,left,top)
var left=e.offsetX
var top=e.offsetY;
document.onmousemove=function(ev){
var e=ev||window.event;
oG.style.left=e.clientX-left+'px';
oG.style.top=e.clientY-top+'px'
}
}
document.onmouseup=function(){
document.onmousemove=''
}
改造1.不能有函数嵌套 2.可以有全局变量
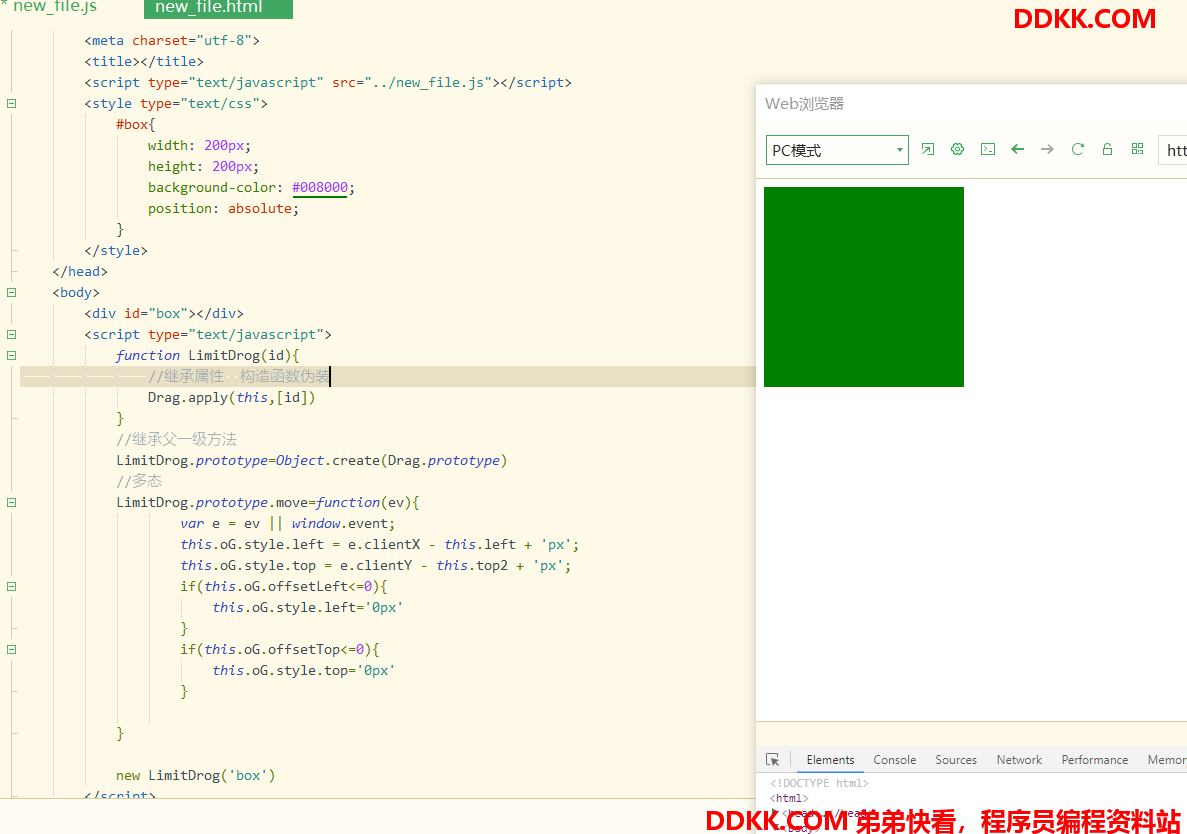
官方构造函数拖拽
function Drag(id){
this.oG=document.getElementById(id);
this.left=0;
this.top2=0;
// 注意:更改this指向 否则事件处理函数的this指向的是它的主人,也就是事件绑定的对象
this.oG.onmousedown = this.down.bind(this)
document.onmouseup = this.up
}
Drag.prototype.down=function(ev){
console.log(this)
var e = ev || window.event;
// var left=e.clientX-oG.offsetLeft;
// var top=e.clientY-oG.offsetTop;
// console.log(e.offsetX,e.offsetY,left,top)
this.left = e.offsetX;
this.top2 = e.offsetY;
// 注意:更改this指向 否则事件处理函数的this指向的是它的主人,也就是事件绑定的对象
document.onmousemove =this.move.bind(this)
}
Drag.prototype.move=function(ev){
console.log(1234,this)
var e = ev || window.event;
this.oG.style.left = e.clientX - this.left + 'px';
this.oG.style.top = e.clientY - this.top2 + 'px'
}
Drag.prototype.up=function(){
document.onmousemove=''
}
window.onload=function(){
new Drag('green')
}
class构造函数拖拽
class Load{
constructor(target){
this.oG=document.getElementById(target);
this.left=0;
this.top2=0;
// 注意:更改this指向 否则事件处理函数的this指向的是它的主人,也就是事件绑定的对象
this.oG.onmousedown = this.down.bind(this)
document.onmouseup = this.up
}
down(ev) {
console.log(this)
var e = ev || window.event;
// var left=e.clientX-oG.offsetLeft;
// var top=e.clientY-oG.offsetTop;
// console.log(e.offsetX,e.offsetY,left,top)
this.left = e.offsetX;
this.top2 = e.offsetY;
document.onmousemove =this.move.bind(this)
}
move(ev) {
console.log(1234,this)
var e = ev || window.event;
this.oG.style.left = e.clientX - this.left + 'px';
this.oG.style.top = e.clientY - this.top2 + 'px'
}
up(){
document.onmousemove=''
}
}
window.onload=function(){
new Load('green')
}
拖拽继承版
选项卡
<!DOCTYPE html>
<html>
<head>
<meta charset="utf-8">
<title></title>
<style type="text/css">
button{
background-color: aquamarine;
}
p{
display: none;
}
.mian{
width: 200px;
height: 200px;
border: 1px dashed darkolivegreen;
}
</style>
</head>
<body>
<button>HTML</button>
<button>CSS</button>
<button>javascript</button>
<div class="mian">
<p>html:jjjjjjj</p>
<p>css:hghjgjhj</p>
<p>javascript:hjhhhhhjhjhhhhj</p
</div>
<script type="text/javascript">
// var obtn=document.getElementsByTagName('button')
// var app=document.getElementsByTagName('p')
// function xunhuan(){
// for(let i=0;i<obtn.length;i++){
// obtn[i].οnclick=function(){
// for(let i=0;i<obtn.length;i++){
// app[i].style.display='none'
// obtn[i].setAttribute('style','background-color:aquamarine;')
// }
// obtn[i].style.backgroundColor='pink'
// app[i].style.display='block'
// }
// }
// }
function Selectcar(target1,target2){
this.obtn=document.getElementsByTagName('button')
this.app=document.getElementsByTagName('p')
for(let i=0;i<this.obtn.length;i++){
this.obtn[i].onclick=this.click.bind(this,i)
}
}
Selectcar.prototype.click=function(i){
for(let i=0;i<this.obtn.length;i++){
this.app[i].style.display='none'
this.obtn[i].setAttribute('style','background-color:aquamarine;')
}
this.obtn[i].style.backgroundColor='pink'
this.app[i].style.display='block'
}
new Selectcar('button','p')
</script>
</body>
</html>