题目地址:https://leetcode.com/problems/climbing-stairs/open in new window
Total Accepted: 106510 Total Submissions: 290041 Difficulty: Easy
题目大意
Youare climbing a stair case. It takes n steps to reach to the top.
Each time you can either climb 1 or 2 steps. In how many distinct ways can you climb to the top?
Note: Given n will be a positive integer.
Example 1:
Input: 2
Output: 2
Explanation: There are two ways to climb to the top.
1. 1 step + 1 step
2. 2 steps
Example 2:
Input: 3
Output: 3
Explanation: There are three ways to climb to the top.
1. 1 step + 1 step + 1 step
2. 1 step + 2 steps
3. 2 steps + 1 step
题目大意
有多少种不同的爬楼梯到达顶部的方式,每次可以走一个台阶或者两个台阶。
解题方法
注意题目中的意思是,有多少种方法,也就是说加入三个台阶,1,2与2,1是不同的。
递归
用费布拉奇数列的方法。
为什么呢?因为每次增加一个台阶可以认为是在前面那个解法中任意的一步增加一步。额,我也说不明白。
写出来前面几个数值就能看出来。
1 --> 1
2 --> 2
3 --> 3
4 --> 5
……
解法:
public class Solution {
public int climbStairs(int n) {
if(n==1) return 1;
if(n==2) return 2;
return climbStairs(n-1)+climbStairs(n-2);
}
}
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8
但是!超时!因为这个方法太慢了,循环次数太多。
记忆化搜索
上面超时的原因主要是同样的n被求了很多遍。如果使用记忆化,那么就不用重复求解。
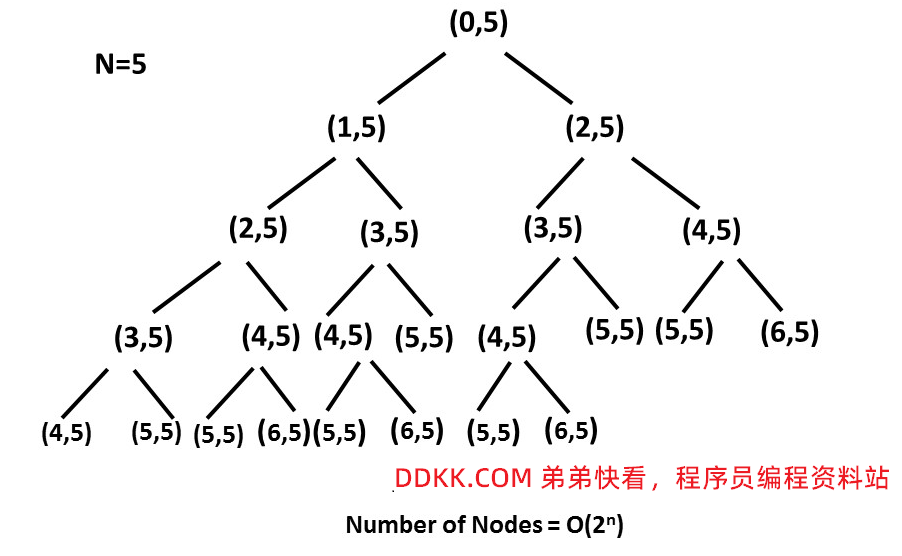
所以使用一个字典用来保存已经求得的结果就好了。
class Solution(object):
def __init__(self):
self.memo = dict()
self.memo[0] = 1
self.memo[1] = 1
def climbStairs(self, n):
"""
:type n: int
:rtype: int
"""
if n in self.memo:
return self.memo[n]
steps = self.climbStairs(n - 1) + self.climbStairs(n - 2)
self.memo[n] = steps
return steps
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16
动态规划
动态规划,需要建立一个数组,然后从头开始遍历,在本题中每个位置的结果就是前两个数相加。看最后一个数值就好了。
这里需要注意的地方是初始化的大小是n+1,因为保存了0的位置步数是1,要求n的步数,所以总的是N+1个状态。
public class Solution {
public int climbStairs(int n) {
int[] counts=new int[n+1];
counts[0]=1;
counts[1]=1;
for(int i=2;i<=n;i++){
counts[i]=counts[i-1]+counts[i-2];
}
return counts[n];
}
}
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12
AC:0ms
DP的Python解法如下:
class Solution(object):
def climbStairs(self, n):
"""
:type n: int
:rtype: int
"""
dp = [0] * (n + 1)
dp[0] = 1
dp[1] = 1
for i in range(2, n + 1):
dp[i] = dp[i - 1] + dp[i - 2]
return dp[-1]
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12
空间压缩DP
我们看到DP的每个状态之和前面两个状态有关,所以可以使用空间压缩,只需要使用三个变量即可,也可以使用大小为3的数组进行循环利用。
Java解法如下:
public class Solution {
public int climbStairs(int n) {
int[] counts=new int[3];
counts[0]=1;
counts[1]=1;
for(int i=2;i<=n;i++){
counts[i%3]=counts[(i-1)%3]+counts[(i-2)%3];
}
return counts[n%3];
}
}
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12
AC:0ms
Python解法如下:
class Solution(object):
def climbStairs(self, n):
"""
:type n: int
:rtype: int
"""
if n == 1:
return 1
first, second = 1, 2
for i in range(3, n + 1):
third = first + second
first = second
second = third
return second
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14
DDKK.COM 弟弟快看-教程,程序员编程资料站,版权归原作者所有
本文经作者:负雪明烛 授权发布,任何组织或个人未经作者授权不得转发