普通的字符串匹配有什么问题?
比如字符串是 aaaaaaaaaaaaaab,匹配串是aaab
遍历字符串,一个个位置比较
aaaaaaaaaaaaaab
aaab
↑
当比较到第三位,才知道匹配失败
然后来到下标1
aaaaaaaaaaaaaab
aaab
↑
还是要比较到匹配串第三位,才知道匹配失败
中间其实有一部分是已经比较过的,现在又重复比较
前置概念:前缀与后缀串的最长匹配长度
比如字符串 abcabck
k前面的 abcabc,前面的abc和后面的abc相等,是前缀与后缀串匹配的最大长度
所以字符k的前缀与后缀串的最长匹配长度是3
abcabck
3
那么aaaaak 呢?
aaaaak
4
那么aabaabs 呢?
aab a a b s
-10 1 0 1 2 3
那么生成的这个数组,记为next数组
next数组是利用匹配串求出的
next数组可以加速匹配过程
怎么加速?
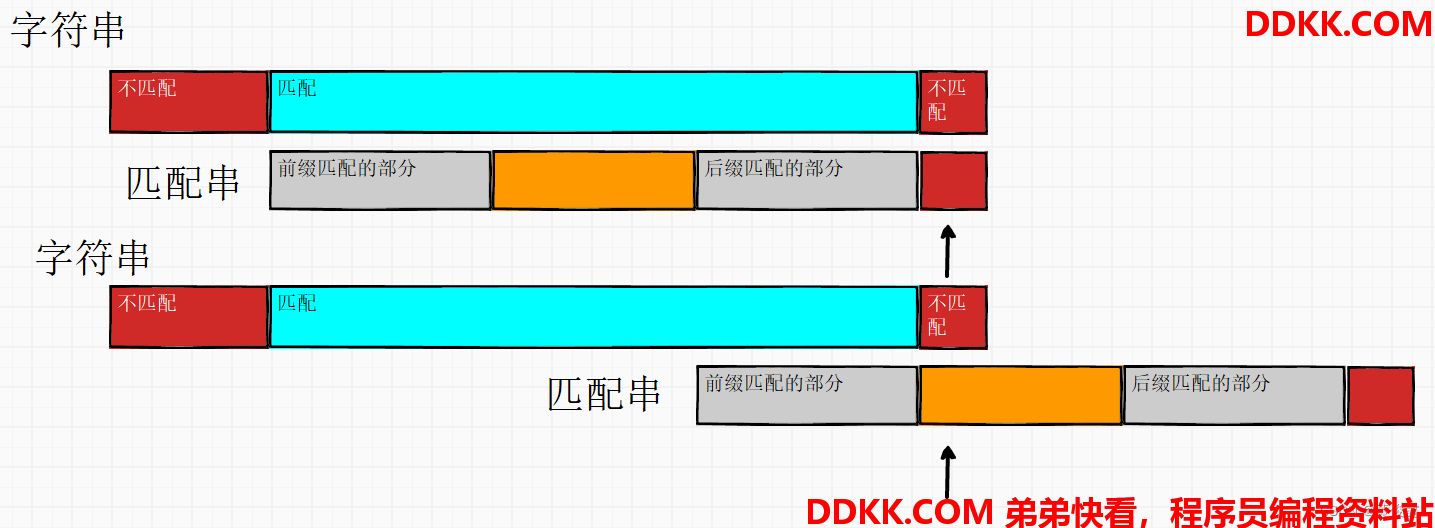
当匹配当不相等的位置,根据next数组保存的前后缀串匹配长度,匹配串可以往右推,前后缀串匹配的部分不需要再比较,而原来的指针保持不变(指针不回退)
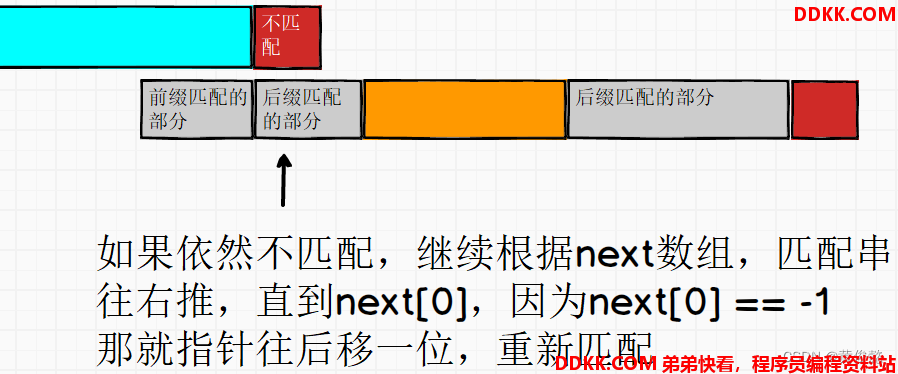
如果依然不匹配,同样的操作,根据next数组,把匹配串往右推
直到遇到next[0]的-1,表示指针指向的开头不可能匹配成功,换一个开头(指针后移),重新匹配
那匹配串往右推,中间略过的部分,为什么肯定它一定不匹配呢?
