我们之前学习的转换算子是无法访问事件的时间戳信息和水位线信息的。而这在一些应用场景下,极为重要。例如MapFunction这样的map转换算子就无法访问时间戳或者当前事件的事件时间。
基于此,DataStream API提供了一系列的Low-Level转换算子。可以访问时间戳、watermark以及注册定时事件。还可以输出特定的一些事件,例如超时事件等。Process Function用来构建事件驱动的应用以及实现自定义的业务逻辑(使用之前的window函数和转换算子无法实现)。例如,FlinkSQL就是使用Process Function实现的。
Flink提供了8个Process Function:
1、 ProcessFunction;
2、 KeyedProcessFunction;
3、 CoProcessFunction;
4、 ProcessJoinFunction;
5、 BroadcastProcessFunction;
6、 KeyedBroadcastProcessFunction;
7、 ProcessWindowFunction;
8、 ProcessAllWindowFunction;
一、 KeyedProcessFunction
这个是相对比较常用的ProcessFunction,根据名字就可以知道是用在keyedStream上的。
KeyedProcessFunction用来操作KeyedStream。KeyedProcessFunction会处理流的每一个元素,输出为0个、1个或者多个元素。所有的Process Function都继承自RichFunction接口,所以都有open()、close()和getRuntimeContext()等方法。而KeyedProcessFunction<K, I, O>还额外提供了两个方法:
1、 processElement(Ivalue,Contextctx,Collectorout),流中的每一个元素都会调用这个方法,调用结果将会放在Collector数据类型中输出Context可以访问元素的时间戳,元素的key,以及TimerService时间服务Context还可以将结果输出到别的流(sideoutputs);
2、 onTimer(longtimestamp,OnTimerContextctx,Collectorout),是一个回调函数当之前注册的定时器触发时调用参数timestamp为定时器所设定的触发的时间戳Collector为输出结果的集合OnTimerContext和processElement的Context参数一样,提供了上下文的一些信息,例如定时器触发的时间信息(事件时间或者处理时间);
测试代码:
package org.flink.processfunction;
import org.flink.beans.SensorReading;
import org.apache.flink.api.common.state.ValueState;
import org.apache.flink.api.common.state.ValueStateDescriptor;
import org.apache.flink.api.java.tuple.Tuple;
import org.apache.flink.configuration.Configuration;
import org.apache.flink.streaming.api.datastream.DataStream;
import org.apache.flink.streaming.api.environment.StreamExecutionEnvironment;
import org.apache.flink.streaming.api.functions.KeyedProcessFunction;
import org.apache.flink.util.Collector;
/**
* @remark processfunction之KeyedProcessFunction
*/
public class ProcessTest1_KeyedProcessFunction {
public static void main(String[] args) throws Exception{
StreamExecutionEnvironment env = StreamExecutionEnvironment.getExecutionEnvironment();
env.setParallelism(1);
// socket文本流
DataStream<String> inputStream = env.socketTextStream("10.31.1.122", 7777);
// 转换成SensorReading类型
DataStream<SensorReading> dataStream = inputStream.map(line -> {
String[] fields = line.split(",");
return new SensorReading(fields[0], new Long(fields[1]), new Double(fields[2]));
});
// 测试KeyedProcessFunction,先分组然后自定义处理
dataStream.keyBy("id")
.process( new MyProcess() )
.print();
env.execute();
}
// 实现自定义的处理函数
public static class MyProcess extends KeyedProcessFunction<Tuple, SensorReading, Integer>{
ValueState<Long> tsTimerState;
@Override
public void open(Configuration parameters) throws Exception {
tsTimerState = getRuntimeContext().getState(new ValueStateDescriptor<Long>("ts-timer", Long.class));
}
@Override
public void processElement(SensorReading value, Context ctx, Collector<Integer> out) throws Exception {
out.collect(value.getId().length());
// context
ctx.timestamp();
ctx.getCurrentKey();
// ctx.output();
ctx.timerService().currentProcessingTime();
ctx.timerService().currentWatermark();
ctx.timerService().registerProcessingTimeTimer( ctx.timerService().currentProcessingTime() + 5000L);
tsTimerState.update(ctx.timerService().currentProcessingTime() + 1000L);
// ctx.timerService().registerEventTimeTimer((value.getTimestamp() + 10) * 1000L);
// ctx.timerService().deleteProcessingTimeTimer(tsTimerState.value());
}
@Override
public void onTimer(long timestamp, OnTimerContext ctx, Collector<Integer> out) throws Exception {
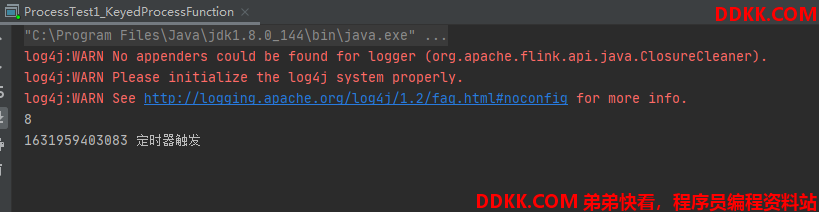
System.out.println(timestamp + " 定时器触发");
ctx.getCurrentKey();
// ctx.output();
ctx.timeDomain();
}
@Override
public void close() throws Exception {
tsTimerState.clear();
}
}
}
输入:
sensor_1,1547718207,36.3
输出:
二、 TimerService和定时器(Timers)
Context 和OnTimerContext 所持有的TimerService 对象拥有以下方法:
1、 longcurrentProcessingTime()返回当前处理时间;
2、 longcurrentWatermark()返回当前watermark的时间戳;
