数组实现栈
/**
* 数组实现栈
*/
public class Stack01 {
private int[] arr;
private int size; // 栈容量
private int index = -1;
public Stack01(int size) {
this.size = size;
arr = new int[size];
}
public int pop() {
if (index == -1) throw new RuntimeException("stack is empty");
return arr[index--];
}
public void push(int num) {
if (index == size - 1) throw new RuntimeException("stack is full");
arr[++index] = num;
}
public boolean empty() {
return index == -1;
}
public int peek() {
if (index == -1) throw new RuntimeException("stack is empty");
return arr[index];
}
}
数组实现队列
一般的实现方式是定义两个指针,然后push和pull时的时候判断两个指针有没有追赶上,但是这种实现方式很麻烦而且容易出错。
更好的方式时用一个size遍历记录队列当前大小,如果size没满(size < limit),则两个指针必然没有追赶上,可以push。pull也是,只要判断size不等于0,
/**
* 数组实现队列
*/
public class Queue01 {
private int[] arr;
private int size;
private int limit;
private int pullIndex;
private int pushIndex;
public Queue01(int limit) {
this.limit = limit;
this.size = 0;
this.pullIndex = 0;
this.pushIndex = 0;
arr = new int[limit];
}
public int pull() {
//size等于0,代表队列已空
if (size == 0) throw new RuntimeException("queue is empry");
size--;
int element = arr[pullIndex++];
//如果pullIndex等于limit,从新返回到0
if (pullIndex == limit) pullIndex = 0;
return element;
}
public void push(int num) {
//size等于limit,代表队列已满
if (size == limit) throw new RuntimeException("queue is full");
size++;
arr[pushIndex++] = num;
//如果pushIndex等于limit,从新返回到0
if (pushIndex == limit) pushIndex = 0;
}
public int size() {
return size;
}
}
用栈实现队列
面试官常见的问法:请使用栈实现宽度优先遍历
此时要想到,宽度优先遍历是用队列实现的,是没法用栈直接实现的,这时候应该要先用栈实现队列,再用这个队列去进行宽度优先遍历
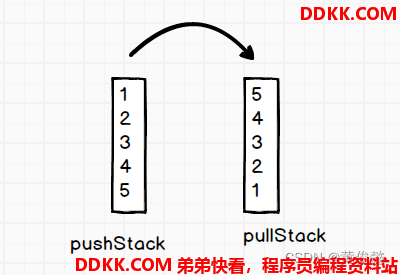
定义一个push栈和pull栈
push时直接push到push栈
pull时检查pull栈是否为空,是则从push栈倒到pull栈,但是要把push一次倒空
/**
* 用栈实现队列
*/
public class Queue02 {
private Stack01 stack1;
private Stack01 stack2;
private int size;
private int limit;
public Queue02(int capacity) {
stack1 = new Stack01(capacity);
stack2 = new Stack01(capacity);
this.size = 0;
this.limit = capacity;
}
public int pull() {
if (size == 0) throw new RuntimeException("queue is empry");
//从队列获取元素时,发现stack2为空,则把stack1中的所有元素倒入stack2中
if (stack2.empty()) {
while (!stack1.empty()) {
stack2.push(stack1.pop());
}
}
size--;
return stack2.pop();
}
public void push(int num) {
if (size == limit) throw new RuntimeException("queue is full");
stack1.push(num);
size++;
}
}
用两个栈来实现,一个用于压入元素,一个用于取出元素,当取出元素时,发现获取元素的栈为空,则一口气把压入元素的栈中的元素全部倒入获取元素的栈中,这样就可以保证元素的先入先出顺序。
用队列实现栈
面试官常见的问法:请使用队列实现深度优先遍历
同理,先用队列实现栈,再用这个栈去实现深度优先遍历
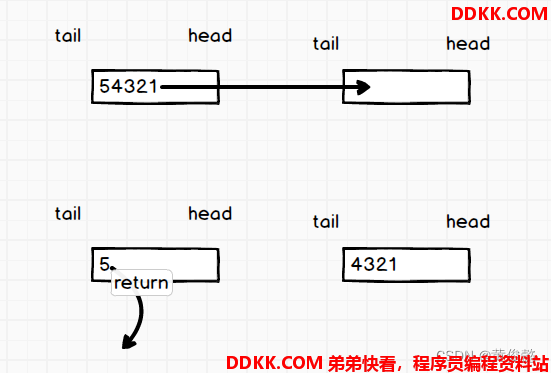
实现方式就是两个队列互相倒
例如定义了queue1和queue2
push了1、2、3、4、5
要弹出一个数返回时,先把queue1中的1,2,3,4挪到queue2去
然后去除5
queue1和queue2交换
然会5
/**
* 用队列实现栈
*/
/**
* 用队列实现栈
*/
public class Stack02 {
private Queue01 q1;
private Queue01 q2;
public Stack02(int size) {
q1 = new Queue01(size);
q2 = new Queue01(size);
}
public int pop() {
//把q1中的元素放入q2,直到q1剩下一个元素
while (q1.size() > 1) {
q2.push(q1.pull());
}
int num = q1.pull();
//q1和q2的引用互相交换
Queue01 temp = q1;
q1 = q2;
q2 = temp;
return num;
}
public void push(int num) {
q1.push(num);
}
}
最小栈
/**
* 最小栈,min方法返回栈中的最小值
*/
public class Stack03 {
private Stack01 dataStack;
private Stack01 minStack;
public Stack03(int size) {
dataStack = new Stack01(size);
minStack = new Stack01(size);
}
public void push(int num) {
dataStack.push(num);
//每次数据栈压入一个数,最小栈也压入一个数,该数为栈顶与当前压入数中较小的一个,保证栈顶总是最小值
if (!minStack.empty() && minStack.peek() > num) minStack.push(num);
else minStack.push(minStack.peek());
}
public int pop() {
//同步把最小栈的栈顶数弹出
minStack.pop();
return dataStack.pop();
}
public int min() {
//最小栈的栈顶就是栈中的最小值
return minStack.peek();
}
}