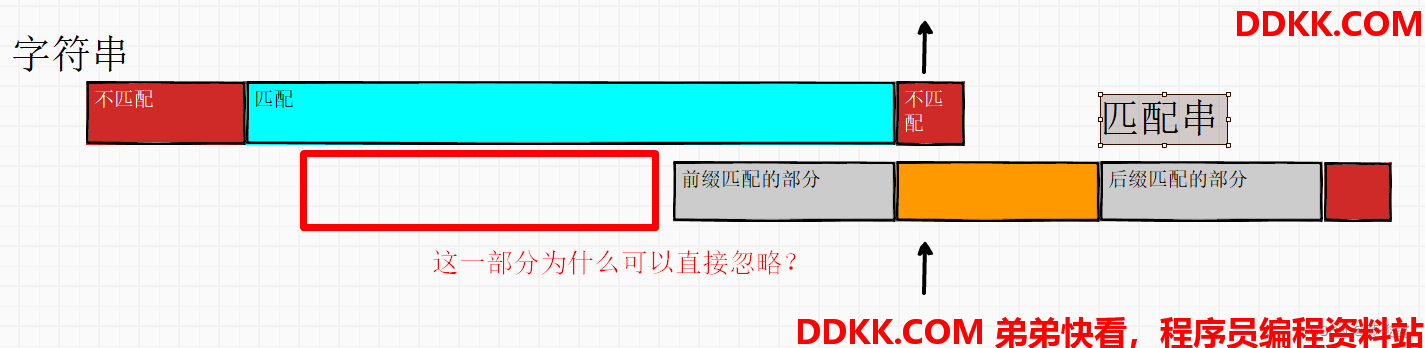
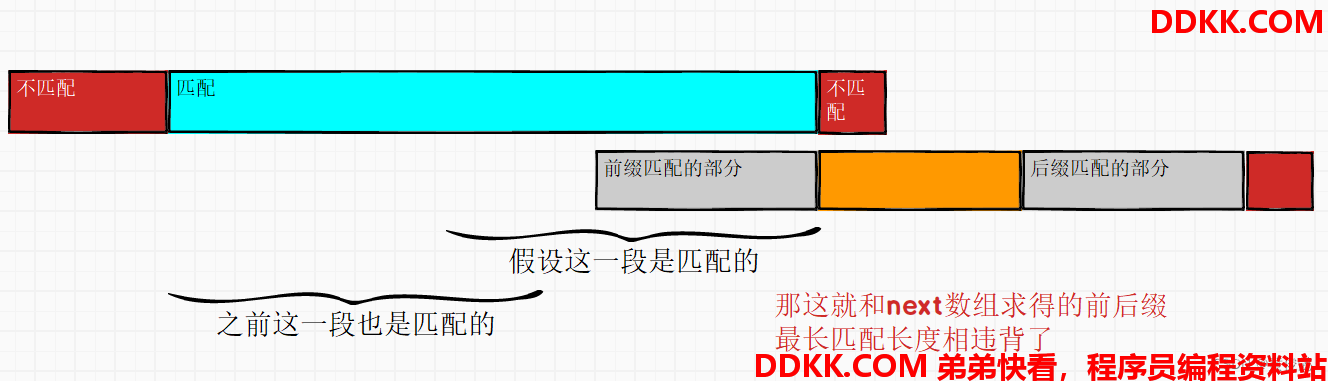
因为如果这一部分的某个开头是可以匹配上的话,就和next数组求得的前后缀最长匹配长度相违背了
那往右推怎么操作?