3、 voidregisterProcessingTimeTimer(longtimestamp)会注册当前key的processingtime的定时器当processingtime到达定时时间时,触发timer;
4、 voidregisterEventTimeTimer(longtimestamp)会注册当前key的eventtime定时器当Watermark水位线大于等于定时器注册的时间时,触发定时器执行回调函数;
5、 voiddeleteProcessingTimeTimer(longtimestamp)删除之前注册处理时间定时器如果没有这个时间戳的定时器,则不执行;
6、 voiddeleteEventTimeTimer(longtimestamp)删除之前注册的事件时间定时器,如果没有此时间戳的定时器,则不执行;
当定时器timer 触发时,会执行回调函数onTimer()。注意定时器timer 只能在keyed streams 上面使用。
测试例子:
下面举个例子说明KeyedProcessFunction 如何操作KeyedStream。
需求:监控温度传感器的温度值,如果温度值在10 秒钟之内(processing time)连续上升,则报警。
代码:
package org.flink.processfunction;
import org.flink.beans.SensorReading;
import org.apache.flink.api.common.state.ValueState;
import org.apache.flink.api.common.state.ValueStateDescriptor;
import org.apache.flink.api.java.tuple.Tuple;
import org.apache.flink.configuration.Configuration;
import org.apache.flink.streaming.api.datastream.DataStream;
import org.apache.flink.streaming.api.environment.StreamExecutionEnvironment;
import org.apache.flink.streaming.api.functions.KeyedProcessFunction;
import org.apache.flink.util.Collector;
/**
* @remark 高温警报案例
*/
public class ProcessTest2_ApplicationCase {
public static void main(String[] args) throws Exception{
StreamExecutionEnvironment env = StreamExecutionEnvironment.getExecutionEnvironment();
env.setParallelism(1);
// socket文本流
DataStream<String> inputStream = env.socketTextStream("10.31.1.122", 7777);
// 转换成SensorReading类型
DataStream<SensorReading> dataStream = inputStream.map(line -> {
String[] fields = line.split(",");
return new SensorReading(fields[0], new Long(fields[1]), new Double(fields[2]));
});
// 测试KeyedProcessFunction,先分组然后自定义处理
dataStream.keyBy("id")
.process( new TempConsIncreWarning(10) )
.print();
env.execute();
}
// 实现自定义处理函数,检测一段时间内的温度连续上升,输出报警
public static class TempConsIncreWarning extends KeyedProcessFunction<Tuple, SensorReading, String>{
// 定义私有属性,当前统计的时间间隔
private Integer interval;
public TempConsIncreWarning(Integer interval) {
this.interval = interval;
}
// 定义状态,保存上一次的温度值,定时器时间戳
private ValueState<Double> lastTempState;
private ValueState<Long> timerTsState;
@Override
public void open(Configuration parameters) throws Exception {
lastTempState = getRuntimeContext().getState(new ValueStateDescriptor<Double>("last-temp", Double.class, Double.MIN_VALUE));
timerTsState = getRuntimeContext().getState(new ValueStateDescriptor<Long>("timer-ts", Long.class));
}
@Override
public void processElement(SensorReading value, Context ctx, Collector<String> out) throws Exception {
// 取出状态
Double lastTemp = lastTempState.value();
Long timerTs = timerTsState.value();
// 如果温度上升并且没有定时器,注册10秒后的定时器,开始等待
if( value.getTemperature() > lastTemp && timerTs == null ){
// 计算出定时器时间戳
Long ts = ctx.timerService().currentProcessingTime() + interval * 1000L;
ctx.timerService().registerProcessingTimeTimer(ts);
timerTsState.update(ts);
}
// 如果温度下降,那么删除定时器
else if( value.getTemperature() < lastTemp && timerTs != null ){
ctx.timerService().deleteProcessingTimeTimer(timerTs);
timerTsState.clear();
}
// 更新温度状态
lastTempState.update(value.getTemperature());
}
@Override
public void onTimer(long timestamp, OnTimerContext ctx, Collector<String> out) throws Exception {
// 定时器触发,输出报警信息
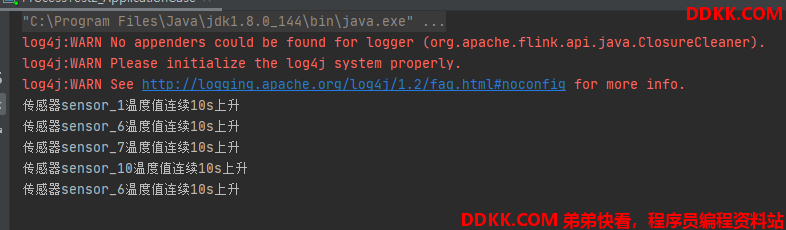
out.collect("传感器" + ctx.getCurrentKey().getField(0) + "温度值连续" + interval + "s上升");
timerTsState.clear();
}
@Override
public void close() throws Exception {
lastTempState.clear();
}
}
}
输入:
sensor_1,1547718199,35.8
sensor_1,1547718199,34.1
sensor_1,1547718199,34.2
sensor_1,1547718199,35.1
sensor_6,1547718201,15.4
sensor_7,1547718202,6.7
sensor_10,1547718205,38.1
sensor_10,1547718205,39
sensor_6,1547718201,18
sensor_7,1547718202,9.1
输出:
三、 侧输出流(SideOutput)
一个数据可以被多个window包含,只有其不被任何window包含的时候(包含该数据的所有window都关闭之后),才会被丢到侧输出流。
简言之,如果一个数据被丢到侧输出流,那么所有包含该数据的window都由于已经超过了"允许的迟到时间"而关闭了,进而新来的迟到数据只能被丢到侧输出流!