因为字符串匹配时需要两个指针的,字符串指针和匹配串指针
匹配串往右推,相当于匹配串指针往回跳,根据next数组的值往回跳
aabaabt
↑
aabaabs
↑
不匹配,匹配串指针往回跳
aabaabt
↑
aabaabs
↑
匹配流程的代码
public static int getIndexOf(String str, String match) {
if (str == null || match == null || match.length() == 0 || match.length() > str.length()) return -1;
// 根据匹配串,求出next数组
int[] next = getNext(match);
int x = 0; // 字符串指针
int y = 0; // 匹配串指针
// 进行匹配
while (x < str.length() && y < match.length()) {
if (str.charAt(x) == match.charAt(y)) {
// 匹配,两个指针++
x++;
y++;
} else if (next[y] != -1) {
// 匹配失败,匹配串指针调回next[y]位置,相当于匹配串往右推
y = next[y];
} else {
// 此时y回到0了,next[0] == -1,表示以x开头不可能匹配上了,x往后移一位
x++;
}
}
// 出来了,如果匹配串指针越界了,表示匹配成功了,否则就是匹配串失败了
return y == match.length() ? x - y : -1;
}
那next数组怎么求?
首先
next[0] = -1;
next[1] = 0;
next[2]就看前面两个是否相等,相等则是1,不等则是0
那么某个位置i呢?next[i]怎么求
假设next数组i位置前面的都已经算好了
那么算next[i]可以利用next[i-1]
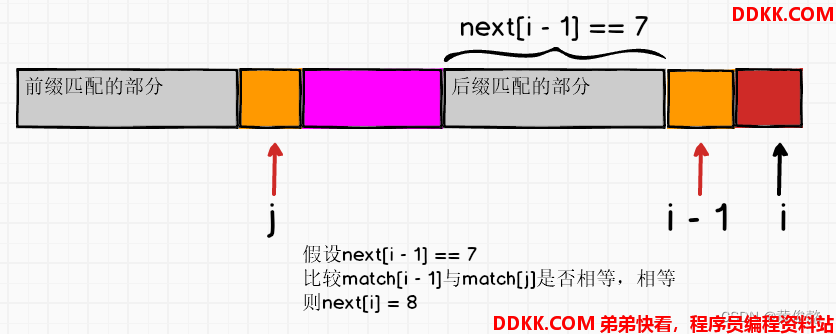
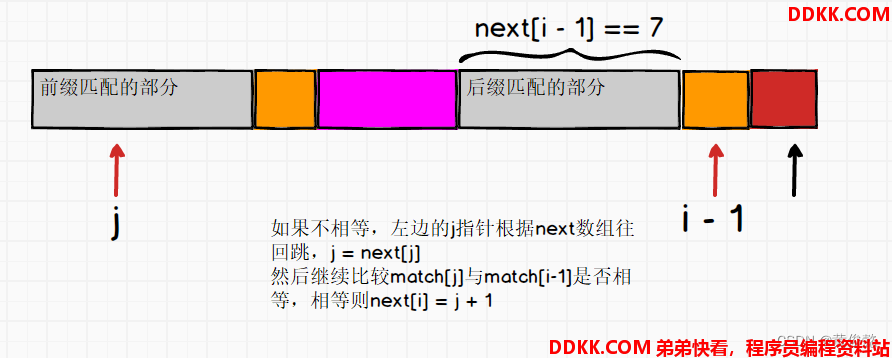
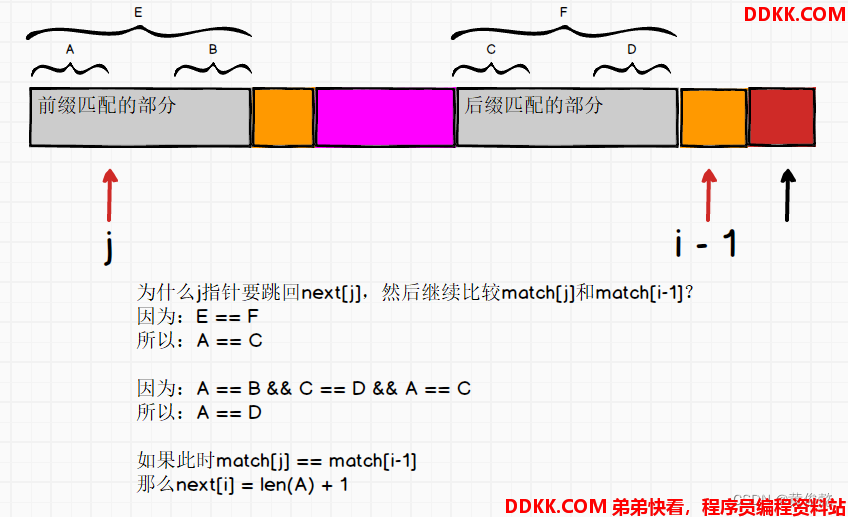
为什么j指针要跳回next[j],然后继续比较match[j]和match[i-1]?
求next数组过程的代码
private static int[] getNext(String match) {
if (match.length() == 1) return new int[]{
-1};
int[] next = new int[match.length()];
next[0] = -1;
next[1] = 0;
int j = 0; // 代表左边前缀串长度,也表示要与i-1位置字符比较的字符的位置
int i = 2; // 现在求next数组i位置的值
while (i < match.length()) {
// 前缀串后一个字符,和i-1位置字符相等,则next[i]就是前缀串长度+1
if (match.charAt(i - 1) == match.charAt(j)) {
next[i++] = ++j;
} else if (j == 0) {
// j都回到0了,还不匹配,那么next[i]只能是0,表示该位置i没有前缀串与后缀串匹配
next[i++] = 0;
} else {
// 不匹配,根据next数组往左跳
j = next[j];
}
}
return next;
}
整体流程代码
/**