大部分的DataStream API 的算子的输出是单一输出,也就是某种数据类型的流。除了split 算子,可以将一条流分成多条流,这些流的数据类型也都相同。
processfunction 的side outputs 功能可以产生多条流,并且这些流的数据类型可以不一样。
一个side output 可以定义为OutputTag[X]对象,X 是输出流的数据类型。
processfunction 可以通过Context 对象发射一个事件到一个或者多个side outputs。
测试代码:
场景:温度>=30放入高温流输出,反之放入低温流输出
代码:
package org.flink.processfunction;
import org.flink.beans.SensorReading;
import org.apache.flink.streaming.api.datastream.DataStream;
import org.apache.flink.streaming.api.datastream.SingleOutputStreamOperator;
import org.apache.flink.streaming.api.environment.StreamExecutionEnvironment;
import org.apache.flink.streaming.api.functions.ProcessFunction;
import org.apache.flink.util.Collector;
import org.apache.flink.util.OutputTag;
/**
* @remark 侧输出流
*/
public class ProcessTest3_SideOuptCase {
public static void main(String[] args) throws Exception{
StreamExecutionEnvironment env = StreamExecutionEnvironment.getExecutionEnvironment();
env.setParallelism(1);
// socket文本流
DataStream<String> inputStream = env.socketTextStream("10.31.1.122", 7777);
// 转换成SensorReading类型
DataStream<SensorReading> dataStream = inputStream.map(line -> {
String[] fields = line.split(",");
return new SensorReading(fields[0], new Long(fields[1]), new Double(fields[2]));
});
// 定义一个OutputTag,用来表示侧输出流低温流
OutputTag<SensorReading> lowTempTag = new OutputTag<SensorReading>("lowTemp") {
};
// 测试ProcessFunction,自定义侧输出流实现分流操作
SingleOutputStreamOperator<SensorReading> highTempStream = dataStream.process(new ProcessFunction<SensorReading, SensorReading>() {
@Override
public void processElement(SensorReading value, Context ctx, Collector<SensorReading> out) throws Exception {
// 判断温度,大于30度,高温流输出到主流;小于低温流输出到侧输出流
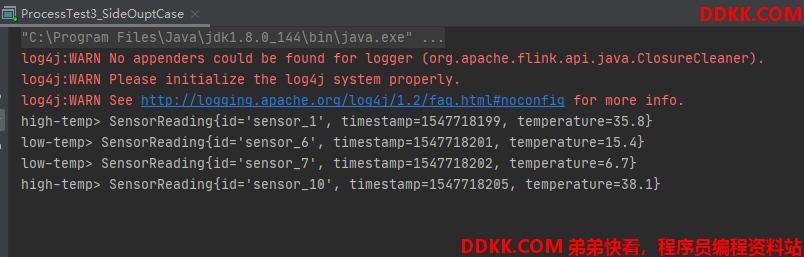
if( value.getTemperature() > 30 ){
out.collect(value);
}
else {
ctx.output(lowTempTag, value);
}
}
});
highTempStream.print("high-temp");
highTempStream.getSideOutput(lowTempTag).print("low-temp");
env.execute();
}
}
输入:
sensor_1,1547718199,35.8
sensor_6,1547718201,15.4
sensor_7,1547718202,6.7
sensor_10,1547718205,38.1
输出:
四、 CoProcessFunction
对于两条输入流,DataStream API 提供了CoProcessFunction 这样的low-level操作。CoProcessFunction 提供了操作每一个输入流的方法: processElement1()和processElement2()。
类似于ProcessFunction,这两种方法都通过Context 对象来调用。这个Context对象可以访问事件数据,定时器时间戳,TimerService,以及side outputs。
CoProcessFunction 也提供了onTimer()回调函数。