* kmp算法
* Created by huangjunyi on 2022/9/4.
*/
public class KMP01 {
public static int getIndexOf(String str, String match) {
if (str == null || match == null || match.length() == 0 || match.length() > str.length()) return -1;
// 根据匹配串,求出next数组
int[] next = getNext(match);
int x = 0; // 字符串指针
int y = 0; // 匹配串指针
// 进行匹配
while (x < str.length() && y < match.length()) {
if (str.charAt(x) == match.charAt(y)) {
// 匹配,两个指针++
x++;
y++;
} else if (next[y] != -1) {
// 匹配失败,匹配串指针调回next[y]位置,相当于匹配串往右推
y = next[y];
} else {
// 此时y回到0了,next[0] == -1,表示以x开头不可能匹配上了,x往后移一位
x++;
}
}
// 出来了,如果匹配串指针越界了,表示匹配成功了,否则就是匹配串失败了
return y == match.length() ? x - y : -1;
}
private static int[] getNext(String match) {
if (match.length() == 1) return new int[]{
-1};
int[] next = new int[match.length()];
next[0] = -1;
next[1] = 0;
int j = 0; // 代表左边前缀串长度,也表示要与i-1位置字符比较的字符的位置
int i = 2; // 现在求next数组i位置的值
while (i < match.length()) {
// 前缀串后一个字符,和i-1位置字符相等,则next[i]就是前缀串长度+1
if (match.charAt(i - 1) == match.charAt(j)) {
next[i++] = ++j;
} else if (j == 0) {
// j都回到0了,还不匹配,那么next[i]只能是0,表示该位置i没有前缀串与后缀串匹配
next[i++] = 0;
} else {
// 不匹配,根据next数组往左跳
j = next[j];
}
}
return next;
}
public static void main(String[] args) {
System.out.println(getIndexOf("abbabbabbac", "abbabbac"));
}
}
判断是否互为旋转数
给定两个字符串,判断是否互为旋转数
旋转串是指字符串左边的某部分挪到字符串右边去
例如123456,则123456是123456的旋转数,
234561也是123456的旋转数
345612也是123456的旋转数
/**
* 给定两个字符串,判断是否互为旋转数
* 旋转串是指字符串左边的某部分挪到字符串右边去
* 例如123456,则123456是123456的旋转数,
* 234561也是123456的旋转数
* 345612也是123456的旋转数
*
* Created by huangjunyi on 2022/9/5.
*/
public class KMP02 {
public static boolean isRotationNumber(String str1, String str2) {
// str1和str2长度不相等,str2不可能是str1的旋转串
if (str1.length() != str2.length()) return false;
// 两个str1拼接起来,生成2倍的str1
str1 = str1 + str1;
// 然后在新字符串中看是否能匹配到str2,能匹配到则表示str2是str1的旋转数
// 因为两个str1拼接,中间包含了所有可能的旋转数了
if (KMP01.getIndexOf(str1, str2) != -1) return true;
return false;
}
}
给定两颗二叉树,t1和t2,判断在t1中是否包含和t2结构相同的子树
给定两颗二叉树,t1和t2,判断在t1中是否包含和t2结构相同的子树
注意:子树是指以某个节点为头,往下包含了所有的子节点,而不是一部分
解法:
1、 把两个树进行先序序列化;
2、 转化为KMP匹配问题;
/**
* 给定两颗二叉树,t1和t2,判断在t1中是否包含和t2结构相同的子树
* 注意:子树是指以某个节点为头,往下包含了所有的子节点,而不是一部分
*
* 解法:
* 1、把两个树进行先序序列化
* 2、转化为KMP匹配问题
*
* Created by huangjunyi on 2022/9/5.
*/
public class KMP03 {
private static class Node {
String value;
Node left;
Node right;
}
public static boolean contains(Node head1, Node head2) {
if (head2 == null) return true;
if (head1 == null) return false;
List<String> list1 = preSerial(head1); // 先序序列化树1
List<String> list2 = preSerial(head2); // 先序序列化树2
String[] arr = list1.toArray(new String[0]); // 转为字符串数组,把数组看成字符串
String[] match = list2.toArray(new String[0]); // 匹配串
if (arr == null || match == null || arr.length < 1 || arr.length < match.length) return false;
int[] next = getNext(match); // 生成next数组
int x = 0; // 字符原串指针
int y = 0; // 匹配串指针
// KMP的匹配流程
while (x < arr.length && y < match.length) {
if (equals(arr[x], match[y])) {
x++;
y++;
} else if (next[y] != -1) {
y = next[y];
} else {
x++;
}
}
// 如果匹配串指针推到了越界位置,匹配成功,表示str2是str1的旋转数
return y == match.length;
}
private static int[] getNext(String[] match) {
if (match.length == 1) return new int[]{
-1};
int[] next = new int[match.length];
next[0] = -1;
next[1] = 0;
int cn = 0;
int i = 2;
while (i < match.length) {
if (equals(match[cn], match[i - 1])) {
next[i++] = ++cn;
} else if (next[cn] != -1) {
cn = next[cn];
} else {
next[i++] = 0;
}
}
return new int[0];
}
private static boolean equals(String str1, String str2) {
if (str1 == null && str2 == null) return true;
else if (str1 == null || str2 == null) return false;
else return str1.equals(str2);
}
private static List<String> preSerial(Node node) {
List<String> res = new ArrayList<>();
Stack<Node> stack = new Stack<>();
stack.push(node);
while (!stack.isEmpty()) {
Node pop = stack.pop();
res.add(pop == null ? null : pop.value);
if (pop != null) {
stack.push(pop.right);
stack.push(pop.left);
}
}
return res;
}
}